|
Logier
Johann Bernhard Logier (9 February 1777 – 27 July 1846) was a German composer, teacher, inventor, and publisher resident in Ireland for much of his life. He invented the chiroplast, a device to help students learn the piano, and developed one of the first systems for attempting to teach music in groups, which faced heavy opposition at the time. Biography Logier was born in Kassel and was first taught music by his father, a violinist. He moved to the England in 1791 and joined the Duke of Abercorn's regimental band as a flutist, later becoming director. After moving to Ireland with the regiment in 1802, he was appointed organist in Westport and in 1808 became director of the band of the Kilkenny Militia. In 1809 he became the musical director of the Royal Hibernian Theatre, before opening a successful music shop at 17 Lower Sackville Street (today: O'Connell Street). Except for a three-year stay in Berlin (1822–26), he spent the remainder of his life in Dublin, where he died i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiroplast
A ''chiroplast'' is an instrument to guide the hands and fingers of pupils in playing on the piano A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ..., invented and patented by Johann Bernhard Logier in 1814.Michael Kassler, A.F.C. Kollmann's Quarterly Musical Register (1812). An annotated edition with an introduction to his life and works, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 15 Dec 2008, pp. 123–31./ref> The instrument was a device that placed the wrist, thumb and fingers of a hand above five consecutive white keys of a keyboard, to overcome the difficulty of retaining their proper position by beginners. The instrument was a key part of Logier's system of teaching, which was one of the first to call for the teaching of multiple students at once. The use of the chiroplast caused a significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Eager
John Eager (1782–1853) was an English organist who taught the pianoforte by a controversial system designed by Johann Bernhard Logier making use of the chiroplast, a teaching instrument. This system was one of the first to allow the teaching of a large number of students at once, and was heavily criticized by conservative musicians, at least partly out of a fear of the creation of a central teaching institution, which would rob them of pupils. Between 1803 and 1833, he taught music in Yarmouth, England. Early life Eager was born in 1782 in Norwich, where his father was a manufacturer of musical instruments. He learned the basics of music from his father, and progressed so quickly that at twelve he attracted the attention of the Duke of Dorset, who took him to Knowle as a page. At Knowle took advantage of the library to educated himself, and likely also acquired skill upon the violin, at which the duke was an amateur. Towards the end of the century the duke became insane, and Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent Bugle
The keyed bugle (also Royal Kent bugle, or Kent bugle) is a wide conical bore brass instrument with tone holes operated by keys to alter the pitch and provide a full chromatic scale. It was developed from the bugle around 1800 and was popular in military bands in Europe and the United States in the early 19th century, and in Britain as late as the 1850s. History The first known mention of a bugle with keys appears on 4 April 1800 in London's ''Morning Chronicle'' newspaper, in an advertisement for an instrument built by instrument maker George Astor.; cited in Lasocki (2009). However, not until 5 May 1810 was a patent on a five-keyed bugle granted to Yorkshireman Joseph Haliday, entitled "Halliday's icImprovements in the Musical Instrument called the Bugle Horn." Shortly thereafter, in 1811 the first known solos on the instrument were performed by trumpeter Henry Willman, brother of the clarinetist Thomas Lindsay Willman. Performances at the Theatre Royal, Dublin were announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Kalkbrenner
Friedrich Wilhelm Michael Kalkbrenner (7 November 1785 – 10 June 1849), also known as ''Frédéric Kalkbrenner'', was a pianist, composer, piano teacher and piano manufacturer. German by birth, Kalkbrenner studied at the Conservatoire de Paris, starting at a young age and eventually settled in Paris, where he lived until his death in 1849. Kalkbrenner composed more than 200 piano works, as well as many piano concertos and operas. When Frédéric Chopin came to Paris, Kalkbrenner suggested that Chopin could benefit by studying in one of Kalkbrenner's schools. It was not until the late 1830s that Kalkbrenner's reputation was surpassed by the likes of Chopin, Thalberg and Liszt. Author of a famous method of piano playing (1831) which was in print until the late 19th century, he ran in Paris what is sometimes called a "factory for aspiring virtuosos" and taught scores of pupils from as far away as Cuba. His pupils included Marie Pleyel, Marie Schauff, and Camille-Marie Stamaty. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony
In music, harmony is the concept of combining different sounds in order to create new, distinct musical ideas. Theories of harmony seek to describe or explain the effects created by distinct pitches or tones coinciding with one another; harmonic objects such as chords, textures and tonalities are identified, defined, and categorized in the development of these theories. Harmony is broadly understood to involve both a "vertical" dimension (frequency-space) and a "horizontal" dimension (time-space), and often overlaps with related musical concepts such as melody, timbre, and form. A particular emphasis on harmony is one of the core concepts underlying the theory and practice of Western music. The study of harmony involves the juxtaposition of individual pitches to create chords, and in turn the juxtaposition of chords to create larger chord progressions. The principles of connection that govern these structures have been the subject of centuries worth of theoretical work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugle
The bugle is a simple signaling brass instrument with a wide conical bore. It normally has no valves or other pitch-altering devices, and is thus limited to its natural harmonic notes, and pitch is controlled entirely by varying the air and embouchure. History :''See also Clarion'' and ''Natural trumpet'' The English word ''bugle'' comes from a combination of words. From French, it reaches back to ''cor buglèr'' and ''bugleret'', indicating a signaling horn made from a small cow's horn. Going back further, it touches on Latin, ''buculus,'' meaning bullock. Old English also influences the modern word with ''bugle'', meaning "wild ox." The name indicates an animal's (cow's) horn, which was the way horns were made in Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The modern bugle is made from metal tubing, and that technology has roots which date back to the Roman Empire, as well as to the Middle East during the Crusades, where Europeans re-discovered metal-tubed trum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Band
A military band is a group of personnel that performs musical duties for military functions, usually for the armed forces. A typical military band consists mostly of wind instrument, wind and percussion instruments. The conducting, conductor of a band commonly bears the title of bandmaster or music director. Ottoman military bands are thought to be the oldest variety of military marching bands in the world, dating from the 13th century. The military band is capable of playing ceremonial and marching music, including the national anthems and patriotic songs of theirs and other nations, both while stationary and as a marching band. Military bands also play a part in military funeral ceremonies. There are two types of historical traditions in military bands. The first is military Field Music (military), field music. This type of music includes Bugle (instrument), bugles (or other natural instruments such as natural trumpets or natural horns), bagpipes or Fife (musical instrument), f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
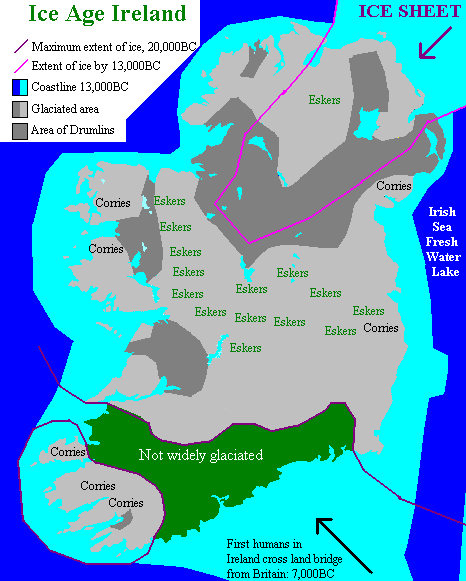
History Of Ireland
The first evidence of human presence in Ireland dates to around 34,000 years ago, with further findings dating the presence of ''Homo sapiens'' to around 10,500 to 7,000 BC. The receding of the ice after the Younger Dryas cold phase of the Quaternary, around 9700 BC, heralds the beginning of Prehistoric Ireland, which includes the archaeological periods known as the Mesolithic, the Neolithic from about 4000 BC, and the Copper Age beginning around 2500 BC with the arrival of the Beaker Culture. The Irish Bronze Age proper begins around 2000 BC and ends with the arrival of the Iron Age of the Celtic Hallstatt culture, beginning about 600 BC. The subsequent La Tène culture brought new styles and practices by 300 BC. Greek and Roman writers give some information about Ireland during the Classical period (see " protohistoric" period), by which time the island may be termed "Gaelic Ireland". By the late 4th century CE Christianity had begun to gradually subsume or replace the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Battle Of Trafalgar, Op
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyers Konversations-Lexikon
or was a major encyclopedia in the German language that existed in various editions, and by several titles, from 1839 to 1984, when it merged with the . Joseph Meyer (publisher), Joseph Meyer (1796–1856), who had founded the publishing house in 1826, intended to issue a universal encyclopaedia meant for a broad public: people having a general knowledge as well as businessmen, technicians and scholars, considering contemporary works like those of and to be Superficiality, superficial or Obsolescence, obsolete. First edition The first part of ' ("Great encyclopaedia for the educated classes") appeared in October 1839. In contrast to its contemporaries, it contained maps and illustrations with the text. There is no indication of the planned number of volumes or a time limit for this project, but little headway had been made by the otherwise dynamic . After six years, 14 volumes had appeared, covering only one fifth of the alphabet. Another six years passed before the last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1777 Births
Events January–March * January 2 – American Revolutionary War – Battle of the Assunpink Creek: American general George Washington's army repulses a British attack by Lieutenant General Charles Cornwallis, in a second battle at Trenton, New Jersey. * January 3 – American Revolutionary War – Battle of Princeton: American general George Washington's army defeats British troops. * January 13 – Mission Santa Clara de Asís is founded in what becomes Santa Clara, California. * January 15 – Vermont declares its independence from New York, becoming the Vermont Republic, an independent country, a status it retains until it joins the United States as the 14th state in 1791. * January 21 – The Continental Congress approves a resolution "that an unauthentic copy, with names of the signers of the Declaration of independence, be sent to each of the United States. *February 5 – Under the 1st Constitution of Georgia, 8 counties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |