|
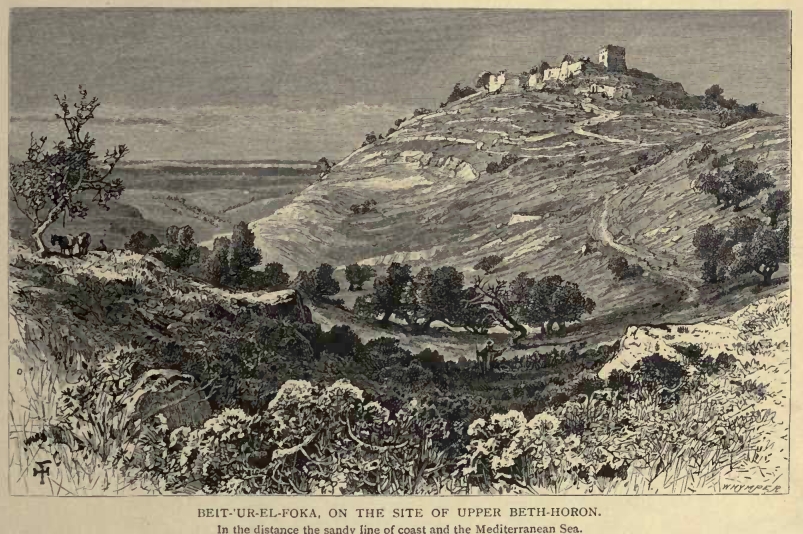
Lower Bethoron
Bethoron (; ), also Beth-Horon, were two neighboring towns in ancient Israel, situated on the Gibeon–Aijalon road. They served as strategic points along the road, guarding the "ascent of Bethoron". While the Hebrew Bible sometimes distinguishes between the two towns—Upper and Lower Bethoron—it often refers to both simply as Bethoron. The towns are mentioned in the Bible and in other ancient sources: Upper Bethoron appears in Joshua, Lower Bethoron in Joshua, both in 1 Chronicles, and the ascent in I Maccabees. The ancient towns of Upper Bethoron and Lower Bethoron are identified respectively with the present-day Palestinian Arab villages of Beit Ur al-Fauqa and Beit Ur al-Tahta, which preserve the ancient names. Archaeological evidence suggests that Lower Bethoron was established first, as the earliest potsherds discovered there date back to the Late Bronze Age, while those from the upper town originate from the Iron Age onward. Etymology The Hebrew name Bethoron (Beit H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haurun
Hauron, Haurun or Hawran (from Egyptian '' ḥwrwnꜣ'') was an ancient Egyptian god worshiped in Giza. He was closely associated with Harmachis, with the names in some cases used interchangeably, and his name as a result could be used as a designation of the Great Sphinx of Giza. While Egyptologists were familiar with Hauron since the nineteenth century, his origin was initially unknown, and only in the 1930s it was established that he originated outside Egypt. Today it is agreed that he was the Egyptian form of a god worshiped in Canaan and further north in the city of Ugarit, conventionally referred to as Horon (, ''ḥrn''; Ḥôrānu or Ḥōrān) in scholarship. In the Ugaritic texts, Hauron appears as a deity associated with magic and exorcisms. This role is also attested for him in Egypt and in Phoenician sources from the first millennium BCE. The best known text focused on him is KTU 1.100, often interpreted as a myth, in which the Ugaritic sun goddess Shapash implor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age. Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations and other peoples.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture ... In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature. Given the information available, one cannot maintain a radical cultural separation between Canaanites and Israelites for the Iron I period." (pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
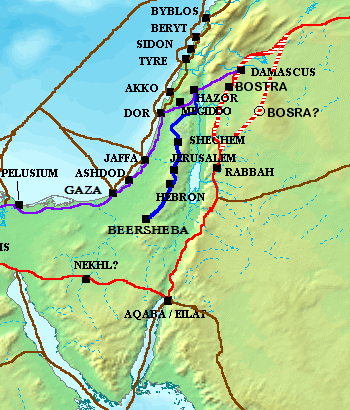
Way Of The Patriarchs
The Road of the Patriarchs or Way of the Patriarchs ( ''Derech haʾAvot'' Lit. ''Way (of) the Fathers'') is an ancient north–south route traversing the land of Israel and the region of Palestine. The modern Highway 60 (Israel-Palestine) follows roughly the route of the Way of the Patriarchs. The name is used by biblical scholars because of mentions in biblical narratives that it was frequently travelled by Abraham, Isaac and Jacob. It is also called the Hill Road or the Ridge Route because it follows the watershed ridge line of the Samarian and Judaean Mountains. It runs from Megiddo and Hazor south to Beersheba by way of Shechem, Bethel, Jerusalem, Ephrath and Hebron. Unlike the Via Maris and the King's Highway which were international roads crossing the territories of many peoples, the Ridge Route was wholly within the territory of ancient Israel. Modern equivalent The modern Highway 60 follows roughly the route of the Way of the Patriarchs (without the more recent b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Maris
Via Maris, or Way of Horus () was an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia – along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syria. In Latin, ''Via Maris'' means "way of the sea", a translation of the Greek ὁδὸν θαλάσσης found in of the Septuagint, itself a translation of the Hebrew דֶּ֤רֶךְ הַיָּם֙. It is a historic road that runs in part along the Israeli Mediterranean coast. It was the most important route from Egypt to Syria (the Fertile Crescent) which followed the coastal plain before crossing over into the plain of Jezreel and the Jordan valley. Other names are "Way of the Philistines", "International Trunk Road" and "International Coastal Highway." Together with the King's Highway, the ''Via Maris'' was one of the major trade routes connecting Egypt and the Levant with Anatolia and Mesopotamia. The ''Via Maris'' was crossed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayalon-Canada Park
Canada Park (, , also Ayalon Park) is a national park stretching over in the Israeli-occupied West Bank. The park is located north of Highway 1 (Tel Aviv-Jerusalem), and is situated near the Ayalon Valley, between the Latrun Interchange and Sha'ar HaGai. It was established following the ethnic cleansing of the ancient Palestinian villages of Yalu, Bayt Nuba and Imwas by Israeli troops during the Six-Day War. Today, the park is full with natural attractions, including man-made forests, Mediterranean woodlands home to many local flowers, and the remains of ancient orchards. The park also has a number of historical interest, including a Hasmonean Jewish fort, burial caves and ritual baths of the Second Temple period and the Bar Kokhba revolt, a Crusader fort, a Roman bathhouse that was turned into a maqam, the remnants of the three depopulated Palestinian villages, and various military memorials. There are also recreation areas, springs, and panoramic several hilltop vie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aijalon
The Ayalon Valley ( or , ''ʾAyyālōn''), also written Aijalon and Ajalon, is a valley in the lowland of the Shephelah in Israel. The Ayalon Valley has been an important route connecting the coastal plain and Jerusalem for generations. Due to its location, several battles were fought in its vicinity. The Hebrew Bible gives the valley its name from Ayalon, a city that the Tribe of Dan possessed before their migration to the north. In the modern period, ancient Ayalon was identified with the former village of Yalo at the base of the Bethoron, Bethoron pass, which preserved the ancient, biblical name. Today, the Ayalon Valley is home to several ''kibbutzim'' and ''moshavim'', including Sha'alvim, Mishmar Ayalon, Nahshon, Israel, Nahshon, and Kfar Bin Nun. The valley is also home to Canada Park, a National parks and nature reserves of Israel, national park, the Yad La-Shiryon, Yad La-Shiryon (Armored Corps Museum), Mini Israel, the Latrun Monastery and Emmaus Nicopolis, an Archaeolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Murray (publishing House)
John Murray is a Scottish publisher, known for the authors it has published in its long history including Jane Austen, Arthur Conan Doyle, Lord Byron, Charles Lyell, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Herman Melville, Edward Whymper, Thomas Robert Malthus, David Ricardo, and Charles Darwin. Since 2004, it has been owned by conglomerate Lagardère Group, Lagardère under the Hachette Livre, Hachette UK brand. History The business was founded in London, England, in 1768 by John Murray (1737–1793), an Edinburgh-born Royal Marines officer, who built up a list of authors including Isaac D'Israeli and published the ''English Review (18th century), English Review''. John Murray the elder was one of the founding sponsors of the London evening newspaper ''The Star (1788), The Star'' in 1788. He was succeeded by his son John Murray II, who made the publishing house important and influential. He was a friend of many leading writers of the day and launched the ''Quarterly Review'' in 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
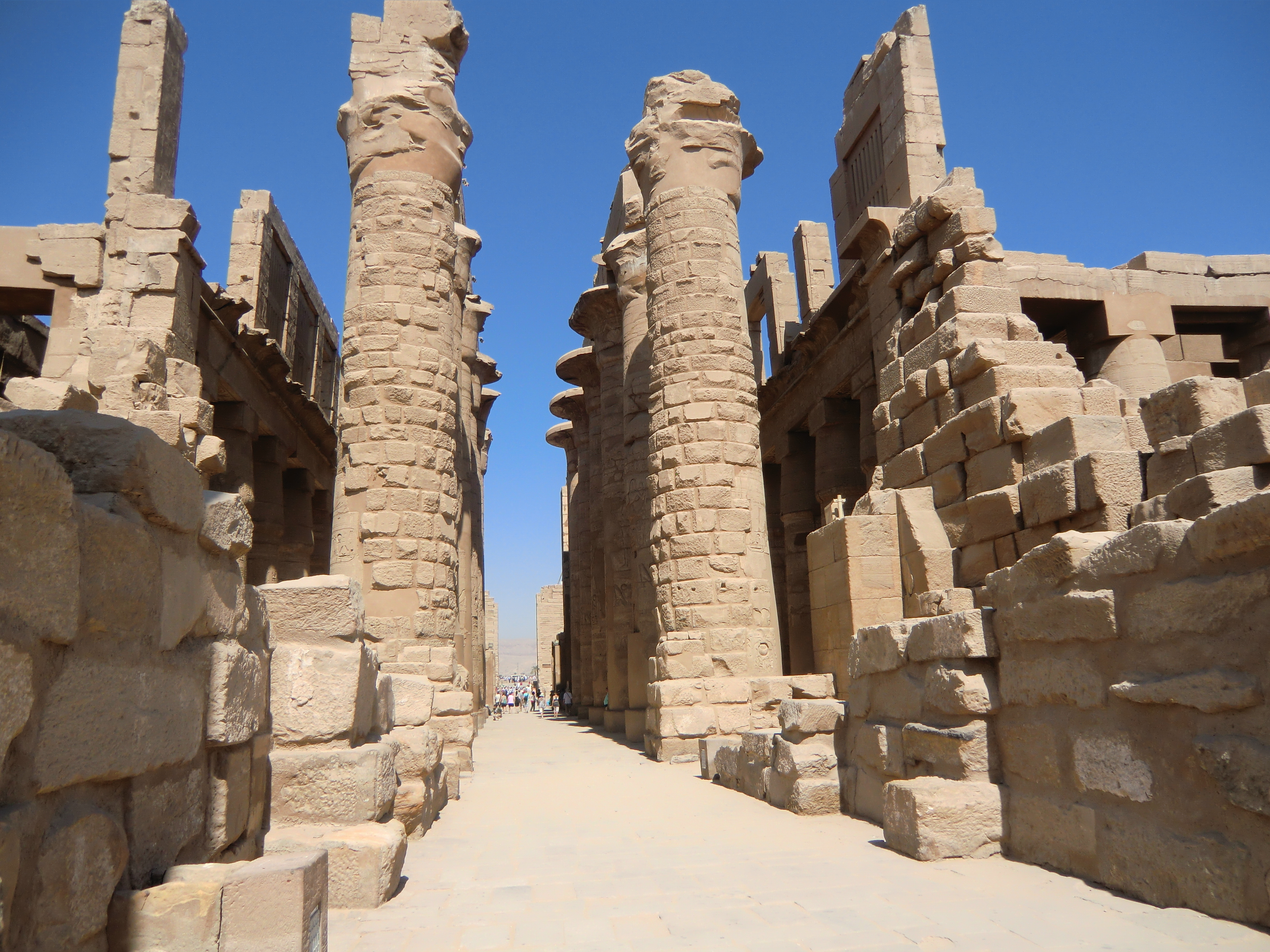
Temple Of Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (), comprises a vast mix of temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BC) in the Middle Kingdom () and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BC), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. Karnak gets its name from the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Name The original name of the temple was ''Ipet-isut'', meaning "The Most Select of Places". The complex's modern name "Karnak" comes from the nearby village of el-Karnak, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubastite Portal
The Bubastite Portal gate is located in Karnak, within the Precinct of Amun-Re temple complex, between the temple of Ramesses III and the second pylon. It records the conquests and military campaigns 925 BC of Shoshenq I, of the Twenty-second Dynasty. Shoshenq has been identified with the biblical Shishaq, such that the relief is also known as the Shishak Inscription or Shishaq Relief. History This gate was erected by the kings of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the "Bubastite Dynasty". It is located to the south-east side of the Temple of Ramesses III. Although Karnak had been known to Europeans since the end of the Middle Ages, the possible significance of the Bubastite Portal was not apparent prior to the decipherment of hieroglyphs. Jean-François Champollion visited Karnak in 1828, six years after his publication of the Rosetta Stone translation. In his letters he wrote: Description One facade shows King Shoshenq I, Takelot I, and Osorkon I of the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheshonq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I (Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned )—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. Family Of Meshwesh ancestry, Shoshenq I was the son of Nimlot A, Great Chief of the Ma, and his wife Tentshepeh A, a daughter of a Great Chief of the Ma herself; Shoshenq was thus the nephew of Osorkon the Elder, a Meshwesh king of the 21st Dynasty. He is generally presumed to be the Shishak mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, and his exploits are carved on the Bubastite Portal at Karnak. Chronology The conventional dates for his reign, as established by Kenneth Kitchen, are 945–924 BC but his time-line has recently been revised upwards by a few years to 943–922 BC, since he may well have lived for up to two to three years after his successful campaign in Israel and Judah, conventionally dated to 925 BC. As Edward Wen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulletin Of The American Schools Of Oriental Research
The ''Bulletin of the American Society of Overseas Research (BASOR)'', formerly the ''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', is one of three academic journals published by the American Society of Overseas Research. It began as the ''Bulletin of the American School of Oriental Research in Jerusalem'', in 1919. The Bulletin took on its current name in 2020. References External links * *JSTOR Early Journal Content, at the Internet Archive: Partial archive, 1919 - 1921Partial archive, 1922 - 1923 Religious studies journals Ancient Near East journals Academic journals established in 1919 Biannual journals {{asia-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |