|
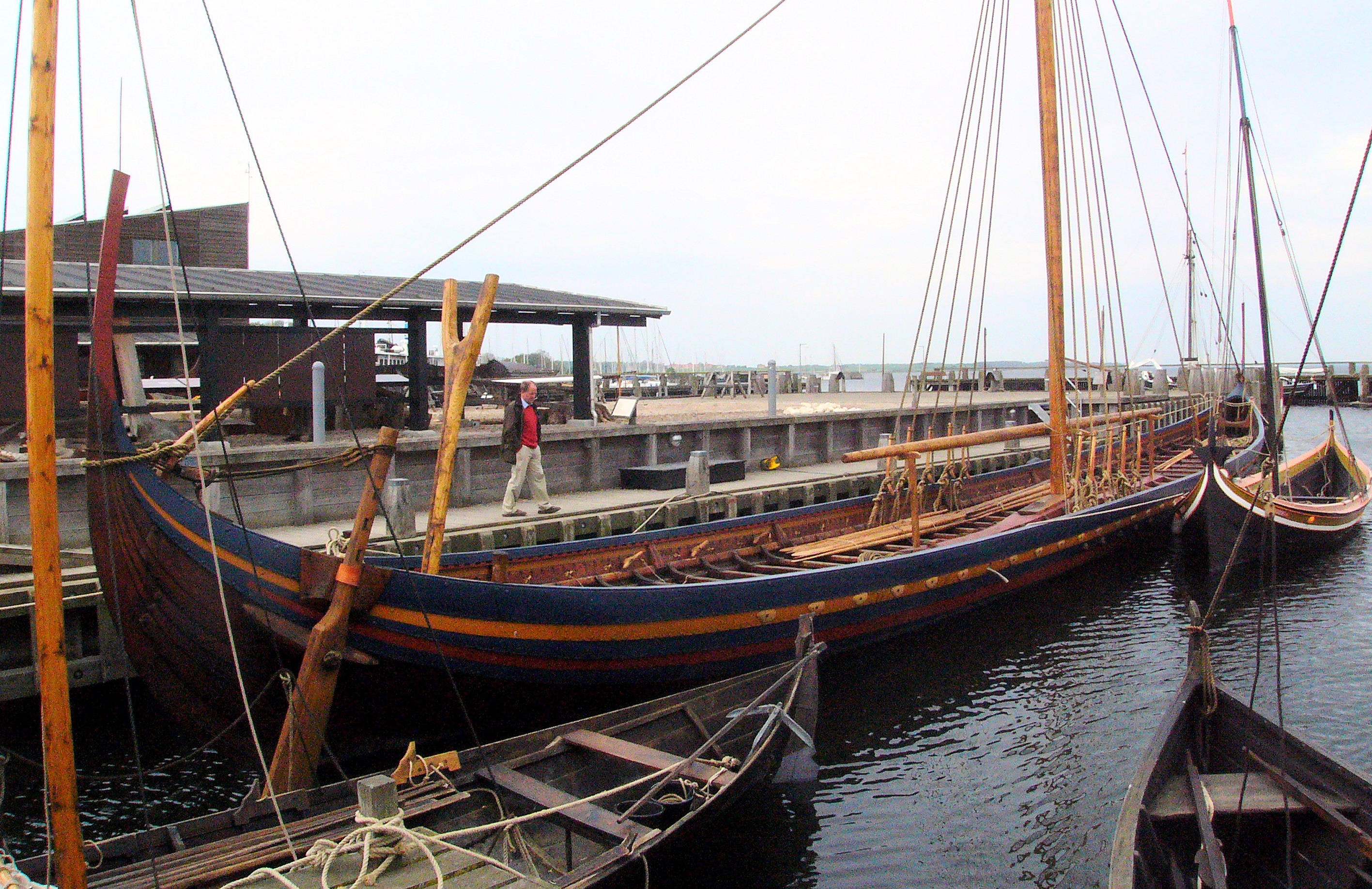
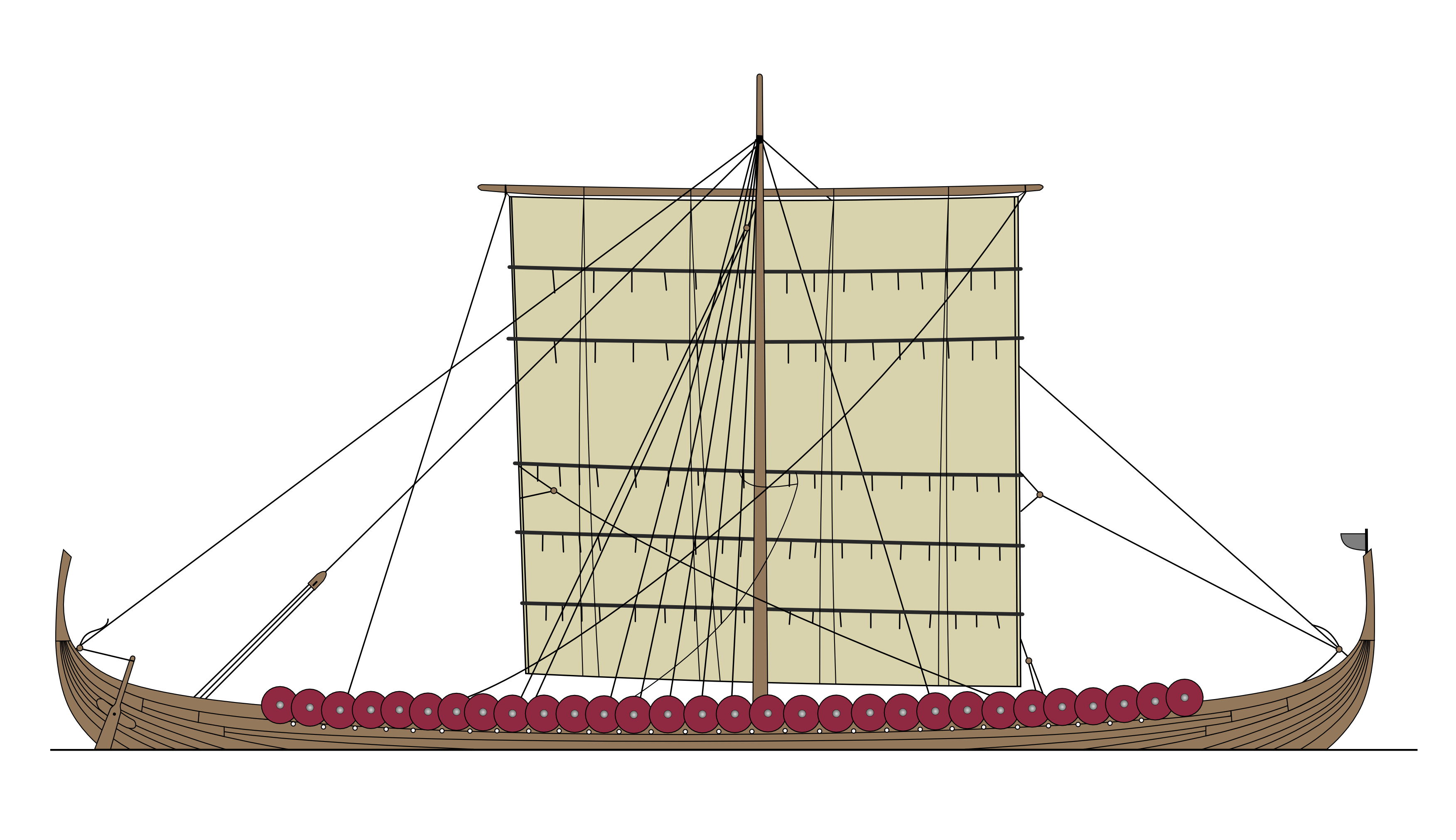
Longship
Longships, a type of specialised Viking ship, Scandinavian warships, have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continued up until the sixth century with Clinker (boat building), clinker-built ships like Nydam Mose#Nydam boat, Nydam. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails (woven wool), and had several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draken Harald Hårfagre
''Draken Harald Hårfagre'' () is a large modern designed longship built in the municipality of Haugesund, Norway. It is a ship that combines ocean-crossing sailing capabilities with a medieval warship's use of oars. Construction Building began in March 2010. Construction was funded by Sigurd Aase, described as a "Norwegian oil and gas tycoon." An oceangoing Norwegian warship The longship is a "25-sesse" (25 pairs of oars); in other words, it is equipped with 50 oars. Each oar is powered by two men. Under sail it requires a crew of 30 people. ''Draken Harald Hårfagre'' is long with a beam of approximately and a displacement (ship), displacement of about 95 metric tons. The longship is constructed in oak and carries of sail. ''Draken Harald Hårfagre'' is the largest long ship built in modern times. In the Viking age, an attack carried out from the ocean would be in the form of a "strandhögg", ''i.e.'', highly mobile hit-and-run tactics. By the High Middle Ages the ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their homeland of Scandinavia but also to any place significantly settled by North Germanic peoples, Scandinavians during the period. Although few of the Scandinavians of the Viking Age were Vikings in the sense of being engaged in piracy, they are often referred to as ''Vikings'' as well as ''Norsemen''. Voyaging by sea from their homelands in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, the Norse people settled in the Viking activity in the British Isles, British Isles, History of Ireland (800–1169), Ireland, the Faroe Islands, Settlement of Iceland, Iceland, Norse settlements in Greenland, Greenland, History of Normandy, Normandy, and the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and along the Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, Dnieper and Volga trade rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Ship
Viking ships were marine vessels of unique structure, used in Scandinavia throughout the Middle Ages. The boat-types were quite varied, depending on what the ship was intended for, but they were generally characterized as being slender and flexible boats, with symmetrical ends with true keel. They were Clinker (boat building), clinker built, which is the overlapping of planks riveted together. Some might have had a dragon's head or other circular object protruding from the bow and stern for design, although this is only inferred from historical sources. Viking ships were used both for military purposes and for long-distance trade, exploration and colonization. In the literature, Viking ships are usually seen divided into two broad categories: merchant ships and warships, the latter resembling narrow "war canoes" with less load capacity, but higher speed. However, these categories are overlapping; some transport ships would also form part of war fleets. As a rule, ship lanes in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, North Africa, the Middle East, Greenland, and Vinland (present-day Newfoundland in Canada, North America). In their countries of origin, and some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the Early Middle Ages, early medieval history of Northern Europe, northern and Eastern Europe, including the political and social development of England (and the English language) and parts of France, and established the embryo of Russia in Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators of their cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seastallion From Glendalough
''Havhingsten fra Glendalough'' ("The Sea Stallion from Glendalough" or just "Sea Stallion") is a reconstruction of ''Skuldelev 2'', one of the Skuldelev ships and the second-largest Viking longship ever to be found. The original vessel was built in the vicinity of Dublin around 1042, using oak from Glendalough in County Wicklow, Ireland, hence the ship's name. The reconstruction was built in Denmark at the shipyard of the Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde between 2000 and 2004 and is used for historical research purposes. The ship is a war machine, built to carry many warriors at high speed. It is a bold design, both heavy and strong enough to carry its 112 m2 sail, but also sufficiently light and long to be rowed by a crew of 60 — a compromise between strength and lightness. The ship has been used during the production of historical fiction television series '' The Last Kingdom''. Research trip to Dublin 2007 The voyage from Roskilde to Dublin and in 2007-2008 was the culmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokstad Ship
The Gokstad ship is a 9th-century Viking ship found in a burial mound at Gokstad in Sandar, Norway, Sandar, Sandefjord, Vestfold, Norway. It is displayed at the Viking Ship Museum (Oslo), Viking Ship Museum in Oslo, Norway. It is the largest preserved Viking ship in Norway. Discovery The site where the boat was discovered, situated on arable land, had long been named ''Gokstadhaugen'' or ''Kongshaugen'' (from the Old Norse words ''konungr'' meaning king and ''wikt:haugr, haugr'' meaning mound), although the relevance of its name had been discounted as folklore, as other sites in Norway bear similar names. In 1880, sons of the owner of Gokstad farm, having heard of the legends surrounding the site, uncovered the Bow (ship), bow of a boat while digging in the still frozen ground. As word of the find got out, Nicolay Nicolaysen, then President of the Society for the Preservation of Ancient Norwegian Monuments, reached the site during February 1880. Having ascertained that the find ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnut
Cnut ( ; ; – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rule are referred to together as the North Sea Empire by historians. As a Danish prince, Cnut won the throne of England in 1016 in the wake of centuries of Viking activity in northwestern Europe. His later accession to the Danish throne in 1018 brought the crowns of England and Denmark together. Cnut sought to keep this power base by uniting Danes and English under cultural bonds of wealth and custom. After a decade of conflict with opponents in Scandinavia, Cnut claimed the crown of Norway in Trondheim in 1028. In 1031, Malcolm II of Scotland also submitted to him, though Anglo-Norse influence over Scotland was weak and ultimately did not last by the time of Cnut's death.ASC, Ms. D, s.a. 1031. Dominion of England lent the Danes an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes a part of northern Finland). In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and cultural similarities. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinker (boat Building)
Clinker-built, also known as lapstrake-built, is a method of boat building in which the edges of longitudinal (lengthwise-running) hull planks overlap each other. The technique originated in Northern Europe, with the first known examples using metal fastenings that join overlapped planks in . It was employed by the Anglo-Saxons, Frisians, and Scandinavians in the early middle ages, and later in the Basque shipbuilding region where the Newport medieval ship was built. It was also used in cogs, the other major ship construction type found in Northern Europe in the latter part of the medieval period. UNESCO named the Nordic clinker boat tradition to its List of Intangible Cultural Heritage on December 14, 2021, in the first approval of a joint Nordic application. Description Clinker construction is a boat and ship-building method in which the hull planks overlap and are joined by nails that are driven through the overlap (often called the "lap"). These fastenings typically go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tune Ship
The Tune ship (''Tuneskipet'') is a Viking ship exhibited in the Viking Ship Museum (''Vikingskipshuset på Bygdøy'') in Bygdøy, Oslo. The Tune ship is of the karve, a small type of longship with broad hull. It was found at the Haugen farm on the island of Rolvsøy in the parish of Tune in Østfold, Norway. It was discovered in a ship burial mound (''Båthaugen'', from the Old Norse words ''båt'' meaning boat and ''haugr'' meaning mound or barrow). It was discovered when the burial mound was opened and the site was excavated by archaeologist Oluf Rygh in 1867. It was named the Tune ship by Professor Rygh after excavation. This is due to the discovery being located in Tune parish. The grave, found attached to the gunwale of the ship, contained a wooden spade, a hand spike, and carved pieces of wood. The ship had clearly been ransacked previous to Rygh’s arrival, and likely contained many more items, including the corpse of a man. The Tune ship is fragmentary, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skuldelev Ships
The Skuldelev ships are five original Viking ships recovered from the waterway of Peberrenden at Skuldelev, north of Roskilde in Denmark. In 1962, the remains of the submerged ships were excavated in the course of four months. The recovered pieces constitute five types of Viking ships and have all been dated to the 11th century. They are thought to have been an early form of blockship, i.e. ships that were scuttled to block potential invasions from the sea. The numbering of the ships is slightly confusing as when the remains were unearthed, they were thought to comprise six ships, but after "Skuldelev 2" and "Skuldelev 4" were later discovered to be parts of one ship, it was decided not to renumber the other vessels. Together, the five Skuldelev ships provide a good source of information about the shipbuilding traditions of the late Viking Age and are now exhibited at the Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde. The museum has built accurate reconstructions of all five of the original Sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |