|
Long Reach Excavator
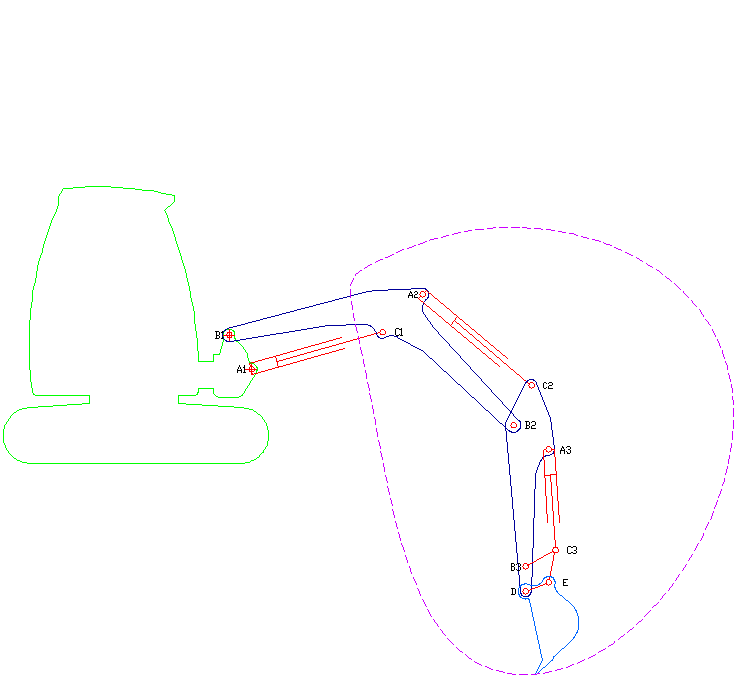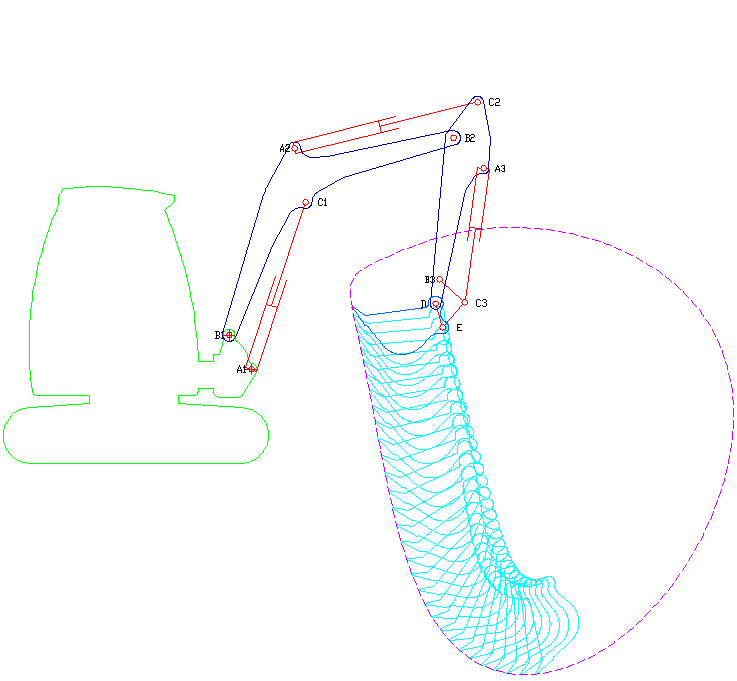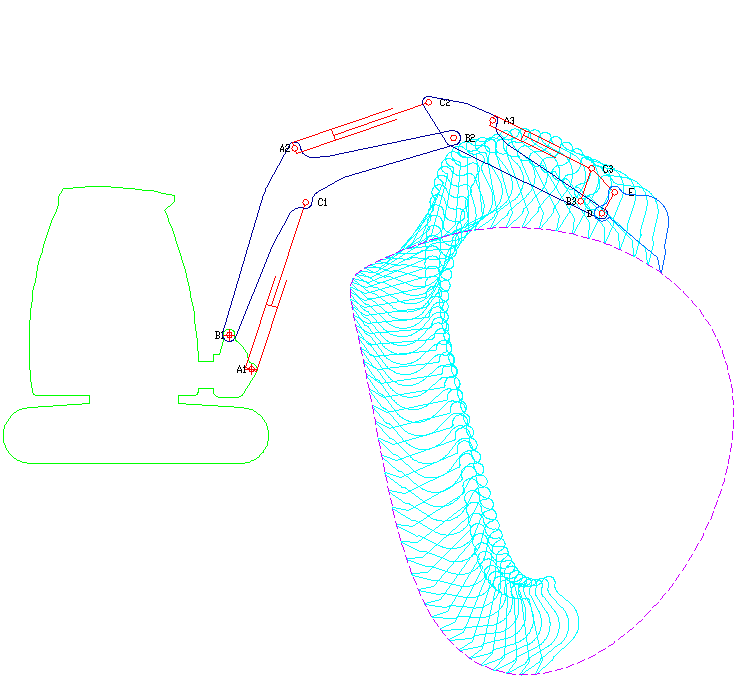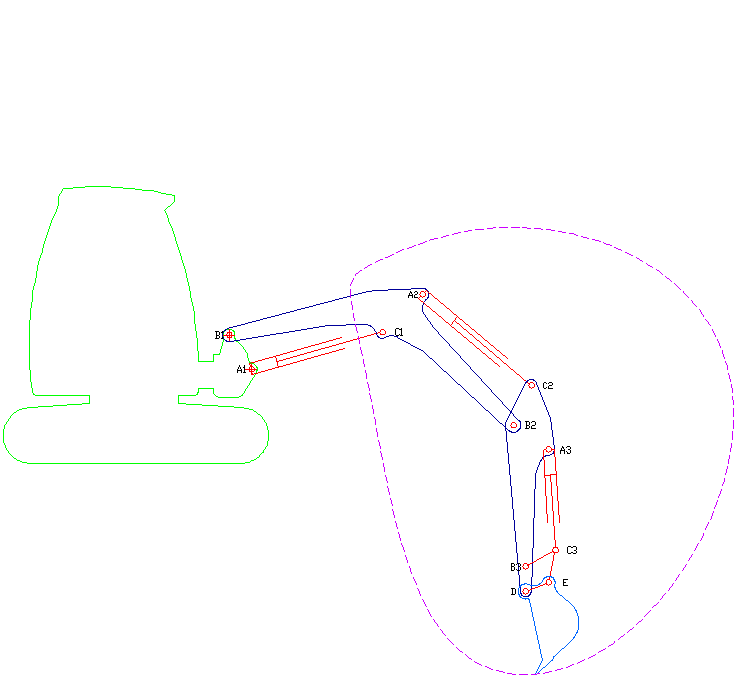
A long reach excavator is a type of excavator where the arm has been extended to reach further than a normal excavator would. It is often used in demolition of buildings, but it can also be used in other applications. History The term ''long reach excavator'' was probably first coined by Richard Melhuish, the Chairman of Land & Water. During the 1970s, Land & Water operated the UK's first hire fleet of these new and innovative long reach hydraulic excavators. In fact they still operate the largest fleet of long-reaches in the UK. Land & Water's first long reach excavator was the Hymac 580 BT All Hydraulic 360 “Waterway” machine, designed for work on waterways. These early machines from Hymac came to be widely preferred to the more traditional drag lines designs. Around the same time Priestman (and later Ruston Bucyrus) VC (Variable Counterweight) excavators started to become more popular. However, the work VC machines could achieve was slightly constrained by design limita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liebherr 934 Long Reach With Engcon Tiltrotator
Liebherr () is a German-Swiss multinational equipment manufacturer based in Bulle, Switzerland, with its main production facilities and origins in Germany. Liebherr consists of over 130 companies organized into 11 divisions: earthmoving, mining, mobile cranes, tower cranes, concrete technology, maritime cranes, aerospace and transportation systems, machine tools and automation systems, domestic appliances, and components. It has a worldwide workforce over 53,000, with fourteen billion euros in revenue for 2023. By 2007, it was the world's largest crane company. Established in 1949 by Hans Liebherr in Kirchdorf, Württemberg-Hohenzollern, West Germany, the business is still entirely owned by the Liebherr family. After his death in 1993, Isolde and Willi Liebherr, Hans' daughter and son led the company, becoming vice president and president of the administrative board respectively of the Switzerland–based Liebherr-International AG in 1999. In March 2023, Stéfanie Wohlfarth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Reach Excavator In Rosslyn (full)
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France People * Long (Chinese surname) * Long (Western surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series * Long, Aeon of Permanence in Honkai: Star Rail Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UHD Delft
UHD may refer to: Technology * Ultra-high-definition television * Ultra HD, any of several high-definition graphics display resolutions * USRP hardware driver, used with Universal Software Radio Peripherals * Ultra HD Blu-ray, an enhanced variant of Blu-ray * Intel UHD Graphics Other uses * Universal HD, an American television network * University of Houston–Downtown *University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust manages three hospitals in South East Dorset conurbation, South East Dorset. It was formed following the merger of Poole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and The Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch H ..., an NHS trust located in the south of England See also * Caleb UHD144, a floppy disk system {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavator
Excavators are heavy equipment (construction), heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a backhoe, boom, dipper (or stick), Bucket (machine part), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with Caterpillar track, tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolition
Demolition (also known as razing and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction (building), deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a Crane (machine), crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rockbreakers attached to excavat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterway
A waterway is any Navigability, navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other ways. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports (Channel (geography), channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters. Where seaports are located inland, they are approached through a waterway that could be termed "inland" but in practice is generally referred to as a "maritime waterway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable energy, railway systems, Health care, healthcare products, and Financial system, financial systems. The company was founded as an electrical machinery manufacturing subsidiary of the Kuhara Mining Plant in Hitachi, Ibaraki by engineer Namihei Odaira in 1910. It began operating as an independent company under its current name in 1920. Hitachi is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and is a key component of the Nikkei 225 and TOPIX Core30 indices. As of June 2024, it has a market capitalisation of 16.9 trillion yen, making it the fourth largest Japanese company by market value. In terms of global recognition, Hitachi was ranked 38th in the 2012 Fortune Global 500 and 129th in the 2012 Forbes Global 2000. Hitachi is a highly globalised conglomerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komatsu Limited
or is a Japanese multinational corporation that manufactures construction, mining, forestry and military heavy equipment, as well as diesel engines and industrial equipment like press machines, lasers and thermoelectric generators. Its headquarters are in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The corporation was named after the city of Komatsu, Ishikawa Prefecture, where the company was founded in 1921. Worldwide, the Komatsu Group consists of Komatsu Ltd. and 258 other companies (215 consolidated subsidiaries and 42 companies accounted for by the equity method). Komatsu is the world's second largest manufacturer of construction equipment and mining equipment after Caterpillar. However, in some areas (Japan, China), Komatsu has a larger share than Caterpillar. It has manufacturing operations in Japan, Asia, Americas and Europe. The word ''ko-matsu'' means "small pine tree" () in Japanese. History Komatsu Iron Works was started by Takeuchi Mining Industry as a subsidiary to make indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing dams, dikes, and other controls for streams and shorelines; and recovering valuable mineral deposits or marine life having commercial value. In all but a few situations the excavation is undertaken by a specialist floating plant, known as a dredger. Usually the main objectives of dredging is to recover material of value, or to create a greater depth of water. Dredging systems can either be shore-based, brought to a location based on barges, or built into purpose-built vessels. Dredging can have environmental impacts: it can disturb marine sediments, creating dredge plumes which can lead to both short- and long-term water pollution, damage or destroy seabed ecosystems, and release legacy human-sourced toxins captured in the sediment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrecking Ball
A wrecking ball is a heavy steel ball, usually hung from a Crane (machine), crane, that is used for Demolition, demolishing large buildings. It was most commonly in use during the 1940s and 1950s. Several wrecking companies claim to have invented the wrecking ball. An early documented use was in the breaking up of the in 1888–1889, by Henry Bath and Co, at Rock Ferry on the River Mersey. In 1993, the wrecking ball was described as "one of the most common forms of large-scale coarse demolition." With the invention of Hydraulic excavator, hydraulic excavators and other machinery, the wrecking ball has become less common at demolition sites as its working efficiency is less than that of long reach excavators. Wrecking balls should be distinguished from overhaul hook balls, which although superficially similar looking, are different and serve a different purpose. Construction and design Modern wrecking balls have had a slight re-shaping, with the metal sphere changed into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Canterbury Earthquake
The 2010 Canterbury earthquake (also known as the Darfield earthquake) struck the South Island of New Zealand with a moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 7.1 at on , and had a maximum perceived intensity of X (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli intensity scale. Some damaging aftershocks followed the main event, the strongest of which was a magnitude 6.3 shock known as the 2011 Christchurch earthquake, Christchurch earthquake that occurred nearly six months later on 22 February 2011. Because this aftershock was centred very close to Christchurch, it was much more destructive and resulted in the deaths of 185 people. The earthquake on 4 September caused widespread damage and several power outages, particularly in the city of Christchurch, New Zealand's second largest city at that time. Two residents were seriously injured, one by a collapsing chimney and a second by flying glass. At least two people died and over 1,700 were injured. Mass fatalities were avoided partly due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
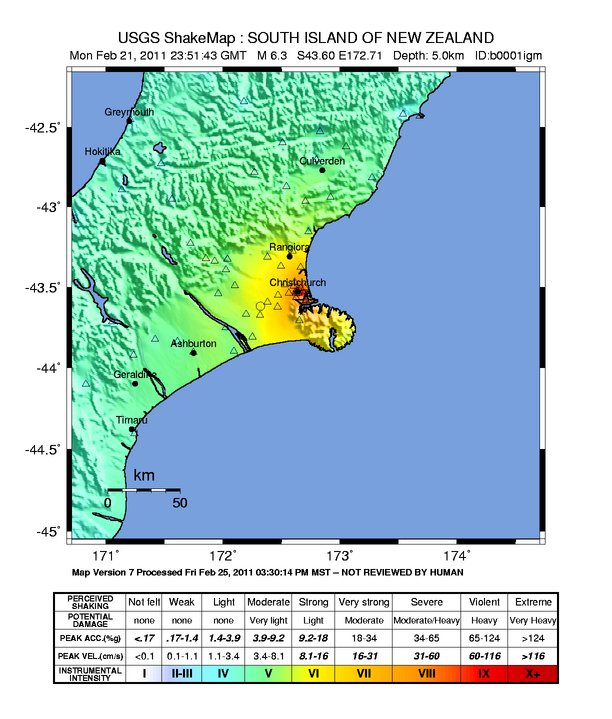
2011 Christchurch Earthquake
A major earthquake occurred in Christchurch on Tuesday 22 February 2011 at 12:51 p.m. New Zealand Daylight Time, local time (23:51 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC, 21 February). The () earthquake struck the Canterbury Region in the South Island, centred south-east of the central business district. It caused widespread damage across Christchurch, killing 185 people in List of disasters in New Zealand by death toll, New Zealand's fifth-deadliest disaster. Scientists classified it as an intraplate earthquake and a potential aftershock of the 2010 Canterbury earthquake, September 2010 Canterbury earthquake. Christchurch's central city and eastern suburbs were badly affected, with damage to buildings and infrastructure already weakened by the 2010 Canterbury earthquake and its aftershocks. Significant soil liquefaction, liquefaction affected the eastern suburbs, producing around 400,000 tonnes of silt. The earthquake was felt across the South Island and parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |