|
Lost Hills Oil Field
The Lost Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in the Lost Hills Range, north of the town of Lost Hills, California, Lost Hills in western Kern County, California, Kern County, California, in the United States. Production While only the 18th-largest oil field in California in size, in total remaining reserves it ranks sixth, with the equivalent of over producible reserves still in the ground, according to the California Division of Oil, Gas and Geothermal Resources (Chevron Corp., the principal operator, estimates considerably more oil in the ground). Production at Lost Hills has been increasing steadily: as of the end of 2006, it was California's second fastest-growing oil field, exceeded only by the nearby Cymric Oil Field, Cymric Field. The Lost Hills field also contains considerable reserves of natural gas. In 1998, one of the field's gas wells was the site of a spectacular blowout, producing a pillar of fire which burned for 14 days and was visible more than away. Setting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that Strike and dip, dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various Stratum, rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geological map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobil
Mobil Oil Corporation, now known as just Mobil, is a petroleum brand owned and operated by American oil and gas corporation ExxonMobil, formerly known as Exxon, which took its current name after history of ExxonMobil#merger, it and Mobil merged in 1999. A direct descendant of Standard Oil, Mobil was originally known as the Standard Oil Company of New York (shortened to Socony) after Standard Oil was Standard Oil Co. of New Jersey v. United States, split into 43 different entities in a 1911 Supreme Court decision. Socony merged with Vacuum Oil Company, from which the Mobil name first originated, in 1931 and subsequently renamed itself to "Socony-Vacuum Oil Company". Over time, Mobil became the company's primary identity, which prompted a renaming in 1955 to the "Socony Mobil Oil Company", and then in 1966 to the "Mobil Oil Corporation". Mobil credits itself with being the first company to introduce Pay at the pump, paying at the pump at its gas stations, the first company to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
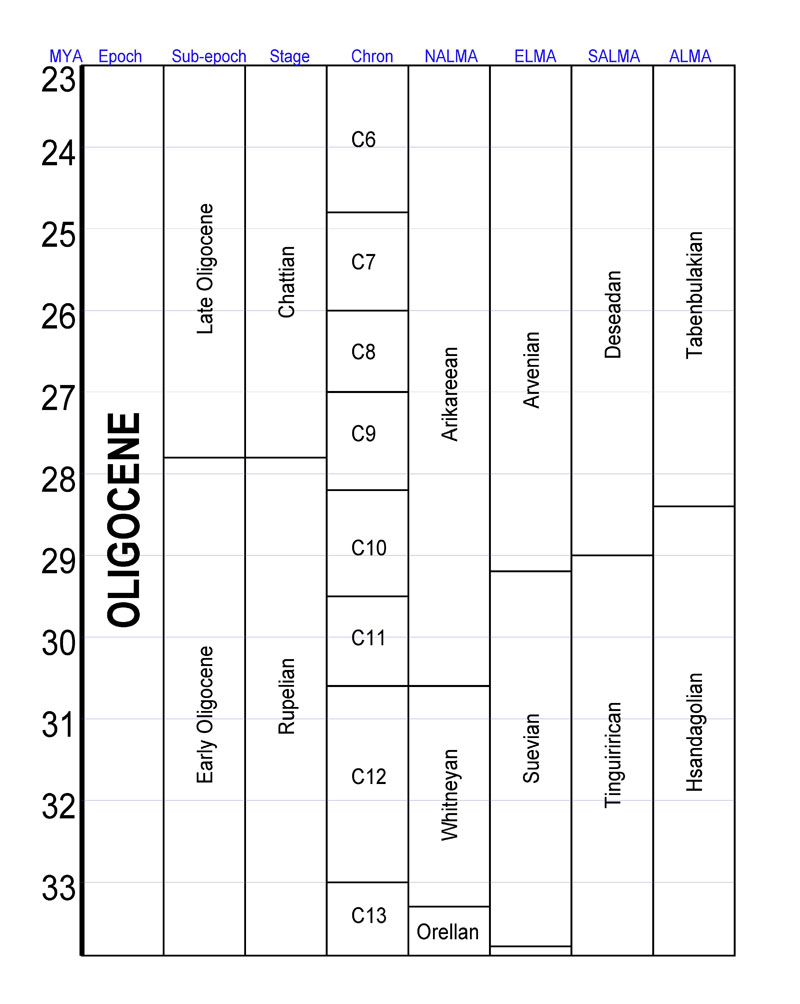
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temblor Formation
The Temblor Formation is a geologic formation in California. It preserves fossils dating back from the Late Oligocene to the Middle Miocene of the Neogene period. It is notable for the famous Sharktooth Hill deposit (otherwise known as Ernst Quarry). Fossils Vertebrates Cartilagenous fishes = Sharks = * ''Carcharias'' * '' Cephaloscyllium'' * '' Cetorhinus'' * †'' Carcharocles megalodon'' Boessenecker, Ehret, D, Long, D, Churchill, M, Martin, E, Boessenecker, S. The Early Pliocene extinction of the mega-toothed shark ''Otodus megalodon'': a view from the eastern north Pacific. PeerJ. 2019 Feb 13;7:e6088. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6088. eCollection 2019. * †'' Galeocerdo aduncus'' * †'' Hemipristis serra'' * '' Heterodontus'' * '' Hexanchus'' * †''Isurus desori'' * †'' Isurus hastalis'' * †'' Isurus planus''Malchow, A. 2009. MIOCENE SHARK TOOTH HILL LOCALITY, KERN COUNTY, CALIFORNIA. Geological Society of America North-Central Section - 43rd Annual Meeting (2-3 April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monterey Formation
The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geology, geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The Type locality (geology), type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for Hydrocarbon exploration, petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and Tectonostratigraphy, tectono-stratigraphic history. The US Energy Information Administration (EIA) estimated in 2014 that the 1,750 square mile Monterey Formation could, as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etchegoin Formation
The Etchegoin Formation is a Pliocene epoch geologic formation in the lower half of the San Joaquin Valley in central California.USGS.gov: "Neogene Gas Total Petroleum System—Neogene Nonassociated Gas Assessment Unit of the San Joaquin Basin Province" Chapter 22 of the ''Petroleum Systems and Geologic Assessment of Oil and Gas in the San Joaquin Basin Province, California''; by Allegra Hosford Scheirer and Leslie B. Magoon.USGS.gov: "The Kern River Formation, Southeastern San Joaquin Valley, California" Geological Sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulare Formation
The Tulare Formation () is a Pliocene to Holocene epoch geologic formation in the central and southern San Joaquin Valley of central California. USGS.gov: "Geology of the Tulare Formation and other continental deposits, Kettleman City area, San Joaquin Valley, California, with a section on ground-water management considerations and use of texture maps" Water-Resources Investigations Report 83-4000; by R.W. Page; 1983. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons. These processes include those of mountain-building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Principles of tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles can help geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth-surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |