|
Lord Kalvan Of Otherwhen
''Lord Kalvan of Otherwhen'' is a 1965 science fiction novel by American writer H. Beam Piper; it is part of his Paratime series of stories, and was expanded by John F. Carr to form the Kalvan series (with some installments co-written by Carr and other writers). It recounts the adventures of a Pennsylvania state trooper who is accidentally transported to a more backward parallel universe. It was published posthumously, making it Piper's final science fiction novel. The book is an expanded version of the novelettes "Gunpowder God", which had been published in the November 1964 issue of Analog Science Fiction and Fact, and "Down Styphon!", which had been published in the November 1965 issue of Analog. "Gunpowder God" itself is a Paratime-series rewrite of the unpublished story " When in the Course", which takes place in the Terro-Human Future History milieu. A sequel, '' Great Kings' War'', was written by Roland Green and John F. Carr. Carr further continued the storylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Gaughan
John Brian Francis "Jack" Gaughan, pronounced like 'gone' (September 24, 1930 – July 21, 1985), was an American science fiction artist and illustrator and multiple winner of the Hugo Award in the category of Hugo Award for Best Professional Artist, Best Professional Artist. Career John Brian Francis Gaughan was born September 24, 1930, in Springfield, Ohio, to James J. and Elizabeth Gaughan. Working primarily with Donald A. Wollheim at Ace Books, and DAW Books from 1971, his simple linear style brought to life images of such works as Andre Norton's ''Witch World'' novels and E. E. Smith's ''Lensmen'' and Skylark series, ''Skylark'' novels (for which he did two related sets of Pyramid Books covers). His broad visual vocabulary enabled him to render the objects, spaceships and scenes in whatever was presented to him as they were described in the books and stories he illustrated. That was especially an accomplishment as many of these authors drew on their knowledge of esoteric s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking lock (firearm), ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also known as the ''flintlock mechanism, true flintlock'', that was introduced in the early 17th century, and gradually replaced earlier firearm-ignition technologies, such as the matchlock, the wheellock, and the earlier flintlock mechanisms such as the snaplock and snaphaunce. The true flintlock continued to be in common use for over two centuries, replaced by percussion cap and, later, the Cartridge (firearms), cartridge-based systems in the early-to-mid 19th century. Although long superseded by modern firearms, flintlock weapons enjoy continuing popularity with Black powder, black-powder shooting enthusiasts. History French court gunsmith Marin le Bourgeoys made a firearm incorporating a flintlock mechanism for King Louis XIII ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jo Walton
Jo Walton (born 1964) is a Welsh-Canadian fantasy and science fiction writer and poet. She is best known for the fantasy novel '' Among Others'', which won the Hugo and Nebula Awards in 2012, and '' Tooth and Claw'', a Victorian-era novel with dragons which won the World Fantasy Award in 2004. Other works by Walton include the ''Small Change'' series, in which she blends alternate history with the cozy mystery genre, comprising '' Farthing'', '' Ha'penny'' and '' Half a Crown''. Her fantasy novel '' Lifelode'' won the 2010 Mythopoeic Award, and her alternate history '' My Real Children'' received the 2015 Tiptree Award. Walton is also known for her non-fiction, including book reviews and SF commentary in the magazine '' Tor.com''. A collection of her articles were published in ''What Makes This Book So Great'' (2014), which won the Locus Award for Best Non-Fiction. Background Walton was born in 1964 in Aberdare, a town in the Cynon Valley of Wales. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Man Theory
The great man theory is an approach to the study of history popularised in the 19th century according to which history can be largely explained by the impact of ''great men'', or heroes: highly influential and unique individuals who, due to their natural attributes, such as superior intellect, heroic courage, extraordinary leadership abilities, or divine inspiration, have a decisive historical effect. The theory is primarily attributed to the Scottish essayist, historian, and philosopher Thomas Carlyle, who gave a series of lectures on heroism in 1840, later published as ''On Heroes, Hero-Worship, & the Heroic in History'', in which he states: This theory is usually contrasted with people's history, which emphasizes the life of the masses creating overwhelming waves of smaller events which carry leaders along with them. Another contrasting school is historical materialism. Overview Carlyle stated that "The History of the world is but the Biography of great men", reflecting hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Tactics
Military tactics encompasses the art of organizing and employing fighting forces on or near the battlefield. They involve the application of four battlefield functions which are closely related – kinetic or firepower, Mobility (military), mobility, protection or security, and Shock tactics, shock action. Tactics are a separate function from command and control and logistics. In contemporary military science, tactics are the lowest of three levels of warfighting, the higher levels being the military strategy, strategic and Operational level of war, operational levels. Throughout history, there has been a shifting balance between the four tactical functions, generally based on the application of military technology, which has led to one or more of the tactical functions being dominant for a period of time, usually accompanied by the dominance of an associated Combat arms, fighting arm deployed on the battlefield, such as infantry, artillery, cavalry or tanks. Tactical functions Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Strategy
Military strategy is a set of ideas implemented by military organizations to pursue desired Strategic goal (military), strategic goals. Derived from the Greek language, Greek word ''strategos'', the term strategy, when first used during the 18th century, was seen in its narrow sense as the "art of the general", or "the art of arrangement" of troops. and deals with the planning and conduct of campaigns. The father of Western modern strategic studies, Carl von Clausewitz (1780–1831), defined military strategy as "the employment of battles to gain the end of war." B. H. Liddell Hart's definition put less emphasis on battles, defining strategy as "the art of distributing and applying military means to fulfill the ends of policy". Hence, both gave the preeminence to political aims over military goals. Sun Tzu (544–496 BC) is often considered as the father of Eastern military strategy and greatly influenced Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese historical and modern war tactics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifling
Rifling is the term for helical grooves machined into the internal surface of a firearms's barrel for imparting a spin to a projectile to improve its aerodynamic stability and accuracy. It is also the term (as a verb) for creating such grooves. The opposite of rifling is smoothbore. Rifling is measured in ''twist rate'', the distance the rifling takes to complete one full revolution, expressed as a ratio with 1 as its base (e.g., 1:). A shorter distance/lower ratio indicates a faster twist, generating a higher spin rate (and greater projectile stability). The combination of length, weight, and shape of a projectile determines the twist rate needed to gyroscopically stabilize it: barrels intended for short, large-diameter projectiles such as spherical lead balls require a very low twist rate, such as 1 turn in 48 inches (122 cm). Barrels intended for long, small-diameter projectiles, such as the ultra-low-drag 80-grain 0.223 inch bullets (5.2 g, 5.56&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trunnion
A trunnion () is a cylinder, cylindrical Boss (engineering), protrusion used as a mounting or pivoting point. First associated with cannons, they are an important military development. In mechanical engineering (see the Trunnion#Trunnion bearings, trunnion bearing section below), it is one part of a rotating joint where a shaft (the trunnion) is inserted into (and turns inside) a full or partial cylinder. Medieval history In a cannon, the trunnions are two projections cast just forward of the center of mass of the cannon and fixed to a two-wheeled movable gun carriage. With the creation of larger and more powerful siege guns in the early 15th century, a new way of mounting them became necessary. Stouter gun carriages were created with reinforced wheels, axles, and “trails” which extended behind the gun. Guns were now as long as in length and they were capable of shooting iron projectiles weighing from . When discharged, these wrought iron balls were comparable in range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
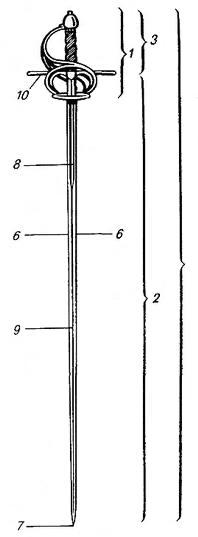
Rapier
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as '' spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It was widely popular in Western Europe throughout the 16th and 17th centuries as a symbol of nobility or gentleman status. It is called because it was carried as an accessory to clothing, generally used for fashion and as a weapon for dueling, self-defense and as a military side arm. Its name is of Spanish origin and appears recorded for the first time in the '' Coplas de la panadera'', by Juan de Mena, written approximately between 1445 and 1450: As fencing spread throughout Western Europe, important sources for rapier fencing arose in Spain, known under the term ("dexterity"), in Italy and France. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct continuation of this tradition of fencing. Rapier fencing form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium nitrate (saltpeter). The sulfur and charcoal act as fuels while the saltpeter is an oxidizer. Gunpowder has been widely used as a propellant in firearms, artillery, rocketry, and pyrotechnics, including use as a blasting agent for explosives in quarrying, mining, building Pipeline transport, pipelines, tunnels, and road#Construction, roads. Gunpowder is classified as a Explosive#Low, low explosive because of its relatively slow decomposition rate, low ignition temperature and consequently low brisance, brisance (breaking/shattering). Low explosives deflagration, deflagrate (i.e., burn at subsonic speeds), whereas high explosives detonation, detonate, producing a supersonic shockwave. Ignition of gunpowder packed behind a projectile generates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |