|
Low-carbon Building
A low-energy house is characterized by an energy-efficient design and technical features which enable it to provide high living standards and comfort with low energy consumption and carbon emissions. Traditional heating and active cooling systems are absent, or their use is secondary. Low-energy buildings may be viewed as examples of sustainable architecture. Low-energy houses often have active and passive solar building design and components, which reduce the house's energy consumption and minimally impact the resident's lifestyle. Throughout the world, companies and non-profit organizations provide guidelines and issue certifications to guarantee the energy performance of buildings and their processes and materials. Certifications include passive house, BBC—Bâtiment Basse Consommation—Effinergie (France), zero-carbon house ( UK), and Minergie (Switzerland). Buildings alone were responsible for 38% of all human Greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) as of 2008, with 20% attributed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivhaus Thermogram Gedaemmt Ungedaemmt
Passive house () is a voluntary standard for efficient energy use, energy efficiency in a building that reduces the building's carbon footprint. Conforming to these standards results in Low-energy house, ultra-low energy buildings that require less energy for space heating or cooling. A similar standard, Minergie, MINERGIE-P, is used in Switzerland. Standards are available for residential properties, and several office buildings, schools, kindergartens and a supermarket have also been constructed to the standard. Energy efficiency is not an attachment or supplement to architectural design, but a design process that integrates with architectural design. Although it is generally applied to new buildings, it has also been used for renovations. In 2008, estimates of the number of passive house buildings around the world ranged from 15,000 to 20,000 structures. In 2016, there were approximately 60,000 such certified structures of all types worldwide. The vast majority of passive ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan Conservation House
The Saskatchewan Conservation House (211 Rink Ave, Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada) is an early exemplar of energy-efficient building construction that introduced best practices for addressing air leakage in houses. It was designed in response to the 1970s energy crisis, energy crisis of the 1970s at the request of the Government of Saskatchewan. The Saskatchewan Conservation House pioneered the use of superinsulation and airtightness in Passive house, passive design and included one of the earliest Heat recovery ventilation, heat recovery systems. The house did not require a furnace, despite prairie winter temperatures as low as at night. In 1977, when it was built at 211 Rink Avenue in the Regina Walsh Acres, Walsh Acres neighborhood of Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada, the house was the world's most airtight house. The cost of the electricity to heat the house was estimated as $30–40 for a year. The house's building envelope continues to perform as designed, more than 40 years later. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directive On The Energy Performance Of Buildings
The Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (2024/1275), the "EPBD") is the European Union's main legislative instrument aiming to promote the improvement of the energy performance of buildings within the European Union. It was inspired by the Kyoto Protocol which commits the EU and all its parties by setting binding emission reduction targets. History Directive 2002/91/EC The first version of the EPBD, directive 2002/91/EC, was approved on 16 December 2002 and entered into force on 4 January 2003.European Commission,DIRECTIVE 2002/91/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 16 December 2002 on the energy performance of buildings, Official Journal of the European Communities, 2003 EU Member States (MS) had to comply with the Directive within three years of the inception date (4 January 2006), by bringing into force necessary laws, regulations and administrative provisions. In the case of lack of qualified and/or accredited experts, the directive allowed for a furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Passive Solar Building Design
The passive solar design of buildings includes consideration of their orientation to the sun and their thermal mass, factors which have been incorporated to a greater or lesser extent in vernacular architecture for thousands of years. Ancient Greeks, Romans, and Chinese were the first to refine and develop the basic principles of passive solar design, but European technological advances were largely abandoned after the Fall of Rome. It was not until the 20th century that interest in the principles of passive solar design had a resurgence in Europe and the U.S.A., with architects such as George F. Keck and Frank Lloyd Wright. In the 21st century, worldwide endeavours to reduce power consumption have kept the interest in passive solar technology alive. Pre-modern history The techniques of passive solar building design were practiced for thousands of years, by necessity, before the advent of mechanical heating and cooling. It has remained a traditional part of vernacular architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
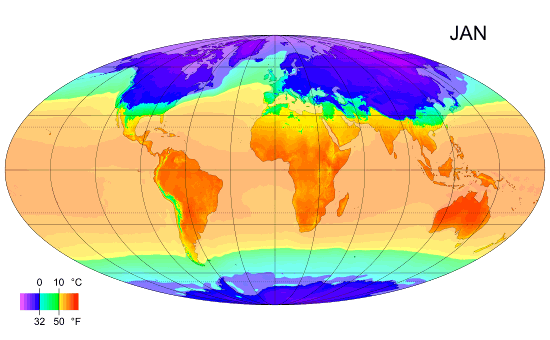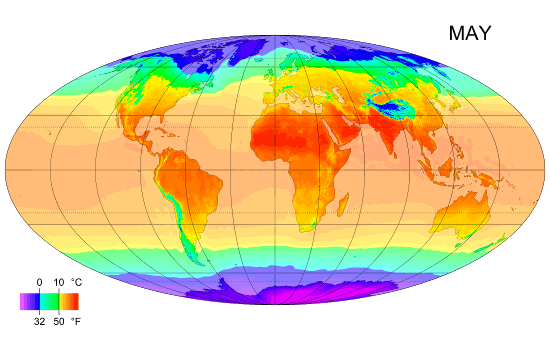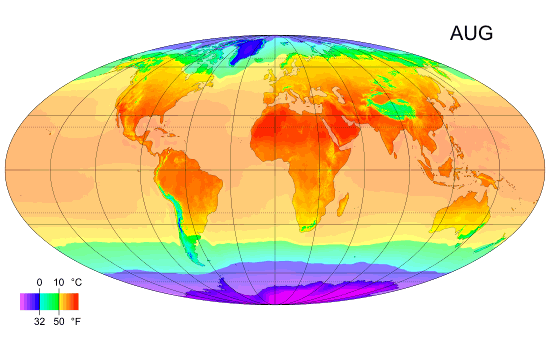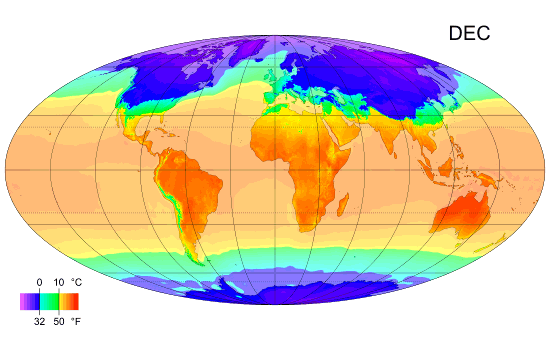
Climate Classification
Climate zones are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. The most used is the Köppen climate classification scheme first developed in 1884. There are several ways to classify climates into similar regimes. Originally, climes were defined in Ancient Greece to describe the weather depending upon a location's latitude. Modern climate classification methods can be broadly divided into ''genetic'' methods, which focus on the causes of climate, and ''empiric'' methods, which focus on the effects of climate. Examples of genetic classification include methods based on the relative frequency of different air mass types or locations within synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic weather disturbances. Examples of empirical, empiric classifications include climate zones defined by plant hardiness, evapotranspiration, or associations with certain biomes, as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Heater
A space heater is a device used to heat a single, small- to medium-sized area. This type of heater can be contrasted with central heating, which distributes heat to multiple areas. Types Dominant mode of heat transfer All space heaters transfer heat to their environment via some combination of the three fundamental modes of heat transfer: convection, radiation, and conduction. Typically heaters are designed with either convection or radiation as the sole dominant mode. Convective heaters ''Convective space heaters'' utilize convection to transfer heat from the power source to a space. These heaters typically either rely on ''natural'' or ''forced'' convection. Natural convection is a phenomenon where temperature variations in an environment generate fluid flow. Forced convection heaters utilize a device like a fan to generate air flow and spread heat at a fast pace. Sometimes called "fan heaters," these are often cheap but lack in efficiency and versatility. Radia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Building
An autonomous building is a hypothetical building designed to be operated independently from infrastructure, infrastructural support services such as the electric power grid, gas grid, municipal water systems, sewage treatment systems, storm drains, communication services, and in some cases, public roads. The literature mostly refers to housing, or the autonomous house. Advocates of autonomous building describe advantages that include reduced environmental impacts, increased security, and lower costs of ownership. Some cited advantages satisfy tenets of green building, not independence per se (see below). Off-grid buildings often rely very little on Civil service, civil services and are therefore safer and more comfortable during civil disaster or military attacks. For example, off-grid buildings would not lose power or water if public supplies were compromised. History 1970s In the 1970s, groups of activists and engineers were inspired by the warnings of imminent resource dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Order 13514
Executive Order 13514 (or EO 13514) was an Executive Order, entitled ''Federal Leadership in Environmental, Energy, and Economic Performance'', which U.S. President Barack Obama issued on October 5, 2009. EO 13514 was replaced by Executive Order 13693, titled ''Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade'',Executive Order 13693—Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade issued March 25, 2015 issued by Obama on March 19, 2015. The Office of the Federal Environmental Executive, whose name was changed to the Office of Federal Sustainability by Executive Order 13693, is housed at the |
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south. With almost 40million residents across an area of , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, largest state by population and List of U.S. states and territories by area, third-largest by area. Prior to European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. European exploration in the 16th and 17th centuries led to the colonization by the Spanish Empire. The area became a part of Mexico in 1821, following Mexican War of Independence, its successful war for independence, but Mexican Cession, was ceded to the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Regulations In The United Kingdom
Building regulations in the United Kingdom are statutory instrument (UK), statutory instruments or statutory regulations that seek to ensure that the policies set out in the relevant legislation are carried out. Building regulations approval is required for most building work in the UK. Building regulations that apply across England and Wales are made under powers set out in the Building Act 1984 (c. 55) while those that apply across Scotland are set out in the Building (Scotland) Act 2003. The Building Act 1984, as amended by the (c. 30), permits detailed regulations to be made by the Secretary of State for England and by a Welsh Minister for Wales. As 'Building Regulations' and 'Building Safety' are devolved areas of law, in the four parts of the UK. The building regulations made under the Building Act 1984 have been periodically updated, rewritten or consolidated, with the latest and current version being the Building Regulations 2010. The UK Government (at Westminster) is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code For Sustainable Homes
The Code for Sustainable Homes was an environmental assessment method for rating and certifying the performance of new homes in United Kingdom. First introduced in 2006, it is a national standard for use in the design and construction of new homes with a view to encouraging continuous improvement in sustainable home building. In 2015 the Government in England withdrew it, consolidating some standards into Building Regulations. History The Code was officially launched in December 2006, and was introduced as a voluntary standard in England in 2007. It complemented the system of Energy Performance Certificates for new homes introduced in 2008 under the European Energy Performance of Buildings Directive, and built on recent changes to Building Regulations in England and Wales. The Government-owned scheme was a successor to the BRE EcoHomes scheme first used in 2000. BRE managed and developed the technical contents of thCode standardfor and on behalf of the Department of Communitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |