|
Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim
LotharHis name is sometimes misspelled as ''Lother''. Wolfgang Nordheim (November 7, 1899, Munich – October 5, 1985, La Jolla, California) was a German-born American theoretical physicist. He was a pioneer in the applications of quantum mechanics to solid-state problems, such as thermionic emission, work function of metals, field electron emission, rectification in metal-semiconductor contacts and electrical resistance in metals and alloys. He also worked in the mathematical foundations of quantum mechanics, cosmic rays and in nuclear physics. Life He obtained his PhD in 1923, under the supervision of Max Born in the University of Göttingen. He also worked with Edward Teller on the muon, sparkling his interest in cosmic rays. As a "physical assistant" to David Hilbert (like his teacher Born before him), he worked with him John von Neumann and Eugene Wigner on the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics in 1928. He wrote extensive articles for the ''Lehrbuch der P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is not a state of its own. It ranks as the 11th-largest city in the European Union. The metropolitan area has around 3 million inhabitants, and the broader Munich Metropolitan Region is home to about 6.2 million people. It is the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, third largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. Munich is located on the river Isar north of the Alps. It is the seat of the Upper Bavaria, Upper Bavarian administrative region. With 4,500 people per km2, Munich is Germany's most densely populated municipality. It is also the second-largest city in the Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect area after Vienna. The first record of Munich dates to 1158. The city ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
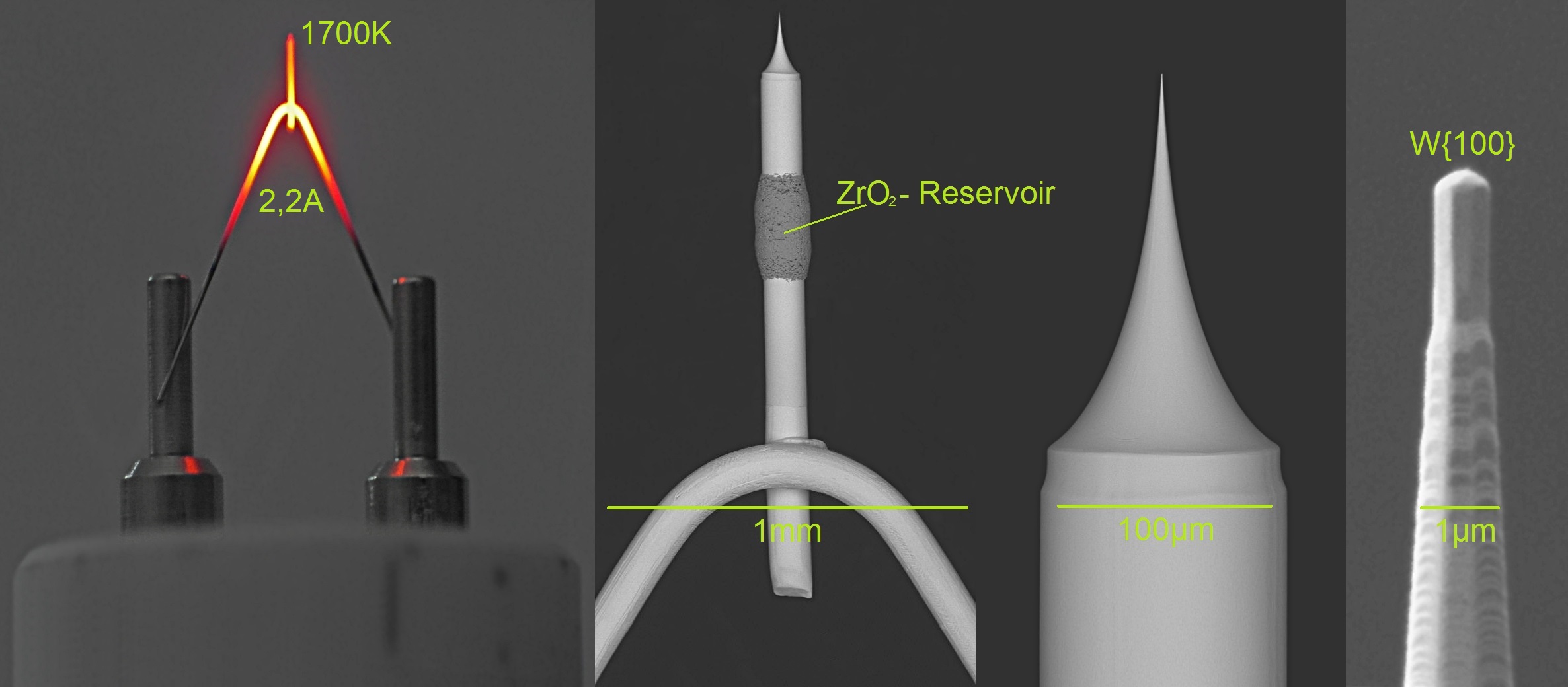
Field Electron Emission
Field electron emission, also known as field-induced electron emission, field emission (FE) and electron field emission, is the emission of electrons from a material placed in an electrostatic field. The most common context is field emission from a solid surface into a vacuum. However, field emission can take place from solid or liquid surfaces, into a vacuum, a fluid (e.g. air), or any non-conducting or weakly conducting dielectric. The field-induced promotion of electrons from the valence (chemistry), valence to conduction band of semiconductors (the Zener effect) can also be regarded as a form of field emission. Field emission in pure metals occurs in high electric fields: the gradients are typically higher than 1 gigavolt per metre and strongly dependent upon the work function. While electron sources based on field emission have a number of applications, field emission is most commonly an undesirable primary source of electrical breakdown, vacuum breakdown and electrical disch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Bethe
Hans Albrecht Eduard Bethe (; ; July 2, 1906 – March 6, 2005) was a German-American physicist who made major contributions to nuclear physics, astrophysics, quantum electrodynamics and solid-state physics, and received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1967 for his work on the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis. For most of his career, Bethe was a professor at Cornell University.James C. Keck Collected Works and Biography () has the class notes taken by one of Bethe's students at Cornell from the graduate courses on Nuclear Physics and on Applications of Quantum Mechanics he taught in the spring of 1947. In 1931, Bethe developed the Bethe ansatz, which is a method for finding the exact solutions for the Eigenvalue, eigenvalues and Eigenvector, eigenvectors of certain one-dimensional quantum many-body models. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in what is called ''positron emission''. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron emission to be energeticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University
Moscow State University (MSU), officially M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,. is a public university, public research university in Moscow, Russia. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches. Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner were affiliated with the university. History Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov and Mikhail Lomonosov promoted the idea of a university in Moscow, and Elizabeth of Russia, Russian Empress Elizabeth decreed its establishment on . The first lectures were given on . Saint Petersburg State University and MSU each claim to be Russia's oldest university. Though Moscow State University was founded in 1755, St. Petersburg which has had a continuous existence as a "university" since 1819 sees itself as the successor of an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Pouillet
Claude Servais Mathias Pouillet (16 February 1790 – 14 June 1868) was a French physicist and a professor of physics at the Sorbonne and member of the French Academy of Sciences (elected 1837). Biography He studied sciences at the École normale supérieure (Paris), and from 1829 to 1849 was associated with the Conservatoire national des arts et métiers, first as a professor, and beginning in 1832, an administrator. After the death of Pierre Louis Dulong in 1838, he attained the chair of physics at the Faculty of Sciences.Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers edited by Virginia Trimble, Thomas R. Williams, Katherine Bracher, Richard Jarrell, Jordan D. Marché, F. Jamil Ragep For a brief period of time, he was chair of physics at the |
Johann Heinrich Jakob Müller
Johann Heinrich Jakob Müller (30 April 1809, Kassel, Kingdom of Westphalia – 3 October 1875, Freiburg im Breisgau) was a German physicist. Biography From 1829 he studied mathematics and physics at the University of Bonn, where one of his instructors was Julius Plücker, then continued his education at the University of Giessen as a student of Justus von Liebig. In 1834 he became a teacher at the Darmstadt gymnasium, and in 1837 returned to Giessen as an instructor at the ''Realschule''. In 1844 he was appointed professor of physics and technology at the University of Freiburg, a position he maintained up until his death in 1875.Müller, Johann Heinrich Deutsche Biographie He conducted research on , |
Mathematical Formulation Of Quantum Mechanics
The mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics are those mathematical formalisms that permit a rigorous description of quantum mechanics. This mathematical formalism uses mainly a part of functional analysis, especially Hilbert spaces, which are a kind of linear space. Such are distinguished from mathematical formalisms for physics theories developed prior to the early 1900s by the use of abstract mathematical structures, such as infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces ( ''L''2 space mainly), and operators on these spaces. In brief, values of physical observables such as energy and momentum were no longer considered as values of functions on phase space, but as eigenvalues; more precisely as spectral values of linear operators in Hilbert space. These formulations of quantum mechanics continue to be used today. At the heart of the description are ideas of ''quantum state'' and ''quantum observables'', which are radically different from those used in previous models of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Wigner
Eugene Paul Wigner (, ; November 17, 1902 – January 1, 1995) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist who also contributed to mathematical physics. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963 "for his contributions to the theory of the atomic nucleus and the elementary particles, particularly through the discovery and application of fundamental symmetry principles". A graduate of the Technical Hochschule Berlin (now Technische Universität Berlin), Wigner worked as an assistant to Karl Weissenberg and Richard Becker (physicist), Richard Becker at the Max Planck Institute for Physics, Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin, and David Hilbert at the University of Göttingen. Wigner and Hermann Weyl were responsible for introducing group theory into physics, particularly the theory of symmetry in physics. Along the way he performed ground-breaking work in pure mathematics, in which he authored a number of mathematical theorems. In particular, Wigner's theorem is a cornerstone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, integrating Basic research, pure and Applied science#Applied research, applied sciences and making major contributions to many fields, including mathematics, physics, economics, computing, and statistics. He was a pioneer in building the mathematical framework of quantum physics, in the development of functional analysis, and in game theory, introducing or codifying concepts including Cellular automaton, cellular automata, the Von Neumann universal constructor, universal constructor and the Computer, digital computer. His analysis of the structure of self-replication preceded the discovery of the structure of DNA. During World War II, von Neumann worked on the Manhattan Project. He developed the mathematical models behind the explosive lense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician and philosopher of mathematics and one of the most influential mathematicians of his time. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas including invariant theory, the calculus of variations, commutative algebra, algebraic number theory, the foundations of geometry, spectral theory of operators and its application to integral equations, mathematical physics, and the foundations of mathematics (particularly proof theory). He adopted and defended Georg Cantor's set theory and transfinite numbers. In 1900, he presented a collection of problems that set a course for mathematical research of the 20th century. Hilbert and his students contributed to establishing rigor and developed important tools used in modern mathematical physics. He was a cofounder of proof theory and mathematical logic. Life Early life and education Hilbert, the first of two children and only son of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the free neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron of the same charge as the muon and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |