|
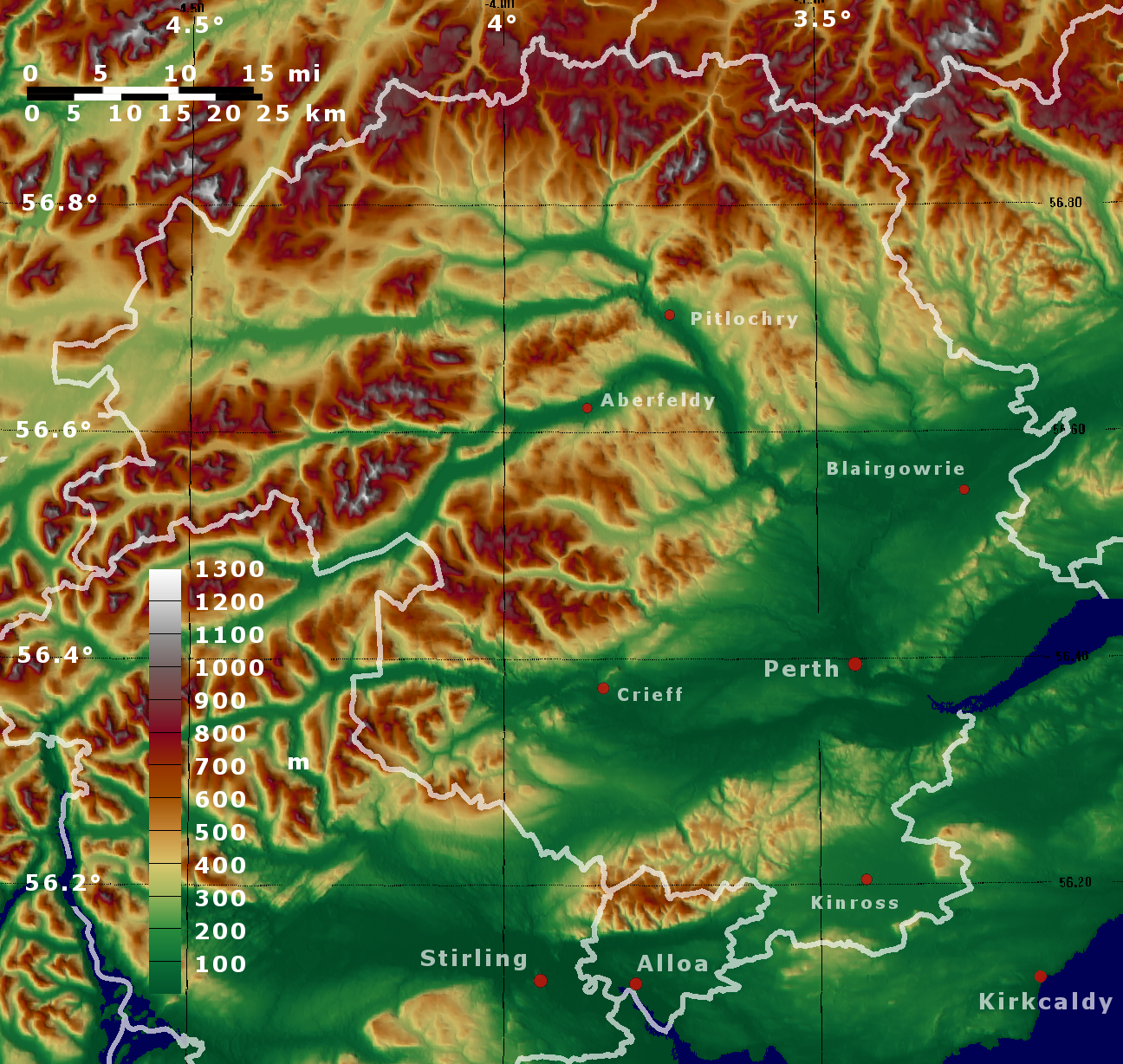
Loch Tummel
Loch Tummel (Scottish Gaelic: Loch Teimheil) is a long, narrow loch, northwest of Pitlochry in the council area of Perth and Kinross, Scotland. It is fed and drained by the River Tummel, which flows into the River Tay about south-east of the Clunie Dam at the loch's eastern end.Ordnance Survey. ''Explorer'' Map 1:25000. Sheet OL49, Pitlochry & Loch Tummel. The loch is traversed by roads to both north and south. Along the northern side the road is numbered as the B8019, and runs from the Pass of Killiecrankie on the A9 in the east to Tummel Bridge at the head of the loch. The road on the southern side is unclassified, and meets the A9 further south, near to Pitlochry. The loch gives its name to the Loch Tummel National Scenic Area (NSA), one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection by restricting certain forms of development. The Loch Tummel Lyon NSA covers , all of which lies within Perth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perth And Kinross
Perth and Kinross (; ) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and a Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area. It is bordered by Highland (council area), Highland and Aberdeenshire to the north, Angus, Scotland, Angus, Dundee, and Fife to the east, Clackmannanshire to the south, and Stirling (council area), Stirling and Argyll and Bute to the west. Geographically the area is split by the Highland Boundary Fault into a more mountainous northern part and a flatter southern part. The northern area is a popular tourist spot, while agriculture makes an important contribution to the southern part of the area. The area is run by Perth and Kinross Council, which is based in Perth, Scotland, Perth. History The area takes its name from the two historical Shires of Scotland, shires of Perthshire and Kinross-shire. Each was administered by a Sheriff principal, sheriff from medieval times, supplemented by Commissioners of Supply, commissioners of supply from 1667 and then by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Weir
Thomas Weir Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire, MBE (29 December 1914 – 6 July 2006) was a Scottish climber, author and broadcaster. He was best known for his long-running television series ''Weir's Way''. Early life and career Weir was born in Springburn, Glasgow, and the younger brother of the actress Molly Weir. After service in the Royal Regiment of Artillery, Royal Artillery during World War II, he worked as a surveying, surveyor for the Ordnance Survey, before commencing a full-time career as a climber, writer and photographer. In 1950 he was a member of the first post-war Himalayas, Himalayan expedition and, in 1952, was one of the first to explore the previously closed mountain ranges of Nepal, east of Kathmandu. Media career and later life Weir became a pioneering campaigner for the protection of the Scottish environment, and wrote a column for ''The Scots Magazine'' for over 50 years. From 1976–1987, he hosted the Scottish Television s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Hucho taimen, Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlantic salmon are found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in rivers that flow into it. Most populations are anadromous, hatching in streams and rivers but moving out to sea as they grow where they mature, after which the adults seasonally move upstream again to spawn. When the mature fish re-enter rivers to spawn, they change in colour and appearance. Some populations of this fish only migrate to large lakes, and are "landlocked", spending their entire lives in freshwater. Such populations are found throughout the range of the species. Unlike Pacific species of salmon, ''S. salar'' is iteroparous, which means it can survive spawning and return to sea to repeat the process again in another year with 5–10% returning to the sea to spawn again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Area Of Conservation
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and approximately 1,000 species listed in annex I and II of the directive which are considered to be of European interest following criteria given in the directive. They must be chosen from the Site of Community Importance, sites of Community importance by the member states and designated SAC by an act assuring the conservation measures of the natural habitat. SACs complement special protection areas and together form a network of protected sites across the European Union called Natura 2000. This, in turn, is part of the Emerald network of Area of Special Conservation Interest, Areas of Special Conservation Interest (ASCIs) under the Convention on the conservation of European wildlife and natural habitats, Berne Convention. Assessment methodol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they flow, drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean, another river, or into an endorheic basin. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob (river), Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NatureScot
NatureScot () is an Scottish public bodies#Executive NDPBs, executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government responsible for Scotland’s natural heritage, especially its nature, natural, genetics, genetic and scenic diversity. It advises the Scottish Government on nature conservation, and acts as a government agent in the delivery of conservation designations, i.e. national nature reserve (Scotland), national nature reserves, local nature reserves, National parks of Scotland, national parks, Site of Special Scientific Interest, Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs), Special Area of Conservation, Special Areas of Conservation, Special Protection Areas and the national scenic area (Scotland), national scenic areas. It receives annual funding from the Scottish Government in the form of Grant in Aid to deliver government priorities for Scotland’s natural heritage. NatureScot is the Scottish Government's adviser on all aspects of nature, wildlife management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perthshire
Perthshire (Scottish English, locally: ; ), officially the County of Perth, is a Shires of Scotland, historic county and registration county in central Scotland. Geographically it extends from Strathmore, Angus and Perth & Kinross, Strathmore in the east, to the Pass of Drumochter in the north, Rannoch Moor and Ben Lui in the west, and Aberfoyle, Scotland, Aberfoyle in the south; it borders the counties of Inverness-shire and Aberdeenshire to the north, Angus, Scotland, Angus to the east, Fife, Kinross-shire, Clackmannanshire, Stirlingshire and Dunbartonshire to the south and Argyllshire to the west. Perthshire is known as the "big county", or "the Shire", due to its roundness and status as the fourth List of Scottish counties by area, largest historic county in Scotland. It has a wide variety of landscapes, from the rich agricultural straths in the east, to the high mountains of the southern Scottish Highlands, Highlands. History Administrative history Perthshire's origins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but from c. 1841 and for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tay Forest Park
Tay Forest Park is a forest park in the council area of Perth and Kinross in Scotland. It consists of a network of forests managed by Forestry and Land Scotland (FLS) that are spread across the Highland parts of Perthshire, and covers in total. The park contains a series of disparate woods that are managed for multiple benefits, with an emphasis on recreation facilities for visitors. The park's main visitor centre is at Queen's View, near Loch Tummel, where there is a café, gift shop and interpretative displays. Other smaller centres are located at the following locations: *Allean, also close to Loch Tummel * Faskally, between Pitlochry and Killiecrankie *Carie on the south side of Loch Rannoch * Grandtully, between Aberfeldy and Ballinluig * Weem, north of Aberfeldy *Drummond Hill on the north side of Loch Tay * Craigvinean, near Dunkeld and Birnam Dunkeld (, , from , "fort of the Caledonians") is a town in Perth and Kinross, Scotland. The location of a historic cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry And Land Scotland
Forestry and Land Scotland (FLS) () is an executive agency responsible for managing and promoting Scotland's national forest estate: land, predominantly covered in forest, owned by the Scottish Government on behalf of the nation. It was formed on 1 April 2019, to take over some of the responsibilities of Forestry Commission Scotland, which was dissolved. The organisation exists alongside Scottish Forestry, also established on 1 April 2019, which is responsible for regulation, policy and support to landowners. Forestry and Land Scotland's key functions are to look after the national forest estate, including unforested land within this portfolio, and to produce and supply timber. Within this remit they are expected to enhance biodiversity, increase public access to the outdoors, encourage tourism and support the rural economy. The agency has been established initially to manage only the national forest estate, however it is intended that in future it may also take over management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Methven
The Battle of Methven took place at Methven, Scotland on 19 June 1306, during the Wars of Scottish Independence. The battlefield was researched to be included in the Inventory of Historic Battlefields in Scotland and protected by Historic Scotland under the Scottish Historical Environment Policy of 2009, but was excluded due to the uncertainty of its location. Background Bruce was crowned King of Scots by Bishop William de Lamberton at Scone, near Perth, on Palm Sunday (25 March 1306). Enraged by the killing of John Comyn, Lord of Badenoch by Bruce and his followers at Dumfries and Bruce’s coronation, Edward I of England named Aymer de Valence, Earl of Pembroke, special lieutenant for Scotland. Pembroke moved quickly, and by the middle of summer he had made his base at Perth, along with Henry Percy and Robert Clifford with an army of about 3000 men drawn from the northern counties. Edward I gave orders that no mercy was to be granted and all taken in arms were to be ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert I Of Scotland
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (), was King of Scots from 1306 until his death in 1329. Robert led Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the First War of Scottish Independence against Kingdom of England, England. He fought successfully during his reign to restore Scotland to an independent kingdom and is regarded in Scotland as a folk hero, national hero. Robert was a fourth-great-grandson of King David I, and his grandfather, Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale, was one of the claimants to the Scottish throne during the "Great Cause". As Earl of Carrick, Robert the Bruce supported his family's claim to the Scottish throne and took part in William Wallace's campaign against Edward I of England. Appointed in 1298 as a Guardian of Scotland alongside his chief rival for the throne, John Comyn of Badenoch, and William Lamberton, Bishop of St Andrews, Robert resigned in 1300 because of his quarrels with Comyn and the apparently imminen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |