|
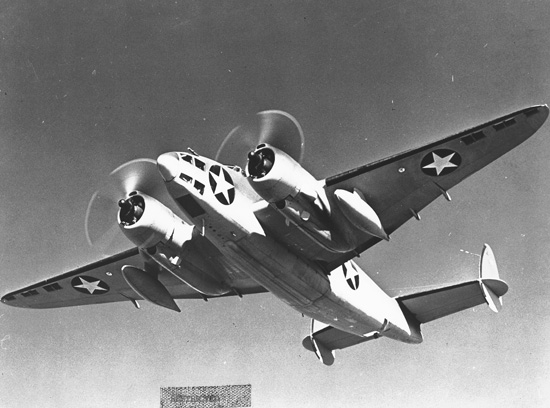
Lockheed 049 Constellation
The Lockheed L-049 Constellation is the first model of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. It entered service as the C-69 military transport aircraft during World War II for the United States Army Air Forces and was the first civilian version after the war. When production ended in 1946 it was replaced by the improved L-649 and L-749 Constellation. History Design and development In June 1939, Howard Hughes, the owner of Transcontinental & Western Air (later Trans World Airlines and abbreviated TWA), held a meeting at his Hancock Park residence in California. Jack Frye (then president of TWA) attended along with three executives from the Lockheed Aircraft Corporation which included designer Clarence "Kelly" Johnson. During the meeting Hughes expressed his concerns for what he called the "airliner of the future". Lockheed's airliner under development at the time, the L-044 Excalibur, did not meet the requirements. When the meeting ended with Hughes and Frye, the execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans World Airlines
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major airline in the United States that operated from 1930 until it was acquired by American Airlines in 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with Ford Trimotors. With American Airlines, American, United Airlines, United, and Eastern Air Lines, Eastern, it was one of the "Legacy carrier#Defunct legacy carriers, Big Four" domestic airlines in the United States formed by the Air Mail scandal, Spoils Conference of 1930. Howard Hughes acquired control of TWA in 1939, and after World War II led the expansion of the airline to serve Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, making TWA a second unofficial flag carrier of the United States after Pan American World Airways, Pan Am. Hughes gave up control in the 1960s, and the new management of TWA acquired Hilton Worldwide, Hilton International and Century 21 Real Estate, Century 21 in an attempt to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed PV-1 Ventura
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II. The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1943 in the Pacific. The bomber was also used by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), which designated it the Lockheed B-34 (''Lexington'') and B-37 as a trainer. British Commonwealth forces also used it in several guises, including antishipping and antisubmarine search and attack. The Ventura was developed from the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar transport, as a replacement for the Lockheed Hudson bombers then in service with the Royal Air Force. Used in daylight attacks against occupied Europe, they proved to have weaknesses and were removed from bomber duty and some used for patrols by Coastal Command. After USAAF monopolization of land-based bombers was removed, the US Navy ordered a revised design which entered service as the PV-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Loewy
Raymond Loewy ( , ; November 5, 1893 – July 14, 1986) was a French-born American industrial designer who achieved fame for the magnitude of his design efforts across a variety of industries. He was recognized for this by ''Time'' magazine and featured on its cover on October 31, 1949. He spent most of his professional career in the United States, becoming a naturalized citizen in 1938. Among his designs were the Shell, Exxon, TWA and the former BP logos, the Greyhound Scenicruiser bus interior, Coca-Cola vending machines and bottle redesign, the Lucky Strike package, Coldspot refrigerators, the Studebaker Avanti and Champion, and the Air Force One livery. He was engaged by equipment manufacturer International Harvester to overhaul its entire product line, and his team also assisted competitor Allis-Chalmers. He undertook numerous railroad designs, including the Pennsylvania Railroad GG1, S-1, and T1 locomotives, the color scheme and Eagle motif for the first st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Trippe
Juan Terry Trippe (June 27, 1899 – April 3, 1981) was an American commercial aviation pioneer, entrepreneur and the founder of Pan American World Airways, one of the iconic airlines of the 20th century. He was involved in the introduction of the Sikorsky S-42, which opened trans-Pacific airline travel, the Boeing 307 Stratoliner which introduced cabin pressurization to airline operations, the Boeing 707 which started a new era in low cost jet transportation, and the Boeing 747 jumbo jets. Trippe's signing of the 747 contract coincided with the 50th anniversary of Boeing. He also founded InterContinental Hotels & Resorts. Early life and education Trippe was born in Sea Bright, New Jersey, on June 27, 1899, the great-great-grandson of Lieutenant John Trippe, captain of the . Because he was named "Juan", he is widely assumed to have been of Hispanic descent, but his family was actually Northern European in ancestry and settled in Maryland in 1664. He was named after Juanita T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Tool Company
Hughes Tool Company was an American manufacturer of drill bits. Founded in 1908, it was merged into Baker Hughes Incorporated in 1987. History The company was established in December 1908 as Sharp-Hughes Tool Company when Howard R. Hughes Sr. patented a roller cutter bit that dramatically improved the rotary drilling process for oil drilling rigs. He partnered with longtime business associate Walter Benona Sharp to manufacture and market the bit. Following her husband's death in 1912, Sharp's widow Estelle Sharp sold her 50% share in the company to Howard Hughes Sr. in 1914. The company was renamed Hughes Tool Company on February 3, 1915. After Hughes Sr. died of a heart attack in 1924, his son Howard Jr. inherited the majority interest in the company, and then convinced his relatives to sell their shares to him as well. Legally emancipated at the age of 18, Howard began using the profits from Hughes Tool to fund his other ventures. Toolco paid Hughes an annual salary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
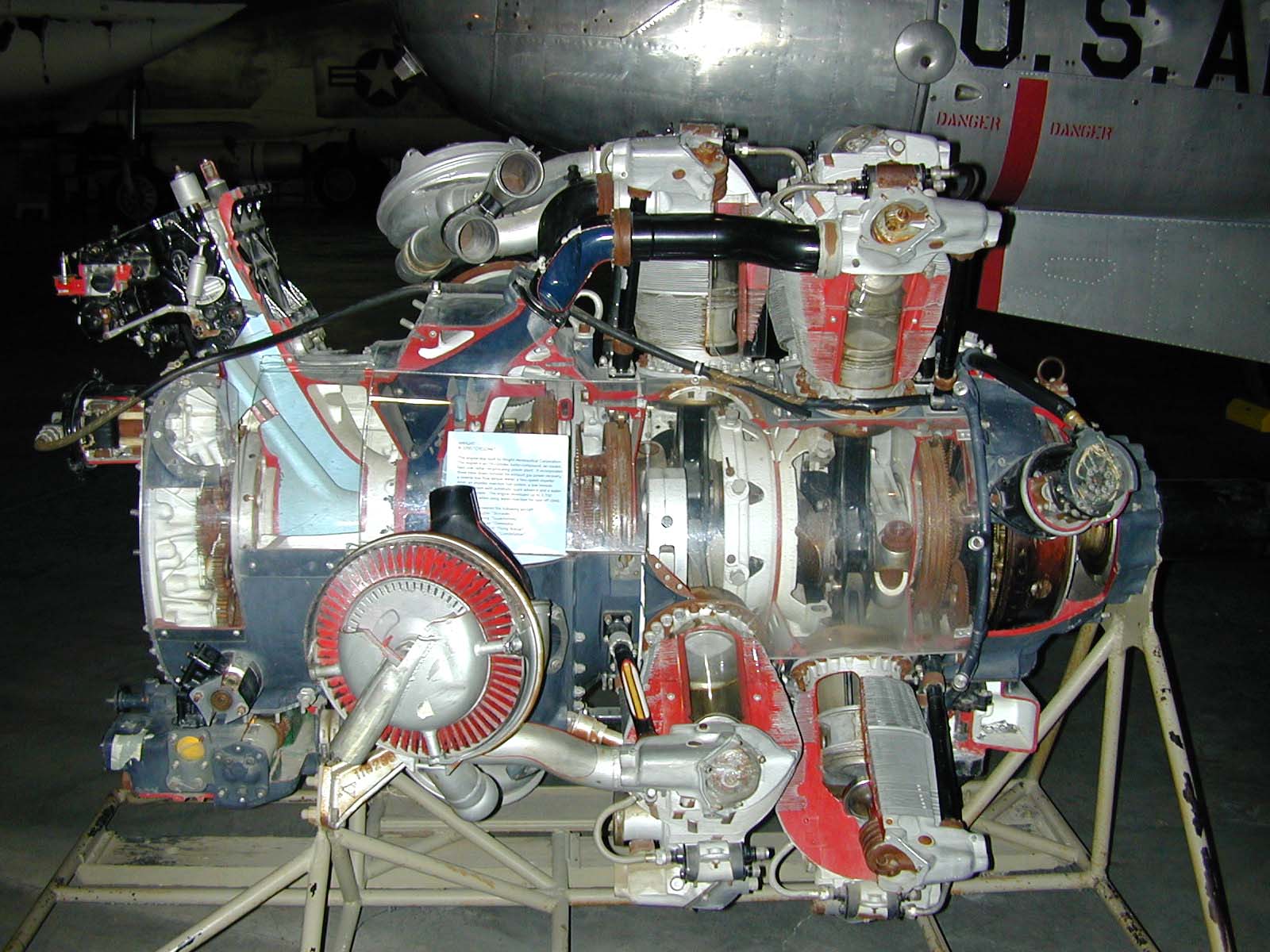
Pratt & Whitney R-2800
The Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp is an American twin-row, 18-cylinder, air-cooled radial aircraft engine with a engine displacement, displacement of , and is part of the long-lived Pratt & Whitney Wasp series, Wasp family of engines. The R-2800 saw widespread use in many important American aircraft during and after World War II. During the war years, Pratt & Whitney continued to develop new ideas to upgrade the engine, including water injection (engines), water injection for takeoff in cargo and passenger planes and to give emergency power in combat. Design and development First run in 1937, near the time that the larger competing 18-cylinder Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, Wright Duplex-Cyclone's development had been started in May of that year, the displacement R-2800 was first flown by 1940, one year before the Duplex-Cyclone. The Double Wasp was more powerful than the world's only other modern 18-cylinder engine, the Gnome-Rhône 18L of . The Double Wasp was mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly . Power ranged from , depending on model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature, and was still experiencing problems with reliability when used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. After the war, the engine had matured sufficiently to be used in many civilian airliners, notably in its turbo-compound forms, and was used in the Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation airliners into the 1950s. Its main rival was the , Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major, which first ran some seven years after the Duplex-Cyclone. The engine is commonly used on Hawker Sea Fury and Grumman F8F Bearcat Unlimited Class Racers at the Reno Air Races. Design and development In 1927, Wright Aeronautical introduced its "Cyclone" engine, which powered a number of designs in the 1930s. After merging with Curtiss to become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-38 Lightning
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twin boom, twin-boom design with a central nacelle containing the cockpit and armament. Along with its use as a general fighter aircraft, fighter, the P-38 was used in various aerial combat roles, including as a highly effective fighter-bomber, a night fighter, and a Range (aircraft), long-range escort fighter when equipped with drop tanks. The P-38 was also used as a bomber-pathfinder, guiding streams of medium bomber, medium and heavy bombers, or even other P-38s equipped with bombs, to their targets."P-38 Lightning" Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright R-1820
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Union as the Shvetsov M-25. Design and development The R-1820 Cyclone 9 represented a further development of the Wright P-2 engine dating back to 1925. Featuring a greater displacement and a host of improvements, the R-1820 entered production in 1931. The engine remained in production well into the 1950s. The R-1820 was built under license by Lycoming, Pratt & Whitney Canada, and also, during World War II, by the Studebaker Corporation. The Soviet Union had purchased a license for the design, and the Shvetsov '' OKB'' was formed to metricate the American specification powerplant for Soviet government-factory production as the '' M-25'', with the R-1820's general design features used by the Shvetsov design bureau for many of their futu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright R-2600
The Wright R-2600 Cyclone 14 (also called Twin Cyclone) is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, and widely used in aircraft in the 1930s and 1940s. History In 1935, Curtiss-Wright began work on a more powerful version of their successful R-1820 Cyclone 9. The result was the R-2600 Twin Cyclone, with 14 cylinders arranged in two rows. The R-2600-3 was originally intended for the C-46 Commando (being fitted to the prototype CW-20A). It was also the original engine choice for the F6F Hellcat; a running change (one which would not stop production) for the CW-20A, and one in late April 1942 for the second XF6F-1, led to the adoption of the Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp in the R-2600's place for both designs. The Twin Cyclone went on to power several important American World War II aircraft, including the A-20 Havoc, B-25 Mitchell, TBF Avenger, SB2C Helldiver, and the PBM Mariner. Over 50,000 R-2600s were built at plants in Paterson, New Jersey, and Cin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-044 Excalibur
The Lockheed Model 44 Excalibur was a proposed American airliner designed by Lockheed. The Model 44 was the first four-engined design from the company, a low-wing monoplane with a retractable tricycle landing gear. Originally fitted with twin fins, the design ended up with three fins. It was to be powered by four Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp radial engines. Pan American Airways was close to ordering the Excalibur when Lockheed abandoned the project to devote its resources to developing the Model 49 Constellation that had been ordered by Trans World Airlines. Design and development In the late 1930s, American aircraft companies such as Boeing and Douglas started developing airliners capable of carrying more passengers at longer ranges than any previous airliner. Douglas, which had the majority of the airliner market with its DC-3, was having trouble finding customers for its proposed Douglas DC-4E (not to be confused with the later DC-4). Around this time, the Lockheed Airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |