|
Long-term Acute Care Facility
A long-term acute care hospital (LTACH), also known as a long-term care hospital (LTCH), is a hospital specializing in treating patients requiring extended hospitalization. Hospitals specializing in long-term care have existed for decades in the form of sanatoriums for patients with tuberculosis and other chronic diseases. The modern hospital known as an LTACH came into existence as a result of the Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP Balanced Budget Refinement Act of 1999. The Act defines an LTACH as “a hospital which has an average inpatient length of stay (as determined by the Secretary of Health and Human Services (the Secretary)) of greater than 25 days.” Traditionally, LTACHs provide care for patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation. LTACHs have a diverse set of characteristics which influence the ways in which they operate. Physically, LTACHs exist in two models, hospital within hospital or free-standing. Hospital within hospital LTACHs are physically located inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Care
Long-term care (LTC) is a variety of services which help meet both the medical and non-medical needs of people with a chronic illness or disability who cannot care for themselves for long periods. Long-term care is focused on individualized and coordinated services that promote independence, maximize patients' quality of life, and meet patients' needs over a period of time. It is common for long-term care to provide custodial and non-skilled care, such as assisting with activities of daily living like dressing, feeding, using the bathroom, meal preparation, functional transfers and safe restroom use. Increasingly, long-term care involves providing a level of medical care that requires the expertise of skilled practitioners to address the multiple long-term conditions associated with older populations. Long-term care can be provided at home, in the community, in assisted living facilities or in nursing homes. Long-term care may be needed by people of any age, although it is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
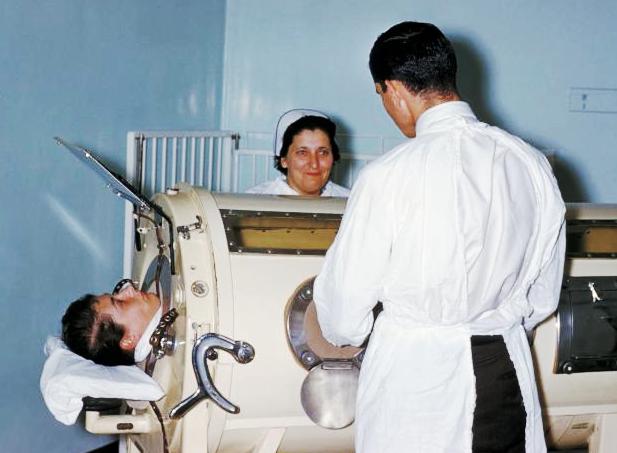
Sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, is a historic name for a specialised hospital for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments, and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often in a healthy climate, usually in the countryside. The idea of healing was an important reason for the historical wave of establishments of sanatoria, especially at the end of the 20th and early 21th centuries. One sought, for instance, the healing of consumptives especially tuberculosis (before the discovery of antibiotics) or alcoholism, but also of more obscure addictions and longings of hysteria, masturbation, fatigue and emotional exhaustion. Facility operators were often charitable associations, such as the Order of St. John and the newly founded social welfare insurance companies. Sanatoriums should not be confused with the Russian sanatoriums from the time of the Soviet Union, which were a type of sanatorium resort residence for workers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicare, Medicaid, And SCHIP Balanced Budget Refinement Act Of 1999
The Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP Balanced Budget Refinement Act of 1999 (also called the Balanced Budget Refinement Act or BBRA) is a federal law of the United States, enacted in 1999. The BBRA was first introduced into the House as H.R. 3075 on October 14, 1999, by Rep. William M. Thomas (R-CA) with 75 cosponsors. It was read twice and then referred to the Senate Committee on Finance. The bill was then slightly altered and reintroduced by Thomas as H.R. 3426 on November 17, 1999. After referral to the House committees on Ways and Means and Commerce, it was incorporated by cross-reference in the conference report into H.R. 3194 on November 18, 1999. The H.R. 3194 bill had been introduced by Rep. Ernest J. Istook Jr. (R-OK) on November 2, 1999, and was enacted with official title: ''Making consolidated appropriations for the fiscal year ending September 30, 2000, and for other purposes''. The State Health Insurance Trial (SCHIP or S. H. 1 - T) was administered by the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis-Related Group
Diagnosis-related group (DRG) is a system to classify hospital cases into one of originally 467 groups, with the last group (coded as 470 through v24, 999 thereafter) being "Ungroupable". This system of classification was developed as a collaborative project by Robert B Fetter, PhD, of the Yale School of Management, and John D. Thompson, MPH, of the Yale School of Public Health.Fetter RB, Shin Y, Freeman JL, Averill RF, Thompson JD (1980) Case mix definition by diagnosis related groups. Medical Care 18(2):1–53 The system is also referred to as "the DRGs", and its intent was to identify the "products" that a hospital provides. One example of a "product" is an appendectomy. The system was developed in anticipation of convincing Congress to use it for reimbursement, to replace "cost based" reimbursement that had been used up to that point. DRGs are assigned by a "grouper" program based on ICD (International Classification of Diseases) diagnoses, procedures, age, sex, discharge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), formally known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) and informally as Obamacare, is a landmark U.S. federal statute enacted by the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 23, 2010. Together with amendments made to it by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, it represents the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since the enactment of Medicare (United States), Medicare and Medicaid in 1965. Most of the act remains in effect. The ACA's major provisions came into force in 2014. By 2016, the uninsured share of the population had roughly halved, with estimates ranging from 20 to 24 million additional people covered. The law also enacted a host of Healthcare industry#Delivery of services, delivery system reforms intended to constrain healthcare costs and improve quality. After it came into effect, increases in overall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |