|
Low Library
The Low Memorial Library (nicknamed Low) is a building at the center of Columbia University's Morningside Heights campus in Upper Manhattan in New York City. The building, located near 116th Street (Manhattan), 116th Street between Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway and Amsterdam Avenue (Manhattan), Amsterdam Avenue, was designed by Charles Follen McKim of the firm McKim, Mead & White. The building was constructed between 1895 and 1897 as the Columbia University Libraries, university's central library, although it has contained the university's central administrative offices since 1934. Columbia University president Seth Low funded the building with $1 million (equivalent to $ million in ) and named the edifice in memory of his father, Abiel Abbot Low. Low's facade and interior are New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission, New York City designated landmarks, and the building is also designated as a National Historic Landmark. Low is arranged in the shape of a Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Libraries
Columbia University Libraries is the library system of Columbia University and one of the largest academic library systems in North America. With 15.0 million volumes and over 160,000 journals and serials, as well as extensive electronic resources, manuscripts, rare books, microforms, maps, and graphic and audio-visual materials, it is the fifth-largest academic library in the United States and the largest academic library in the State of New York. Additionally, the closely affiliated Jewish Theological Seminary Library holds over 400,000 volumes, which combined makes the Columbia University Libraries the third-largest academic library, and the second-largest private library in the United States. The services and collections are organized into 19 libraries and various academic technology centers, including affiliates. The organization is located on the university's Morningside Heights campus in New York City and employs more than 500 professional and support staff. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of Roman architecture, ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer, more complete, and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a National Register of Historic Places property types, building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500, or roughly three percent, of over 90,000 places listed on the country's National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) are recognized as National Historic Landmarks. A National Historic Landmark District may include many contributing properties that are buildings, structures, sites or objects, and it may also include non-contributing properties. Contributing properties may or may not also be separately listed as NHLs or on the NRHP. History The origins of the first National Historic Landmark was a simple cedar post, placed by the Lewis and Clark Expedition on their 1804 outbound trek to the Pacific Ocean in commemoration of the death from natural causes of Sergeant Charles Floyd (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Hall
Earl Hall is a building on the campus of Columbia University. Built in 1900–1902 and designed by McKim, Mead & White, the building serves as a center for student religious life. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2018 for its historic role in serving as a venue for meetings and dances of the Columbia Student Homophile League, the oldest LGBTQ student organization in the United States. On April 2, 2025, in a continuation of protests at Columbia during the Gaza War The Gaza war is an armed conflict in the Gaza Strip and southern Israel fought since 7 October 2023. A part of the unresolved Israeli–Palestinian conflict, Israeli–Palestinian and Gaza–Israel conflict, Gaza–Israel conflicts dating ..., students chained themselves to the gates outside of Earl Hall to demand accountability from the university in the detention of Mahmoud Khalil. References {{National Register of Historic Places in New York 1902 establishments in New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisohn Hall
Lewisohn Hall is a building on the Columbia University campus in Manhattan, New York. Completed in 1905, it was designed by Arnold W. Brunner in imitation of the other McKim, Mead & White buildings on campus, and named after banker and mining magnate Adolph Lewisohn. The building currently houses the School of General Studies and School of Professional Studies. The '' Le Marteleur'' was formerly located in front of Lewisohn, when the building housed the School of Mines A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of ...; it was relocated to the Mudd Building when the later moved there in the 1960s. References External links * Columbia University campus University and college buildings in the United States School buildings completed in 1905 {{New York-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller Theatre
Miller Theatre at Columbia University is located on the Morningside Heights, Manhattan, Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University. It is a performing arts producer dedicated to developing and presenting new music. Originally named the Emerson McMillin, McMillin Theater, it was renovated and renamed the Kathryn Bache Miller Theatre in 1988, with George Steel (musician), George Steel as its first executive director. The current director, Melissa Smey, took over from Steel in 2009. Miller Theatre is particularly known for its Composer Portraits Series. Each concert in the series focuses on the work of a single composer. References External links Miller Theatre {{Authority control Music venues in Manhattan Columbia University campus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butler Library
Butler Library is located on the Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University at 535 West 114th Street, in Manhattan, New York City. It is the university's largest single library with over 2 million volumes, as well as one of the largest buildings on the campus. It houses the Columbia University Libraries collections in the humanities, history, social sciences, literature, philosophy, and religion, and the Columbia Rare Book and Manuscript Library. The Neoclassical style building was built in 1931–1934 to a design by James Gamble Rogers. Butler Library remains at least partially open 24 hours a day during the academic year. History Planning and construction Butler was built from 1931 to 1934 in order to replace the existing Low Library, which was completed in 1897, but by the 1920s had already proved inadequate for the needs of the university's expanding library. The first proposal to build a new library building was made in 1922 by Nicholas Murray Butler, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur W
The Countess (French language, French: ''La Comtesse''; born Arthur Berloget), also known as Pauline and Arthur W, was a French transgender courtesan, demimondaine, singer, artist, and writer who was prominent in Parisian society throughout the 1850s and 1860s. She was the mistress of a French nobility, nobleman and later became a singer in Parisian cafés and cabarets. Berloget was an active member of an LGBT community in Paris, whose members were called ''filles'', ''mignons'' and ''tribade sisters''. She was drafted to serve in the French Army, and was forced to temporarily de-transition. She was arrested in 1861 for robbery and for desertion, deserting her post, and was sentenced to ten years in prison. In 1874, she authored an autobiography ''The Secret Confessions of a Parisian: The Countess, 1850-1871'', which was published in 1895. Her autobiography describes intimate details of her life living as a woman during the Second French Empire and the beginning of Belle Époque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avery Architectural And Fine Arts Library
Avery Architectural and Fine Arts Library, the world's largest architecture library, is located in Avery Hall on the Morningside Heights campus of Columbia University in New York City. Serving Columbia's Graduate School of Architecture, Planning and Preservation and the Department of Art History and Archaeology, Avery Library collects books and periodicals in architecture, historic preservation, art history, painting, sculpting, graphic arts, decorative arts, city planning, real estate, and archaeology, as well as archival materials primarily documenting 19th and 20th-century American architects and architecture. The architectural, fine arts, Ware, and archival collections are non-circulating. The Avery-LC Collection, primarily newer print books, does circulate. History Avery Library is named for New York architect Henry Ogden Avery, a friend of William Robert Ware, who was the first professor of architecture at Columbia University in 1881. Soon after Avery's death in 1890, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Stack
In library science and architecture, a stack or bookstack (often referred to as a library building's ''stacks'') is a book storage area, as opposed to a reading area. More specifically, this term refers to a narrow-aisled, multilevel system of iron or steel shelving that evolved in the 19th century to meet increasing demands for storage space. An "open-stack" library allows its patrons to enter the stacks to browse for themselves; "closed stacks" means library staff retrieve books for patrons on request. Early development French architect Henri Labrouste, shortly after making pioneering use of iron in the Bibliotheque Sainte-Genevieve of 1850, created a four-story iron stack for the Bibliothèque nationale de France. In 1857, multilevel stacks with grated iron floors were installed in the British Library. In 1876, William R. Ware designed a stack for Gore Hall at Harvard University. In contrast to the structural relationship found in most buildings, the floors of these bookst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotunda (architecture)
A rotunda () is any roofed building with a circular ground plan, and sometimes covered by a dome. It may also refer to a round room within a building (an example being the one below the dome of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.). The Pantheon in Rome is perhaps the most famous, and is the most influential rotunda. A ''band rotunda'' is a circular bandstand, usually with a dome. Classical architecture The terminology of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture distinguishes between two types of rotunda: a tholos is enclosed by a wall, while a monopteros is just a circular colonnade with a roof (like a modern bandstand or park pavilion). It is not clear that any Greek example was actually a Greek temple, but several were Roman temples, though mostly much smaller than the Pantheon, and with very different designs. The Temple of Hercules Victor and Temple of Vesta in Rome, along with the Temple of Vesta, Tivoli, are the best known and best prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
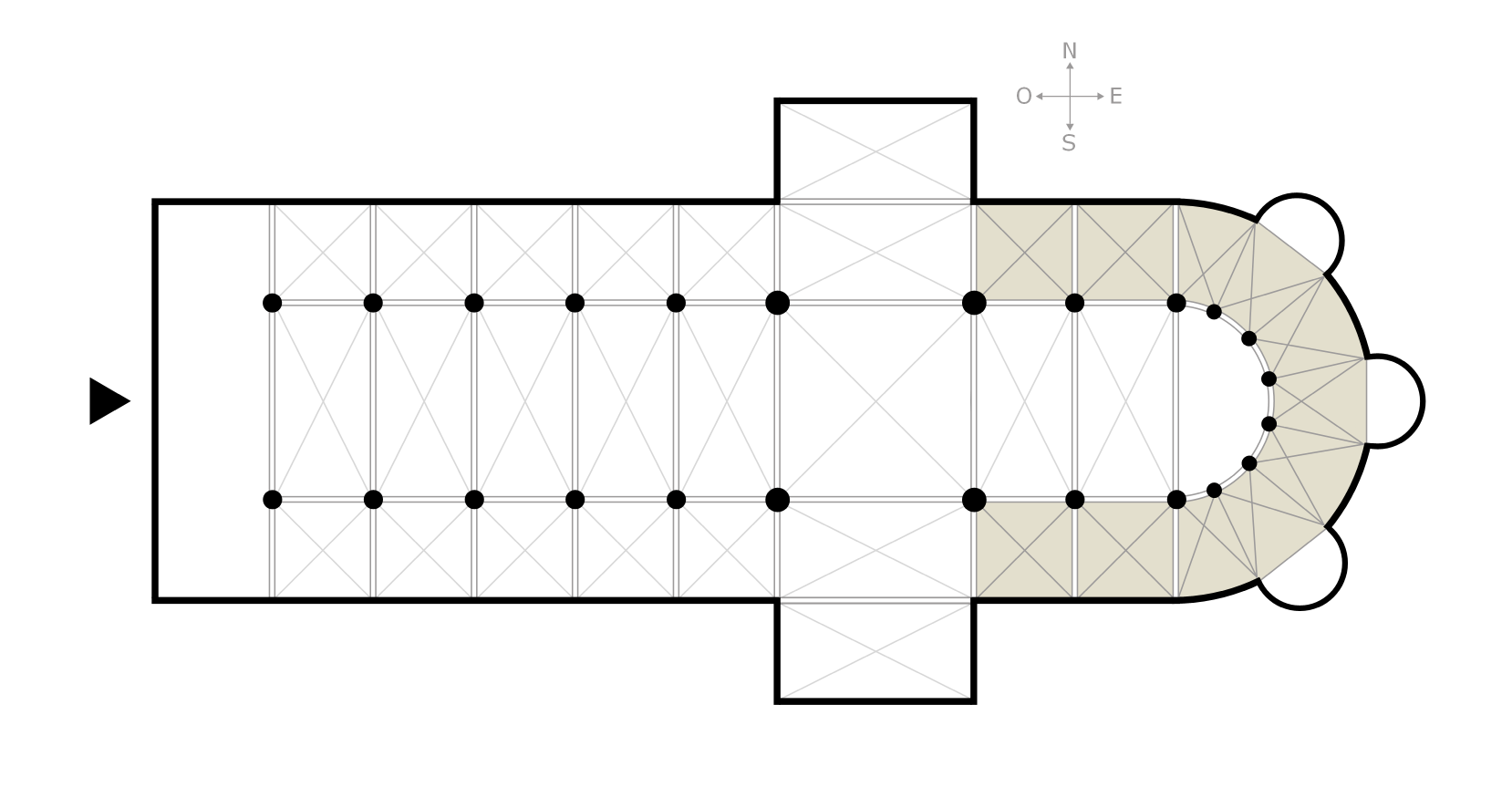
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |