|
Lockheed E-XX
The Lockheed Martin E-130J is a planned airborne command post and communication relay aircraft based on the C-130J-30. The E-130J is intended to replace the Boeing E-6 Mercury in the TACAMO role for the US Navy, but not the associated "Looking Glass" role for the US Air Force. The replacement of the E-6B fleet is to begin in FY2028. Development In the 1990s, the US Navy and US Air Force consolidated their respective airborne command post and communication relay requirements into a single aircraft program operated by the Navy. The Boeing 707-based E-6 Mercury replaced the EC-130Q in the "Take Charge and Move Out" (TACAMO) role in 1989. As the EC-135 was retired, the E-6B Mercury replaced it in the "Looking Glass" role while the E-4 replaced it in the Airborne Command Post (ABNCP) role. The Boeing 707 production line closed following the delivery of the last E-6 Mercury and consequently spare parts for the platform are scarce and operations have become increasingly expensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
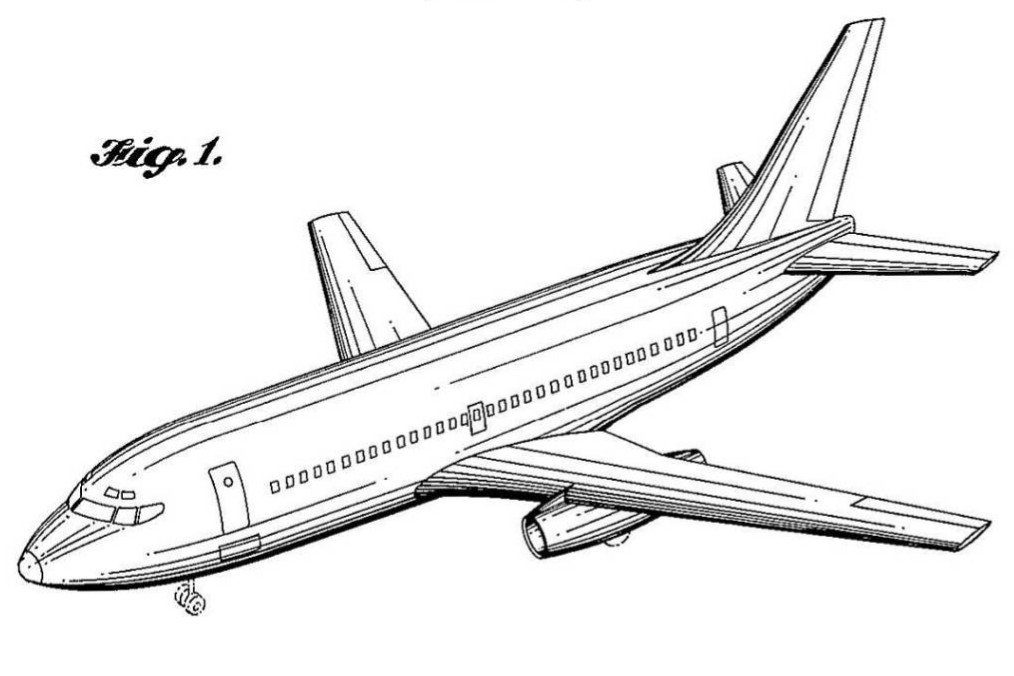
Boeing 737
The Boeing 737 is an American narrow-body aircraft, narrow-body aircraft produced by Boeing at its Boeing Renton Factory, Renton factory in Washington (state), Washington. Developed to supplement the Boeing 727 on short and thin routes, the twinjet retained the Boeing 707, 707 fuselage width and six abreast seating but with two underwing Pratt & Whitney JT8D low-bypass turbofan engines. Envisioned in 1964, the initial 737-100 made its first flight in April 1967 and entered service in February 1968 with Lufthansa. The lengthened 737-200 entered service in April 1968, and evolved through four generations, offering several variants for 85 to 215 passengers. The First Generation 737-100/200 variants were powered by Pratt & Whitney JT8D low-bypass turbofan engines and offered seating for 85 to 130 passengers. Launched in 1980 and introduced in 1984, the Second Generation Boeing 737 Classic, 737 Classic -300/400/500 variants were re-engine, upgraded with more fuel-efficient CFM In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Jamming
Radio jamming is the deliberate blocking of or interference with wireless communications.https://apps.fcc.gov/edocs_public/attachmatch/DA-12-347A1.pdf Enforcement Advisory No. 2012-02 FCC Enforcement Advisory Cell Jammers, GPS Jammers, and Other Jamming Devices Consumer Alert: Using or Importing Jammers is Illegal In some cases, jammers work by the transmission of radio signals that disrupt telecommunications by decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The concept can be used in wireless data networks to disrupt information flow. It is a common form of censorship in totalitarian countries, in order to prevent foreign radio stations in border areas from reaching the country. Jamming is usually distinguished from interference that can occur due to device malfunctions or other accidental circumstances. Devices that simply cause interference are regulated differently. Unintentional "jamming" occurs when an operator transmits on a busy frequency without first checking whether it is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encryption
In Cryptography law, cryptography, encryption (more specifically, Code, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Despite its goal, encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption Key (cryptography), key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information. The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message signal onto a carrier signal to be transmitted. For example, the message signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the message signal does. This is because it is impractical to transmit signals with low frequencies. Generally, receiving a radio wave requires a radio antenna with a length that is one-fourth of the wavelength of the transmitted wave. For low frequency radio waves, wavelength is on the scale of kilometers and building such a large antenna is not practical. Another purpose of modulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Extremely High Frequency
Advanced Extremely High Frequency (AEHF) is a constellation of communications satellites operated by the United States Space Force. They are used to relay secure communications for the United States Armed Forces, the British Armed Forces, the Canadian Armed Forces, the Netherlands Armed Forces and the Australian Defence Force. The system consists of six satellites in geostationary orbits. The final satellite was launched on 26 March 2020. AEHF is backward compatible with, and replaces, the older Milstar system and will operate at 44 GHz uplink (extremely high frequency (EHF) band) and 20 GHz downlink (super high frequency (SHF) band). The AEHF system is a joint service communications system that provides survivable, global, secure, protected, and jam-resistant communications for high-priority military ground, sea and air assets. Overview AEHF satellites use many narrow spot beams directed towards the Earth to relay communications to and from users. Crosslinks between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Low Frequency
Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters (an obsolete metric unit equal to 10 kilometers). Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low- data-rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations (broadcasting time signals to set radio clocks) and secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines. Propagation characteristics Because of their long wavelengths, VLF radio waves can diffract around large obstacles and so are not blocked by mountain ranges, and they can propagate as ground wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be emitted and received by antenna (radio), antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most building materials. Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon energies and the shortest wavelengths—much smaller than an atomic nucleus. Gamma rays, X-rays, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
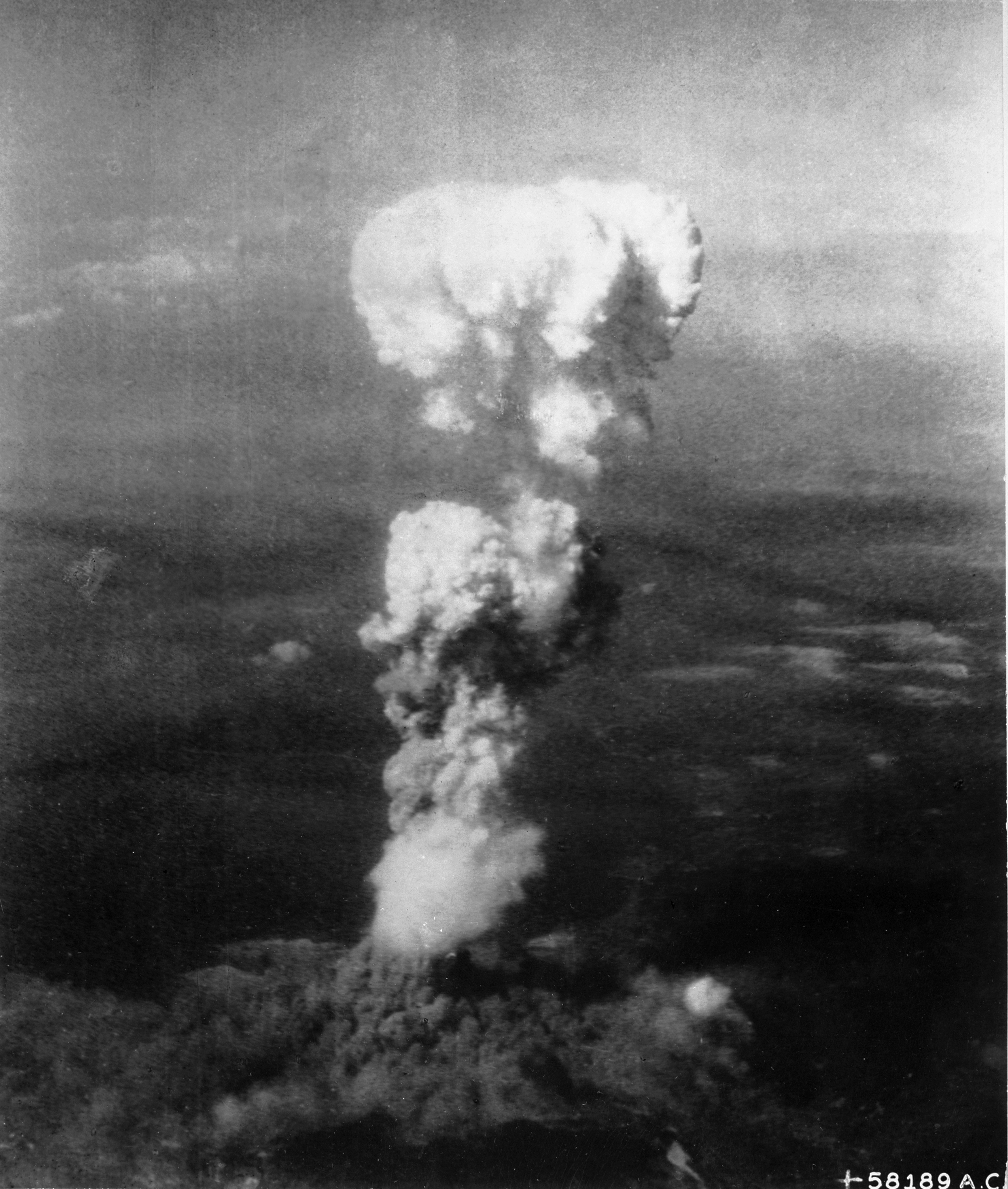
Nuclear Warfare
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a War, military conflict or prepared Policy, political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological warfare, radiological result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the Nuclear fallout, fallout released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter", nuclear famine, and societal collapse. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including human extinction. To date, the only use of nuclear weapons in armed conflict occurred in 1945 with the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. On August 6, 1945, a uranium Nuclear weapon design, gun-type device (code name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deterrence Theory
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats of using force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy during the Cold War with regard to the use of nuclear weapons and is related to but distinct from the concept of mutual assured destruction, according to which a full-scale nuclear attack on a power with second-strike capability would devastate both parties. The central problem of deterrence revolves around how to credibly threaten military action or nuclear punishment on the adversary despite its costs to the deterrer. Deterrence in an international relations context is the application of deterrence theory to avoid conflict. Deterrence is widely defined as any use of threats (implicit or explicit) or limited force intended to dissuade an actor from taking an action (i.e. maintain the status quo). Deterrence is unlike compellence, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Command Authority (United States)
The National Command Authority (NCA) is a term that was formerly used by the Department of Defense of the United States to refer to the ultimate source of lawful military orders. The NCA was first alluded to in a 1960 Department of Defense document. It included at least the president of the United States as commander-in-chief and the secretary of defense. The term has no statutory or constitutional basis and was replaced in 2002 in favor of explicitly referring to the president and/or the secretary of defense. The term also refers to communications with the commanding officers of the Unified Combatant Commands to put U.S. forces into action. Authorization of a nuclear or strategic attack Only the president can direct the use of nuclear weapons by U.S. Armed Forces, through plans like OPLAN 8010-12. The president has unilateral authority as commander-in-chief to order that nuclear weapons be used for any reason at any time. See also * Designated survivor * Goldwater–Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |