|
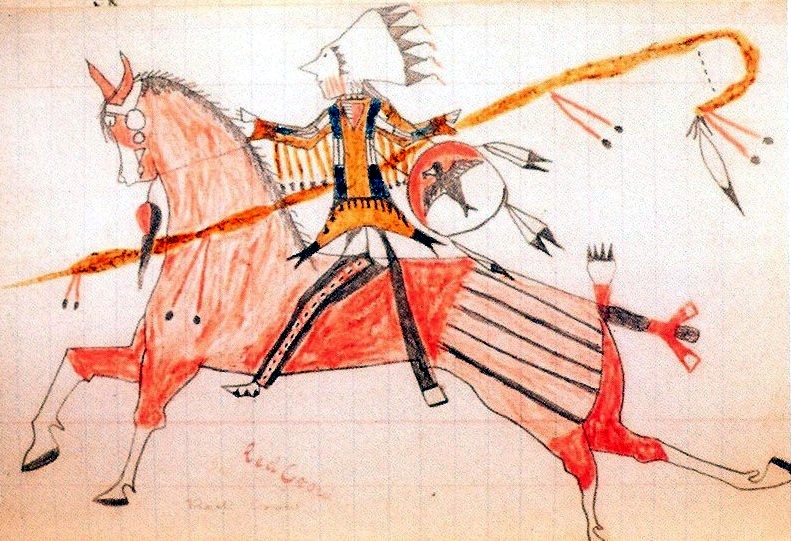
Low Dog
''Low Dog'' (Lakota: Šúŋka Khúčiyela) (c. 1846–1894) (aka. Phil Cosgrove) was an Oglala Lakota chief who fought with Sitting Bull at the Little Bighorn. He became a war chief at age 14. After surrendering in 1881, he lived at Standing Rock Agency The Standing Rock Sioux Tribe of North & South Dakota controls the Standing Rock Reservation (), which straddles the border between North Dakota, North and South Dakota in the United States, and is inhabited by ethnic "Hunkpapa Lakota, Hunkp .... Low Dog's account of the Battle of the Little Bighorn was published in the Leavenworth, Kansas Weekly Times of August 18, 1881: "WE WERE in camp near Little Bighorn river. We had lost some horses, and an Indian went back on the trail to look for them. We did not know that the white warriors were coming after us. Some scouts or men in advance of the warriors saw the Indian looking for the horses and ran after him and tried to kill him to keep him from bringing us word, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oglala Lakota
The Oglala (pronounced , meaning 'to scatter one's own' in Lakota language, Lakota) are one of the seven subtribes of the Lakota people who, along with the Dakota people, Dakota, make up the Sioux, Očhéthi Šakówiŋ (Seven Council Fires). A majority of the Oglala live on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, the eighth-largest Indian reservation, Native American reservation in the United States. The Oglala are a List of federally recognized tribes, federally recognized tribe whose official title is the called the Oglala Sioux Tribe of the Pine Ridge Reservation, South Dakota. History Oglala elders relate stories about the origin of the name "Oglala" and their emergence as a distinct group, probably sometime in the 18th century. Conflict with the European settlers In the early 19th century, Europeans and American passed through Lakota territory in increasing numbers. They sought furs, especially beaver fur at first, and later bison fur. The fur trade changed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota people, Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes and the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army. It took place on June 25–26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River in the Crow Indian Reservation in southeastern Montana Territory. The battle, which resulted in the defeat of U.S. forces, was the most significant action of the Great Sioux War of 1876. Most battles in the Great Sioux War, including the Battle of the Little Bighorn, were on lands those natives had taken from other tribes since 1851. The Lakotas were there without consent from the local Crow tribe, which had a treaty on the area. Already in 1873, Crow chief Blackfoot had called for U.S. military actions against the native intruders. The steady Lakota incursions into treaty ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakota Language
Lakota ( ), also referred to as Lakhota, Teton or Teton Sioux, is a Siouan languages, Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. Lakota is mutually intelligible with the two dialects of the Dakota language, especially Dakota language#Comparison of the dialects, Western Dakota, and is one of the three major variety (linguistics), varieties of the Sioux language. Speakers of the Lakota language make up one of the largest Native American language speech communities in the United States, with approximately 2,000 speakers, who live mostly in the northern plains states of North Dakota and South Dakota. Many communities have immersion programs for both children and adults. Like many indigenous languages, the Lakota language did not have a written form traditionally. However, efforts to develop a written form of Lakota began, primarily through the work of Christian missionaries and linguists, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The orthography has since evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitting Bull
Sitting Bull ( ; December 15, 1890) was a Hunkpapa Lakota people, Lakota leader who led his people during years of resistance against Federal government of the United States, United States government policies. Sitting Bull was killed by Indian agency police accompanied by U.S. officers and supported by U.S. troops on the Standing Rock Indian Reservation during an attempt to arrest him at a time when authorities feared that he would join the Ghost Dance movement. Before the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull had a vision in which he saw many soldiers, "as thick as grasshoppers", falling upside down into the Lakota camp, which his people took as a foreshadowing of a major victory in which many soldiers would be killed. About three weeks later, the confederated Lakota tribes with the Northern Cheyenne defeated the 7th Cavalry Regiment, 7th Cavalry under Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer on June 25, 1876, annihilating Custer's battalion and seeming to fulfill Sitting Bull's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Rock Indian Reservation
The Standing Rock Sioux Tribe of North & South Dakota controls the Standing Rock Reservation (), which straddles the border between North and South Dakota in the United States, and is inhabited by ethnic "Hunkpapa and Sihasapa bands of Lakota Oyate and the Ihunktuwona and Pabaksa bands of the Dakota Oyate," as well as the Hunkpatina Dakota (Lower Yanktonai). The Ihanktonwana Dakota are the Upper Yanktonai, part of the collective of Wiciyena. The sixth-largest Native American reservation in land area in the US, Standing Rock includes all of Sioux County, North Dakota, and all of Corson County, South Dakota, plus slivers of northern Dewey and Ziebach counties in South Dakota, along their northern county lines at Highway 20. The reservation has a land area of , twice the size of the U.S. State of Delaware, and has a population of 8,217 as of the 2010 census. There are 15,568 enrolled members of the tribe. The largest communities on the reservation are Fort Yates, Cannon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leavenworth Times
''Leavenworth Times'' is an American daily newspaper published in Leavenworth, Kansas. The newspaper is owned by CherryRoad Media. History Founded in 1856 by future United States Senator Robert Crozier, the ''Times'' claims to be the oldest daily newspaper in Kansas. Daniel R. Anthony, brother of Susan B. Anthony, bought the paper in 1871 and the paper remained in the Anthony family until the 1960s, even after Daniel Anthony shot and killed rival publisher R.C. Satterlee of the ''Kansas Herald'', in 1871 (he was acquitted at trial), and then was shot himself by rival editor William Embry of the ''Daily Appeal'' in 1875 (he survived). In 1966, The Thomson Corporation bought the ''Leavenworth Times'', selling it in 1995 to American Publishing Company (later Hollinger International). During Hollinger's divestment of most of its small papers, Liberty Publishing (later called GateHouse Media) bought the ''Times'' in 1999. The ''Times'' is one of two daily newspapers GateHouse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1840s Births
__NOTOC__ Year 184 ( CLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Eggius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 937 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 184 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place China * The Yellow Turban Rebellion and Liang Province Rebellion break out in China. * The Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions ends. * Zhang Jue leads the peasant revolt against Emperor Ling of Han of the Eastern Han dynasty. Heading for the capital of Luoyang, his massive and undisciplined army (360,000 men), burns and destroys government offices and outposts. * June – Ling of Han places his brother-in-law, He Jin, in command of the imperial army and sends them to attack the Yellow Turban rebels. * Winter – Zhang Jue dies of illness while his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1894 Deaths
Events January * January 4 – A military alliance is established between the French Third Republic and the Russian Empire. * January 7 – William Kennedy Dickson receives a patent for motion picture film in the United States. * January 9 – New England Telephone and Telegraph installs the first battery-operated telephone switchboard, in Lexington, Massachusetts. February * February 12 – French anarchist Émile Henry sets off a bomb in a Paris café, killing one person and wounding twenty. * February 15 ** In Korea, peasant unrest erupts in the Donghak Peasant Revolution, a massive revolt of followers of the Donghak movement. Both China and Japan send military forces, claiming to come to the ruling Joseon dynasty government's aid. ** French anarchist Martial Bourdin dies of an accidental detonation of his own bomb, next to the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. March * March 1 – The Local Government Act (coming into effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |