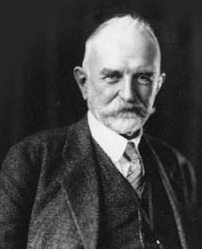|
Looking Glass Self
The looking-glass self is a concept introduced by American sociologist Charles Horton Cooley in ''Human Nature and the Social Order'' (1902). The term describes the process by which individuals develop their self-concept based on their understanding of how others perceive them. According to Cooley, individuals form their self-image by imagining how they appear to others, interpreting others’ reactions, and internalizing these perceptions. This reflective process functions like a mirror, wherein individuals use social interactions to observe themselves indirectly. Over time, these imagined evaluations by others can influence and shape one's self-assessment. Sociologist Lisa McIntyre, in ''The Practical Skeptic: Core Concepts in Sociology'', further elaborates that the looking-glass self encapsulates the tendency for individuals to interpret and understand their identities through the lens of others' perceived judgments. Cooley's three steps Cooley takes into account three step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Cooley
Charles Horton Cooley (August 17, 1864 – May 7, 1929) was an American sociologist. He was the son of Michigan Supreme Court Judge Thomas M. Cooley. He studied and went on to teach economics and sociology at the University of Michigan. He was a founding member of the American Sociological Association in 1905 and became its eighth president in 1918. He is perhaps best known for his concept of the looking-glass self, which is the concept that a person's self grows out of society's interpersonal interactions and the perceptions of others. Biography Charles Horton Cooley was born in Ann Arbor, Michigan, on August 17, 1864, to Mary Elizabeth Horton and Thomas M. Cooley. Thomas Cooley was the Supreme Court Judge for the state of Michigan, and he was one of the first three faculty members to found the University of Michigan Law School in 1859. He served as dean of the law school from 1859 to 1884. Cooley's mother, Mary, took an active interest in public affairs and traveled with h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-concept
In the psychology of self, one's self-concept (also called self-construction, self-identity, self-perspective or self-structure) is a collection of beliefs about oneself. Generally, self-concept embodies the answer to the question ''"Who am I?".'' The self-concept is distinguishable from self-awareness, which is the extent to which self-knowledge (psychology), self-knowledge is defined, consistent, and currently applicable to one's Attitude (psychology), attitudes and dispositions. Self-concept also differs from self-esteem: self-concept is a cognitive or descriptive component of one's self (e.g. "I am a fast runner"), while self-esteem is evaluative and opinionated (e.g. "I feel good about being a fast runner"). Self-concept is made up of one's self-schemas, and interacts with self-esteem, self-knowledge, and the social self to form the self as a whole. It includes the past, present, and future selves, where future selves (or possible selves) represent individuals' ideas of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyberpsychology
Cyberpsychology (also known as Internet psychology, web psychology, or digital psychology) is a scientific Interdisciplinarity, inter-disciplinary domain that focuses on the Psychology, psychological phenomena which emerge as a result of the Interpersonal relationship, human interaction with digital technology, particularly the Internet. Cyberpsychology is a field that explores the psychological phenomena associated with cyberspace which includes study of human behaviour, emotions in online environments slike social media, virtual reality and many more gaming platforms. Cyberpsychology also interacts with the areas like neuroscience, sociology and media studies that offers insights into how digital tool shape individual and collective experiences. Overview Cyberpsychology is a broadly used term for inter-disciplinary research that commonly describes how humans interact with others over technology, how human behavior and psychological states are affected by technology, and how tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive, long-term pattern of significant interpersonal relationship instability, an acute fear of Abandonment (emotional), abandonment, and intense emotional response, emotional outbursts. People diagnosed with BPD frequently exhibit self-harming behaviours and engage in risky activities, primarily due to Emotional dysregulation, challenges regulating emotional states to a healthy, stable baseline. Symptoms such as Dissociation (psychology), dissociation (a feeling of Emotional detachment, detachment from reality), a pervasive sense of emptiness, and distorted sense of self are prevalent among those affected. The onset of BPD symptoms can be triggered by events that others might perceive as normal, with the disorder typically manifesting in early adulthood and persisting across diverse contexts. BPD is often Comorbidity, comorbid with substance use disorders, depressive disorders, and eating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolic Interaction
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to humans' particular use of shared language to create common symbols and meanings, for use in both intra- and interpersonal communication. It is particularly important in microsociology and social psychology. It is derived from the American philosophy of pragmatism and particularly from the work of George Herbert Mead, as a pragmatic method to interpret social interactions. According to Mead, symbolic interactionism is "The ongoing use of language and gestures in anticipation of how the other will react; a conversation". Symbolic interactionism is "a framework for building theory that sees society as the product of everyday interactions of individuals". In other words, it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds, and in return, how these worlds shape individual behaviors. It is a framework that help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingroups And Outgroups
In social psychology and sociology, an in-group is a social group to which a person self-categorization theory, psychologically identifies as being a member. By contrast, an out-group is a social group with which an individual does not identify. People may for example identify with their peer group, family, community, sports team, political party, gender, sexual orientation, religion, or nation. It has been found that the psychological membership of social groups and categories is associated with a wide variety of phenomena. The terminology was made popular by Henri Tajfel and colleagues beginning in the 1970s during his work in formulating social identity theory. The significance of in-group and out-group categorization was identified using a method called the minimal group paradigm. Tajfel and colleagues found that people can form self-preferencing in-groups within a matter of minutes and that such groups can form even on the basis of completely arbitrary and invented discri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-categorization Theory
Self-categorization theory is a theory in social psychology that describes the circumstances under which a person will perceive collections of people (including themselves) as a group, as well as the consequences of perceiving people in group terms. Although the theory is often introduced as an explanation of psychological group formation (which was one of its early goals), it is more accurately thought of as general analysis of the functioning of categorization processes in social perception and interaction that speaks to issues of individual identity as much as group phenomena. It was developed by John Turner and colleagues, and along with social identity theory it is a constituent part of the social identity approach. It was in part developed to address questions that arose in response to social identity theory about the mechanistic underpinnings of social identification. Haslam, A. S. (2001). Psychology in Organizations. London, SAGE Publications. Self-categorization theory ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Influence
Social influence comprises the ways in which individuals adjust their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment. It takes many forms and can be seen in conformity, socialization, peer pressure, obedience (human behavior), obedience, leadership, persuasion, sales, and marketing. Typically social influence results from a specific action, command, or request, but people also alter their attitudes and behaviors in response to what they perceive others might do or think. In 1958, Harvard psychologist Herbert Kelman identified three broad varieties of social influence. #Compliance (psychology), Compliance is when people appear to agree with others but actually keep their dissenting opinions private. #Identification (psychology), Identification is when people are influenced by someone who is liked and respected, such as a famous celebrity. #Internalisation (sociology), Internalization is when people accept a belief or behavior and agree both publicly and privately. Morton Deu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Constructionism
Social constructionism is a term used in sociology, social ontology, and communication theory. The term can serve somewhat different functions in each field; however, the foundation of this Conceptual framework, theoretical framework suggests various facets of social reality—such as concepts, beliefs, Social norm, norms, and Value (ethics and social sciences), values—are formed through continuous interactions and negotiations among society's members, rather than Empirical research, empirical observation of Reality, physical reality. The theory of social constructionism posits that much of what individuals perceive as 'reality' is actually the outcome of a dynamic process of construction influenced by Convention (norm), social conventions and Social structure, structures. Unlike phenomena that are innately determined or biologically predetermined, these social constructs are collectively formulated, sustained, and shaped by the social environment, social contexts in which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Herbert Mead
George Herbert Mead (February 27, 1863 – April 26, 1931) was an American philosopher, Sociology, sociologist, and psychologist, primarily affiliated with the University of Chicago. He was one of the key figures in the development of pragmatism. He is regarded as one of the founders of symbolic interactionism, and was an important influence on what has come to be referred to as the Chicago school (sociology), Chicago School of Sociology. Biography George Herbert Mead was born on February 27, 1863, in South Hadley, Massachusetts. He was raised in a Protestantism, Protestant, middle-class family comprising his father, Hiram Mead, his mother, Elizabeth Storrs Mead (née Billings), and his sister Alice. His father was a former Congregationalist pastor from a lineage of farmers and clergymen and who later held the chair in Sacred Rhetoric and Pastoral Theology at Oberlin College's theological seminary. Elizabeth taught for two years at Oberlin College and subsequently, from 1890 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expectancy Effect (other) – when expectations of a subject (e.g., a patient or research participant) influences themselves and their outcome
{{Disambig ...
Expectancy effect, also known as effects caused by expectations, may refer to: * Observer-expectancy effect – when expectations of an observer (e.g., a clinician or researcher) influences a subject and their outcome * Subject-expectancy effect In scientific research and psychotherapy, the subject-expectancy effect, is a form of reactivity that occurs when a research subject expects a given result and therefore unconsciously affects the outcome, or reports the expected result. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |