|
Lolium Pratense
''Festuca pratensis'', the meadow fescue, is a perennial species of grass, which is often used as an ornamental grass in gardens, and is also an important forage crop. It grows in meadows, roadsides, old pastures, and riversides on moist, rich soils, especially on loamy and heavy soils. It is a tall, tufted grass similar to the tall fescue, ''Festuca arundinacea''. Tall fescue differs by having minute hairs on the auricles. It can hybridise with ''Lolium perenne'' and ''Lolium multiflorum''. Description It is a perennial bunchgrass, (i.e. grows in tufts), which grows , flowering from June until August. The panicles are green to purplish. The spikelets have 5 to 14 flowers. It has a short, blunt ligule compared to other grasses 1 mm high. The leaves are bright green and up to 4 mm across.Grasses by C E Hubbard, 1978, published by Penguin books Gallery Image:festuca_pratensis.jpeg, ''Festuca pratensis'' Image:festuca_pratensis_blatt.jpeg, The base of the leaf I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hudson (botanist)
William Hudson Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (1730 in Kendal – 23 May 1793) was a British botanist and apothecary based in London. His main work was ''Flora Anglica'', published in 1762. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1761. Life and work Hudson was born between 1730 and 1732 at the White Lion Inn, Kendal, which was kept by his father. He was educated at Kirkbie Kendal School, Kendal grammar school, Hudson was subsequently apprenticed to an apothecary in London. He obtained the prize for botany given by the Apothecaries' Company which was a copy of John Ray, Ray's ''Synopsis''. However, he also paid attention to mollusca and insects and in Thomas Pennant, Pennant's ''British Zoology'' he is mentioned as the discoverer of ''Trochus terrestris''. From 1757 to 1768 Hudson was resident sub-librarian of the British Museum, and his studies in the Chelsea Physic Garden, Sloane herbarium enabled him to adapt the Linnean nomenclature to the plants described by Ray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornamental Grass
Ornamental grasses are grasses grown as ornamental plants. Ornamental grasses are popular in many colder hardiness zones for their resilience to cold temperatures and aesthetic value throughout fall and winter seasons. Classifications Along with true grasses (Poaceae), several other families of grass-like plants are typically marketed as ornamental grasses. These include the sedges (Cyperaceae), rushes (Juncaceae), restios (Restionaceae), and cat-tails (Typhaceae). All are monocotyledons, typically with narrow leaves and parallel veins. Most are herbaceous perennials, though many are evergreen and some develop woody tissues. They bring striking linear form, texture, color, motion, and sound to the garden, throughout the year. Habits Almost all ornamental grasses are perennials, coming up in spring, from their roots, which have stored large quantities of energy, and in fall or winter go dormant. Some, notably bamboos, are evergreen, and a few are annuals. Many are b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of books or individual stories in the public domain. All files can be accessed for free under an open format layout, available on almost any computer. , Project Gutenberg had reached 50,000 items in its collection of free eBooks. The releases are available in plain text as well as other formats, such as HTML, PDF, EPUB, MOBI, and Plucker wherever possible. Most releases are in the English language, but many non-English works are also available. There are multiple affiliated projects that provide additional content, including region- and language-specific works. Project Gutenberg is closely affiliated with Distributed Proofreaders, an Internet-based community for proofread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligule
A ligule (from "strap", variant of ''lingula'', from ''lingua'' "tongue") is a thin outgrowth at the junction of leaf and leafstalk of many Poaceae, grasses (Poaceae) and Cyperaceae, sedges. A ligule is also a strap-shaped extension of the corolla (flower), corolla, such as that of a ray floret in plants in the daisy family Asteraceae. Poaceae and Cyperaceae The ligule is part of the leaf that is found at the junction of the blade and sheath of the leaf. It may take several forms, but it is commonly some form of translucent membrane or a fringe of hairs. The membranous ligule can be very short 1–2 mm (Kentucky bluegrass, ''Poa pratensis'') to very long 10–20 mm (Johnson grass, ''Sorghum halepense''), it can also be smooth on the edge or very ragged. Some grasses do not have a ligule, for example barnyardgrass (''Echinochloa crus-galli''). A ligule can also be defined as a membrane-like tissue or row of delicate hairs typically found in grasses at the juncti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
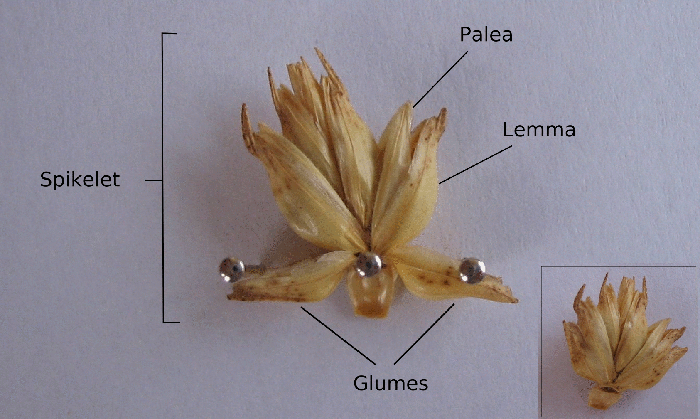
Spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicle A panicle is a much-branched inflorescence. (softcover ). Some authors distinguish it from a compound spike inflorescence, by requiring that the flowers (and fruit In botany, a fruit is the seed-bear |
.jpg)