|
Louth (barony)
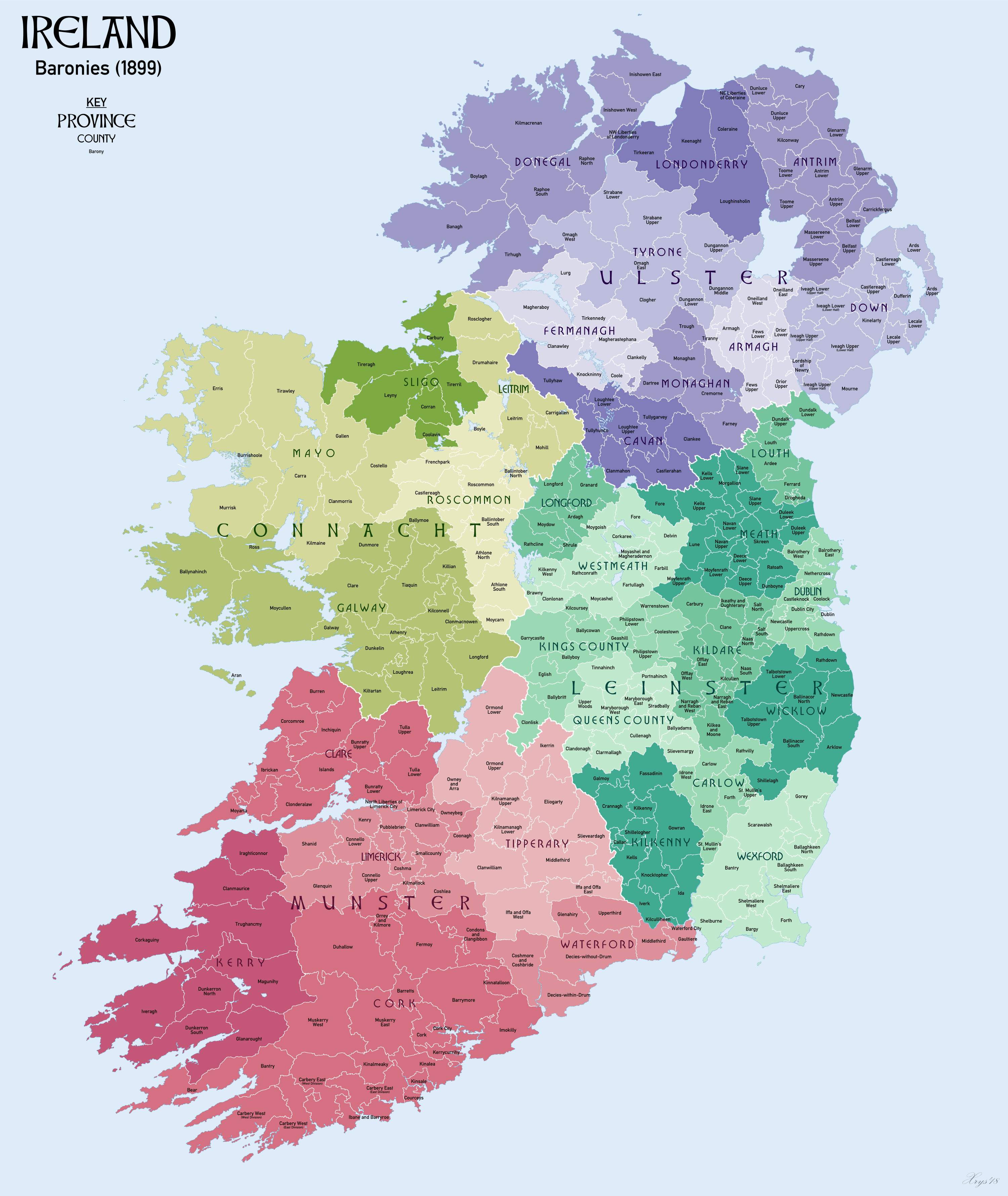
Louth () is a barony in County Louth, Republic of Ireland. Etymology Louth barony is named after the village of Louth (Irish: ''Lú'', named after the god Lugh). Location Louth barony is found in central County Louth, mostly between the River Glyde and River Fane. Louth barony is bordered to the north by Dundalk Upper; to the south by Ardee; and to the west by Farney, County Monaghan. History Louth barony was formed from Ludha, or Lugha, the country of the Ó Cearbhaill Oirialla (O'Carroll of Oriel). List of settlements Below is a list of settlements in Louth barony: *Louth *Tallanstown Tallanstown ( ga, Baile an Tallúnaigh) is a village in County Louth, Ireland. It lies on the R171 Regional road and on the banks of the River Glyde, 11 km southwest of Dundalk Dundalk ( ; ga, Dún Dealgan ), meaning "the fort of ... References {{County Louth Baronies of County Louth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (an Caighdeán Oifigiúil, Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous language, indigenous to the Ireland, island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became Linguistic imperialism, dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as County Cork, Cork, County Donegal, Donegal, County Galway, Galway, and County Kerry, Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties County Mayo, Mayo, County Meath, Meath, and County Waterford, Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second language, second-language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Glyde
The River Glyde ( ga, an Casán) is a river in eastern Ireland, flowing from County Cavan to County Louth. Course The Glyde rises in the town of Bailieborough in Cavan, the upper reaches are sometimes known as the Lagan River, but after the Killanny River joins, exclusively as the Glyde. Another tributary is the River Dee. The Glyde flows in a south-easterly direction before entering the sea at Annagassan in Louth, site of the recently rediscovered ninth-century Viking longphort Linn Duachaill. The river is Ordnance Survey of Ireland: Rivers and their Catchment Basins 1958 (Table of Reference) long. Leisure The salmon and sea trout season here is from 1 February – 20 August. The Killanny River contain stocks of sea trout and salmon. The Glyde Rangers Gaelic Athletic Association The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA; ga, Cumann Lúthchleas Gael ; CLG) is an Irish international amateur sporting and cultural organisation, focused primarily on promoting indigenous Gael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airgíalla
Airgíalla (Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel, Latin: ''Ergallia'') was a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor kingdoms, all independent of each other but paying nominal suzerainty to an overking, usually from the most powerful dynasty. Airgíalla at its peak roughly matched the modern dioceses of Armagh and Clogher, spanning parts of counties Armagh, Monaghan, Louth, Fermanagh, Tyrone and Londonderry. Its main towns were Armagh and Clogher. The name's usage survives as a cultural area of folk tradition in South East Ulster and adjoining areas of County Louth. According to legend, Airgíalla was founded by the Three Collas, who are said to have conquered what is now central Ulster from the Ulaid. The decisive victory was the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, said to have been fought around the year 331. However, this tale is thought to be mostly fiction, and the actual y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Carroll
O'Carroll ( ga, Ó Cearbhaill), also known as simply Carroll, Carrol or Carrell, is a Gaelic Irish clan which is the most prominent sept of the Ciannachta (also known as Clan Cian). Their genealogies claim that they are kindred with the Eóganachta (themselves led by the MacCarthys), descended paternally from Ailill Aulom. From the Middle Ages until 1552, the family ruled an area within the Kingdom of Munster known as Éile. The last monarch Tiege Cian O'Carroll surrendered and regranted to the Tudor Kingdom of Ireland. Etymology Notable is the history of the Ó Cearbhaill whose territory, known as Ely O'Carroll in Éile, consisted of the pasture lands of Ballycrinass, Rosscullenagh and Drumcan, extending to the Lake of Leghagh, commonly Laghaghirisallive and bounded on the west by the lands called Laghenagarken and on the east adjoining or near to Glencrokin. This was always known as Ely O'Carroll. The mountain land extended from the Laghanagerah (Lochan na gCaorach) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farney (barony)
Farney () is a barony in County Monaghan, Republic of Ireland. Etymology Farney takes its name from the ancient kingdom of Fernmag ("plain of alders"). Location Farney is found in southeast County Monaghan, north of the River Lagan, west of the River Fane and south of Lough Muckno. Farney is bordered to the north by Cremorne, County Monaghan; to the east by Dundalk Upper, Louth and Ardee, County Louth; to the south by Lower Slane, County Meath; and to the west by Clankee, County Cavan. History O'Ciaran or O'Kieran is given as a chief of Fearnmuigh as a clan of Tír Eoghain. The O'Larkin sept is cited as chiefs alongside the O'Neills and MacCanns in the old territory of Airgíalla (Oriel), where they were chiefs of Farney and West Uí Breasail (in County Armagh). O Cosgro (ve) (O Cosgraigh) was the name of the chiefs of Feara Ruis (Fir Rois) near Carrickmacross and Ardee. MacArdle, a branch of the MacMahons of Oriel are noted here, as well as septs of Callan, O'Finn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardee (barony)
Ardee () is a barony in County Louth, Republic of Ireland. Ity is named after the town of Ardee (Irish: ''Baile Átha Fhirdhia'', "town of Ferdiad's ford").Ardeeis located in central County Louth, between the Keeran River and Dundalk Bay. The barony is bordered to the north by Louth; to the south by Ferrard; and to the west by Lower Slane, County Meath and Farney, County Monaghan. The barony was formed from the district of Uí Seanchain (Hy Segan, Hy Seanghain, O'Shanaghan). In 841, Vikings established a longphort (raiding base) at Linn Duachaill, Annagassan. Baron Ardee is a courtesy title of the heir of the Earl of Meath. List of settlements *Ardee *Castlebellingham Castlebellingham () is a village and townland in County Louth, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The village has become quieter since the construction of the new M1 motorway, which bypasses it. The population of Castlebellingham-Kilsaran (named for ... References {{County Louth, state=collapsed Baronies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundalk Upper
Dundalk Upper () is a barony in County Louth, Republic of Ireland. Etymology Dundalk Upper is named after the town of Dundalk (Irish: ''Dún Dealgan'', "Dalgan's dún"). Location Dundalk Upper is found in north County Louth, containing the valleys of the Castletown River and River Fane. Dundalk Upper is bordered to the east by Dundalk Lower ( ga, Dún Dealgan Íochtarach), to the south by Louth ( ga, Lú), to the west by Farney ( ga, Fearnaigh), County Monaghan, and to the north by Orior Upper ( ga, Na hOirthir Uachtaracha) and Fews Upper ( ga, Na Feá Uachtaracha), County Armagh. History Dundalk Upper was formed from Uí Mac Uais Breg, the country of the Mac Scanlans. The barony of Dundalk was the ancient home of the Conaille Muirtheimhne. The barony was split in half by 1821. Civil Parishes There are 14 civil parishes. * Ballybarrack (6 townlands) * Barronstown (14 townlands) * Castletown (8 townlands) * Creggan (10 townlands) * Dunbin (9 townlands) * Dundalk (21 tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Fane
The River Fane ( ga, Abhainn Átha Féan) is a river flowing from County Monaghan to Dundalk Bay in County Louth, Ireland. Course Originating in Lough Ross on the border of County Monaghan and County Armagh, and so of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland, the Fane flows east towards Dundalk Bay, straddling the border between Counties Monaghan, Louth and Armagh flowing through Inniskeen, Knockbridge, before meeting Dundalk Bay near Blackrock, County Louth. The Fane River is 38.25 miles long and drains an area of 350 km2 Water extraction The Fane is, through the Cavan Hill pumping station, a major source of fresh water for Dundalk and the surrounding area in northern Louth. Pollution Runoff from illegal fuel laundering operations, carried out in the region, is a major source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons which have severely affected Atlantic salmon stocks in the region. See also *Rivers of Ireland Shown here are all the major rivers and tributaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugh
Lugh or Lug (; ga, label= Modern Irish, Lú ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a savior.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Gods of the Celts and the Indo-Europeans''. University of Innsbruck, 1994. p.117 He is associated with skill and mastery in multiple disciplines, including the arts.Monaghan, Patricia. ''The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore''. Infobase Publishing, 2004. pp.296-297 Lugh also has associations with oaths, truth and the law, and therefore with rightful kingship.Koch, John T. ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. ABC-CLIO, 2006. p.1200 Lugh is linked with the harvest festival of Lughnasadh, which bears his name. His most common epithets are ''Lámfada'' ("long hand" or "long arm", possibly for his skill with a spear or his ability as a ruler) and ''Samildánach'' ("equally skilled in many arts"). In mythology, Lugh is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louth, County Louth
Louth () is a village at the heart of County Louth, Ireland. It is roughly 11 km south-west of the town of Dundalk, 10.9 km to neighbouring town Ardee. The village is approximately 15 km south-east of Carrickmacross town in County Monaghan. The village gave its name to the county. Etymology The village is named after Lugh, a god of the ancient Irish, and may once have been the site of a shrine dedicated to the god. Historically, the place-name was spelt in variously different ways such as; "''Lughmhagh"'', "''Lughmhadh"'' and "''Lughbhadh"''. The first is thought to mean "Lugh's plain" or "Lugh's field", but the meaning of the other two is unclear. ''Lú'' is the modern simplified spelling. History According to tradition, Mochta—a Christian missionary from Britain—founded a monastery at Louth in the 6th century, known today as St. Mochta's House. In the 1920s the structure was completely dismantled and rebuilt in an attempt to save it from damage ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)