|
Luapula Swamps
The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu (Zambia), which are fed by the Chambeshi River. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo before emptying into Lake Mweru. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province.Terracarta/International Travel Maps, Vancouver Canada: "Zambia, 2nd edition", 2000 Source and upper Luapula The Luapula drains Lake Bangweulu and its swamps into which flows the Chambeshi River, the source of the Congo. There is no single clear channel connecting the two rivers and the lake, but a mass of shifting channels, lagoons and swamps, as the explorer David Livingstone found to his cost. (He died exploring the area, and one of his last acts was to question Chief Chitambo about the course of the Luapula.)Blaikie, William Garden (1880): ''The Personal Life Of David Livingstone''Project Gutenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luvua - Luapula - Chambeshi River DRC
The Luvua River (or ''Lowa River'') () is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for to its confluence with the Lualaba River opposite the town of Ankoro. The Lualaba becomes the Congo River below the Boyoma Falls. Course Lake Mweru, at an elevation of about , is a floodplain lake that has been formed by a process of erosion where the wind has carried off alluvium. The Luvua River leaves the north end of the lake at Pweto in the DRC. The river flows about northwest to Ankoro, where it meets the Lualaba. The middle course of the river is obstructed by a series of rapids, torrents and cataracts as it drops down from the plateau into the Congo Basin. At Piana Mwanga the falls are used to generate electricity for the Manono and Kitotolo mines. The river can be navigated in shallow-draft boats for of its lower course below Kiambi. The Luvua has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chibemba
Bemba (natively known as ''Chibemba, Ichibemba'' and ''Chiwemba''), is a Bantu language spoken primarily in north-eastern Zambia by the Bemba people. History Bemba is spoken in rural and urban areas of the region, and is one of Zambia's seven recognized regional languages. Dialects Bemba has several dialects, which include Chishinga, Lomotwa, Ngoma, Nwesi, Lala, Luunda, Mukulu, and Ng’umbo. The Twa of Bangweulu speak another dialect of Bemba. Phonology and orthography The orthographical system in common use, originally introduced by Edward Steere, is quite phonetic. Its letters, with their approximate phonetic values, are given below. It has become increasingly common to use 'c' in place of 'ch'. In common with other Bantu languages, as affixes are added, combinations of vowels may contract and consonants may change. For example, 'aa' changes to a long 'a', 'ae' and 'ai' change to 'e', and 'ao' and 'au' change to 'o' (in other cases, a 'y' is often used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
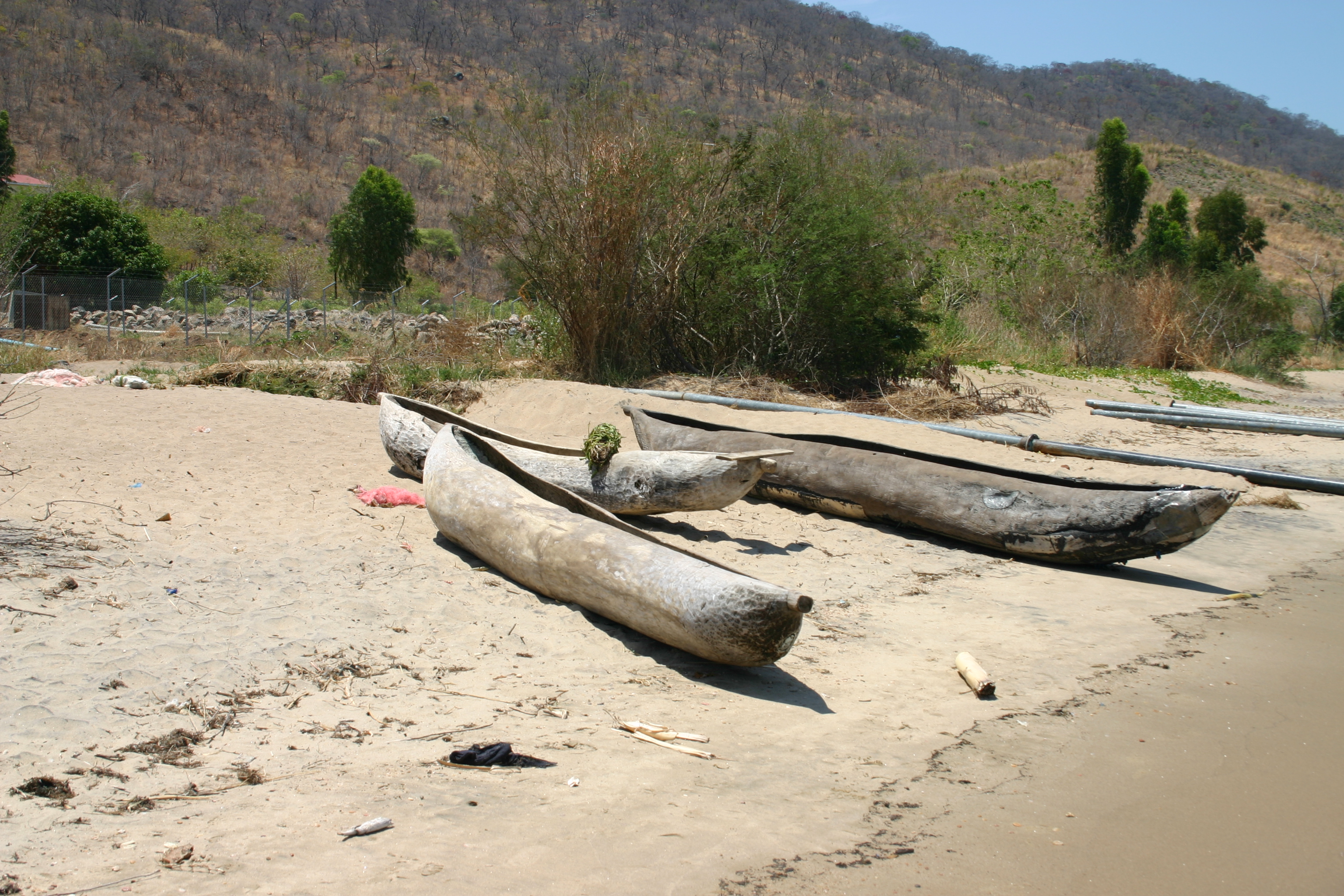
Dugout (boat)
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + ''wikt:ξύλον, ξύλον xylon'' (tree)and is mostly used in classic Greek texts. In German language, German, they are called Einbaum ("one tree" in English). Some, but not all, pirogues are also constructed in this manner. Dugouts are the oldest boat type archaeologists have found, dating back about 8,000 years to the Neolithic Stone Age. This is probably because they are made of massive pieces of wood, which tend to preserve better than others, such as bark canoes. Construction Construction of a dugout begins with the selection of a log of suitable dimensions. Sufficient wood must be removed to make the vessel relatively light in weight and buoyant, yet still strong enough to support the crew and cargo. Specific types of wood were often preferred based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
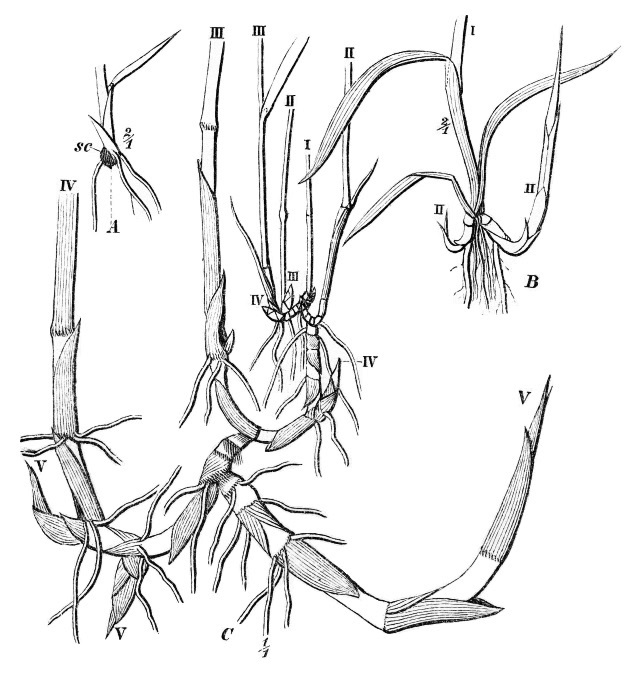
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial plant, perennial reed (plant), reed Poaceae, grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' (Antonio José Cavanilles, Cav.) Carl Bernhard von Trinius, Trin. ex Steud. – The cosmopolitan common reed * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * ''Phragmites karka'' (Anders Johan Retzius, Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * ''Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius Wildlife in reed beds ''Phragmites'' stands can provide food and shelter resources for a number of birds, insects, and other animals. Habitat benefits are often optimal when stands are thinner, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyperus Papyrus
''Cyperus papyrus'', better known by the common names papyrus, papyrus sedge, paper reed, Indian matting plant, or Nile grass, is a species of aquatic plant, aquatic flowering plant belonging to the sedge family Cyperaceae. It is a Hardiness (plants), tender herbaceous perennial, forming tall stands of reed-like swamp vegetation in shallow water. In nature, it grows in full sun, in flooded swamps, and on lake margins throughout Africa (where it is native), Madagascar, and the Mediterranean region. It has been introduced to tropical regions worldwide, such as the Indian subcontinent, South America, and the Caribbean. Along with its close relatives, papyrus sedge has a very long history of use by humans, notably by the Ancient Egyptians (as it is the source of papyrus paper, one of the first types of paper ever made). Parts of the plant can be eaten, and the highly buoyant stems can be made into boats. It is now often cultivated as an ornamental plant. Description This tall, robu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mofwe Lagoon
The Mofwe Lagoon is the largest of several lagoons in the Luapula River swamps south of Lake Mweru, in the Luapula Province of Zambia. Geography Its size and shape depends on the season and amount of water flowing into the swamps, especially from the Mbereshi River to the southeast, its main supplier. Generally its north–south axis is about 14 km and its east–west axis is about 6 km. Floating islands of sedge are usually found in an east–west line across its middle, which may effectively cut it in two, and at times vegetation has covered much of the southern half. The importance of the Mofwe lies in its fishery, which attracted Mwata Kazembe to settle in the town of Kanyembo on its eastern edge in the 19th century.Macola, Giacomo (2003)''The kingdom of Kazembe: history and politics in North-Eastern Zambia and Katanga to 1950 (Studies on African History)'' Lit Verlag, p. 50. The Mofwe does not have a definite shore and is not easily accessed, being lined by a den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrobleme
An impact structure is a generally circular or craterlike geologic structure of deformed bedrock or sediment produced by impact on a planetary surface, whatever the stage of erosion of the structure. In contrast, an impact crater is the surface expression of an impact structure. In many cases, on Earth, the impact crater has been destroyed by erosion, leaving only the deformed rock or sediment of the impact structure behind.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. This is the fate of almost all old impact craters on Earth, unlike the ancient pristine craters preserved on the Moon and other geologically inactive rocky bodies with old surfaces in the Solar System. Impact structure is synonymous with the less commonly used term astrobleme meaning "star wound". In an impact structure, the typical visible and topographic expressions of an impact crater are no lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luizi Crater
Luizi is a meteorite impact structure that lies on the Kundelungu Plateau of Haut-Katanga Province, Haut-Katanga province, in an underexplored region of southeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. The crater, ~17 kilometer in diameter, is visible from satellite imagery, and has been confirmed in 2011 bFerrièreet al. as being caused by a large impact event. This complex meteorite impact crater is so far the only recognized one in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and even in the whole Central Africa. The crater was initially described as a semi-circular basin by German geologist E. Grosse in 1919.E. Grosse, 1919. Grundlinien der Geologie und Petrographie des östlichen Katanga. ''Neues Jahrbuch Mineralogie, Geologie and Paläontologie'', 42, 272–419Google Book/ref> See also *Luapula River References Impact craters of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Haut-Katanga Province {{HautKatanga-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lualaba River
The Lualaba River (, , ) flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the River source, source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi River, Chambeshi. The Lualaba is long. Its headwaters are in the country's far southeastern corner near Musofi and Lubumbashi in Katanga Province, next to the Zambian Copperbelt. Course The source of the Lualaba River is on the Katanga plateau, at an elevation of above sea level. The river flows northward to end near Kisangani, where the name Congo River officially begins. From the Katanga plateau it drops, with waterfalls and rapids marking the descent, to the Manika plateau. As it descends through the upper Upemba Depression (Kamalondo Trough), in . Near Nzilo Falls it is dammed for hydroelectric power at the Nzilo Hydroelectric Power Station, Nzilo Dam. At Bukama in Haut-Lomami District the river becomes navigable for about through a series of mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luvua River
The Luvua River (or ''Lowa River'') () is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for to its confluence with the Lualaba River opposite the town of Ankoro. The Lualaba becomes the Congo River below the Boyoma Falls. Course Lake Mweru, at an elevation of about , is a floodplain lake that has been formed by a process of erosion where the wind has carried off alluvium. The Luvua River leaves the north end of the lake at Pweto in the DRC. The river flows about northwest to Ankoro, where it meets the Lualaba. The middle course of the river is obstructed by a series of rapids, torrents and cataracts as it drops down from the plateau into the Congo Basin. At Piana Mwanga the falls are used to generate electricity for the Manono and Kitotolo mines. The river can be navigated in shallow-draft boats for of its lower course below Kiambi. The Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertine Rift
The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tanganyika. The geographical term includes the valley and the surrounding mountains. Geology The Albertine Rift and the mountains are the result of tectonic movements that are gradually splitting the Somali Plate away from the rest of the African continent. The mountains surrounding the rift are composed of uplifted Pre-Cambrian basement rocks, overlaid in parts by recent volcanic rocks. Lakes and rivers The northern part of the rift is crossed by two large mountain ranges, the Rwenzori Mountains between Lake Albert and Lake Rutanzige (formerly Lake Edward) and the Virunga Mountains between Lake Rutanzige and Lake Kivu. The Virungas form a barrier between the Nile Basin to the north and east and the Congo Basin to the west and south. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. It is the world's longest freshwater lake. The lake is shared among four countries—Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (the DRC), Burundi, and Zambia—with Tanzania (46%) and the DRC (40%) possessing the majority of the lake. It drains via the Lukuga River into the Congo River system, which ultimately discharges at Banana, Democratic Republic of the Congo into the Atlantic Ocean. Geography Lake Tanganyika is situated within the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift, and is confined by the mountainous walls of the valley. It is the largest rift lake in Africa and the second-largest freshwater lake by volume in the world. It is the deepest lake in Africa and holds the greatest volume of fresh water on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |