|
Lode Vertonghen
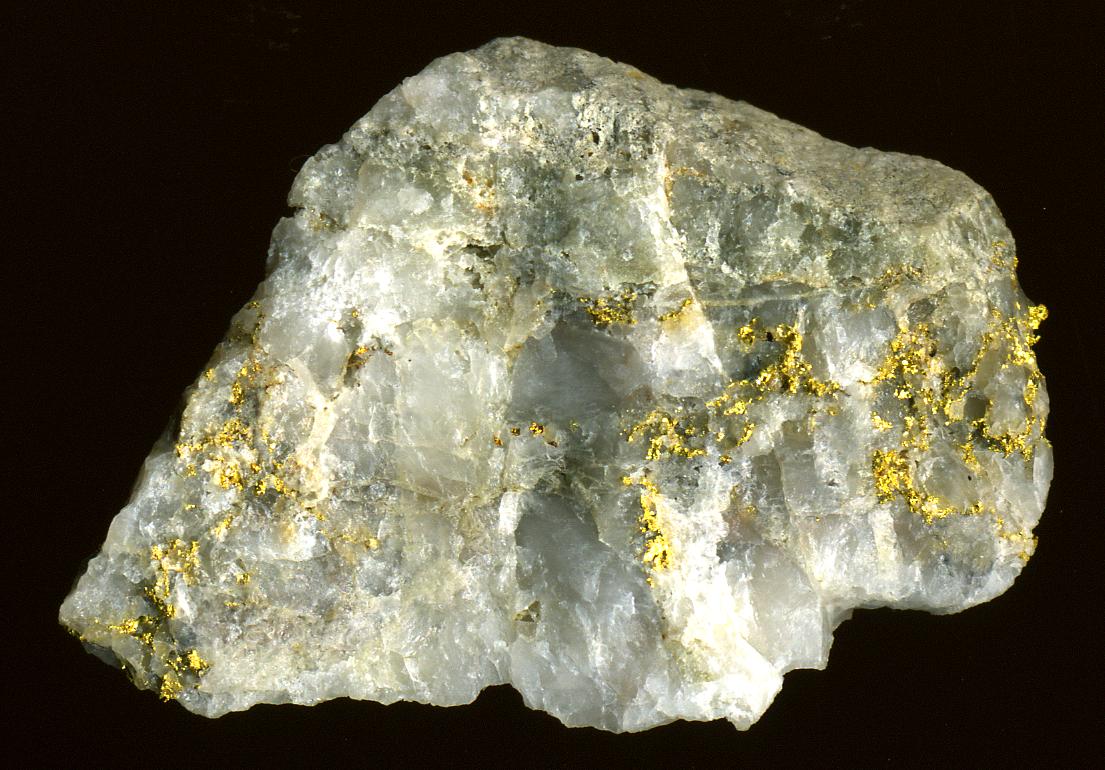
In geology, a lode is a deposit of metalliferous ore that fills or is embedded in a fracture (or crack) in a rock formation or a vein of ore that is deposited or embedded between layers of rock. The current meaning (ore vein) dates from the 17th century, being an expansion of an earlier sense of a "channel, watercourse" in Late Middle English, which in turn is from the 11th-century meaning of ''lode'' as a "course, way". The generally accepted hydrothermal model of lode deposition posits that metals dissolved in hydrothermal solutions (hot spring fluids) deposit the gold or other metallic minerals inside the fissures in the pre-existing rocks. Lode deposits are distinguished primarily from placer deposits, where the ore has been eroded out from its original depositional environment and redeposited by sedimentation. A third process for ore deposition is as an evaporite. A stringer lode is one in which the rock is so permeated by small veinlets that rather than mining the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporite
An evaporite () is a water- soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean deposits, and non-marine, which are found in standing bodies of water such as lakes. Evaporites are considered sedimentary rocks and are formed by chemical sediments. Formation Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. This is usually an arid environment with a small drainage basin fed by a limited input of water. When evaporation occurs, the remaining water is enriched in salts, and they precipitate after the water becomes saturated. Depositional environments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publishing in public records, made by a sovereign entity. While land patents are still issued by governments to indicate property is privately held, they are also often used by sovereign citizens and similar groups in illegitimate attempts to gain unlawful possession of property, or avoid taxes and foreclosure. Land patents are the right, title, and interest to a defined area. It is usually granted by a central, federal, or state government to an individual, partnership, trust, or private company. The land patent is not to be confused with a land grant. Patented lands may be lands that had been granted by a sovereign authority in return for services rendered or accompanying a title or otherwise bestowed ''gratis'', or they may be lands priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Mining Act Of 1872
The General Mining Act of 1872 is a United States federal law that authorizes and governs prospecting and mining for economic minerals, such as gold, platinum, and silver, on federal Public land#United States, public lands. This law, approved on May 10, 1872, codified the informal system of acquiring and protecting mining claims on Public land#United States, public land, formed by prospectors in California and Nevada from the late 1840s through the 1860s, such as during the California Gold Rush. All citizens of the United States of America 18 years or older have the right under the 1872 mining law to locate a lode (hard rock) or placer (gravel) mining claim on federal lands open to mineral entry. These claims may be located once a discovery of a locatable mineral is made. Locatable minerals include but are not limited to platinum, gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, uranium and tungsten. Western miners' codes Miners and prospectors in the California Gold Rush of 1849 found themselv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thickness (geology)
Thickness in geology and mining refers to the distance across a packet of rock, whether it be a facies, stratum, bed, seam, lode etc. Thickness is measured at right angles to the surface of the seam or bed and thus independently of its spatial orientation. The concept of thickness came originally from mining language, where it was used mainly to indicate the workability of seams. It has since become an established term in earth science, for example in geology, for the depth of sedimentary rocks, in hydrogeology for the vertical extent of groundwater – i.e. the distance from the base of the groundwater layer to its surface – or in soil science for the vertical extent of soil horizon A soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. ...s. Literature * Walter Bischoff, Heinz Bram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ore Genesis
Various theories of ore genesis explain how the various types of mineral deposits form within Earth's crust. Ore-genesis theories vary depending on the mineral or commodity examined. Ore-genesis theories generally involve three components: source, transport or conduit, and trap. (This also applies to the petroleum industry: petroleum geologists originated this analysis.) *''Source'' is required because metal must come from somewhere, and be liberated by some process. *''Transport'' is required first to move the metal-bearing fluids or solid minerals into their current position, and refers to the act of physically moving the metal, as well as to chemical or physical phenomena which encourage movement. *''Trapping'' is required to concentrate the metal via some physical, chemical, or geological mechanism into a concentration which forms mineable ore. The biggest deposits form when the source is large, the transport mechanism is efficient, and the trap is active and ready at the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
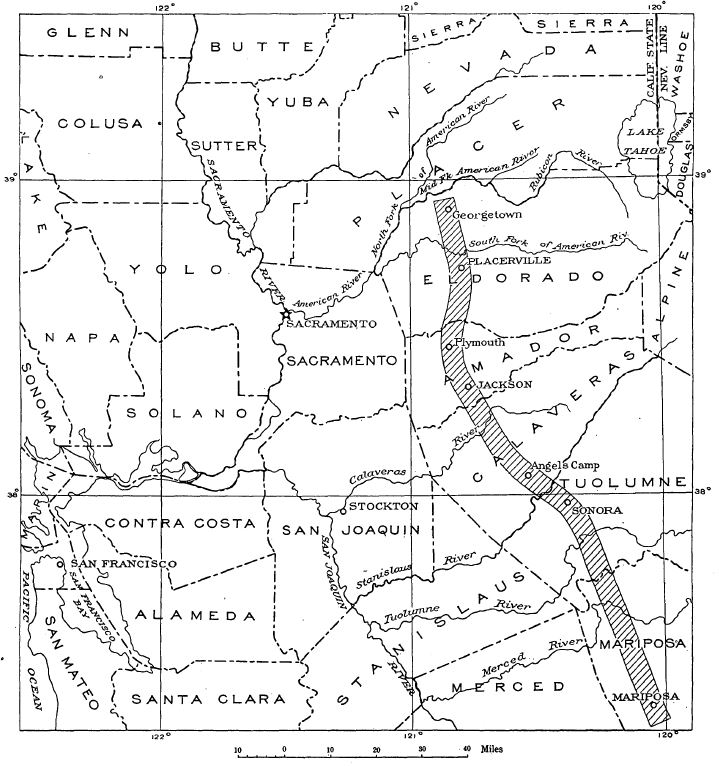
Mother Lode
Mother lode is a principal vein or zone of gold or silver ore. The term is also used colloquially to refer to the real or imaginary origin of something valuable or in great abundance. Term The term probably came from a literal translation of the Spanish ''veta madre'', a term common in old Mexican mining. ''Veta madre,'' for instance, is the name given to an silver vein discovered in 1548 in Guanajuato, New Spain (modern-day Mexico). California Mother Lode In the United States, ''Mother Lode'' is most famously the name given to a long alignment of hard-rock gold deposits stretching northwest-southeast in the Sierra Nevada of California, bounded on the east by the Melones Fault Zone. It was discovered in the early 1850s, during the California gold rush. The California Mother Lode is a zone from wide and long, between Georgetown on the north and Mormon Bar on the south. The Mother Lode coincides with the suture line of a terrane, the Smartville Block. The zone contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Oxford American Dictionary
The ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' (''NOAD'') is a single-volume dictionary of American English compiled by American editors at the Oxford University Press. ''NOAD'' is based upon the '' New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (''NODE''), published in the United Kingdom in 1998, although with substantial editing, additional entries, and the inclusion of illustrations. It is based on a corpus linguistics analysis of Oxford's 200 million word database of contemporary American English. ''NOAD'' includes a diacritical respelling scheme to convey pronunciations, as opposed to the Gimson phonemic IPA system that is used in ''NODE''. Editions First edition Published in September 2001, the first edition was edited by Elizabeth J. Jewell and Frank Abate. Second edition Published in May 2005, the second edition was edited by Erin McKean. The edition added nearly 3,000 new words, senses, and phrases. It was in a large format, with 2096 pages, and was 8½" by 11" in size. It included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodestone
Lodestones are naturally magnetization, magnetized pieces of the mineral magnetite. They are naturally occurring magnets, which can attract iron. The property of magnetism was first discovered in Ancient history, antiquity through lodestones. Pieces of lodestone, suspended so they could turn, were the first magnetic compasses, and their importance to early navigation is indicated by the name ''lodestone'', which in Middle English means "course stone" or "leading stone", from the now-obsolete meaning of '':wikt:lode, lode'' as "journey, way". Lodestone is one of only a very few minerals that is found naturally magnetized. Magnetite is black or brownish-black, with a metallic lustre (mineralogy), luster, a Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs hardness of 5.5–6.5 and a black streak (mineralogy), streak. Origin The process by which lodestone is created has long been an open question in geology. Only a small amount of the magnetite on the Earth is found magnetized as lodest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken Hill Ore Deposit
The Broken Hill Ore Deposit is located underneath Broken Hill in western New South Wales, Australia, and is the namesake for the town. It is arguably the world's richest and largest zinc-lead ore deposit. History Discovery Charles Sturt made a pencil sketch of the area in 1844 and noted iron ore along an isolated hill. In 1866 the Mount Gipps sheep station named their paddock, which embraced the lode outcrop, Broken Hill. However, the hill was thought to be mullock. On 5 September 1883, a Mount Gipps boundary rider named Charles Rasp staked a claim on the outcrop because it looked like tin oxide as described in his prospecting guide book. With six others he staked the entire outcrop. In 1884, the syndicate reorganized as the Broken Hill Mining Company. Horn silver was discovered in 1885 and the Broken Hill Proprietary Company Limited was incorporated. Charles Rasp discovered the gossan or weathered sulfide outcrop of massive lead-zinc sulfides on a feature know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestake Mine (South Dakota)
The Homestake Mine was a deep underground gold mine (8,000 feet or 2,438 m) located in Lead, South Dakota. Until it closed in 2002, it was the largest and deepest gold mine in the Western Hemisphere. The mine produced more than of gold during its lifetime. This is about or a volume of gold roughly equal to 18,677 US gallons. The mine has since reopened and has been owned and operated by Dakota Gold Corp since 2022. The Homestake Mine is famous in scientific circles because of the work of a deep underground laboratory that was established there in the mid-1960s. This was the site where the solar neutrino problem was first discovered, in what is known as the Homestake Experiment. Raymond Davis Jr. conducted this experiment in the mid-1960s, which was the first to observe solar neutrinos. On July 10, 2007, the mine was selected by the National Science Foundation as the location for the Deep Underground Science and Engineering Laboratory (DUSEL). It won over several candi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannington Mine
The Cannington Silver and Lead Mine is an Australian underground mine located in north-west Queensland, in the Shire of McKinlay, about southeast of Mount Isa. The deposit was discovered by BHP in 1990.Abstract The mine was the supplier of silver for the Sydney and the Beijing . Cannington takes its name from the pastoral property near the deposit. Geography Cannington lies on a broad plain with a few low[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |