|
Local Mail And Rayon Stamps Of Switzerland
The local mail and rayon stamps of 1850 and 1852 constituted the first series of postage stamps issued by the Swiss Post. In philately, they are among the most sought-after Swiss stamps, with a 5 rappen ''Rayon I'' stamp selling for the record price of CHF 348,000 (USD 293,000) at auction in 2008. After the reconstitution of Switzerland as a federal state in 1848, the authority to operate a postal service passed from the cantons to the Confederation, and the federal postal service was founded in 1849. Its local mail and rayon stamps were the first definitive stamps valid in all of Switzerland, although the stamps issued by the postal authorities of the cantons of Geneva, Basel-Stadt and Zürich remained concurrently valid until 1854, when all stamps were supplanted by the "Sitting Helvetia" series of federal stamps. Rayons The first Swiss postal regulations divided Switzerland, for the purpose of mailing letters weighing no more than half a lot, into four ''rayons''. These were defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postage Stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper issued by a post office, postal administration, or other authorized vendors to customers who pay postage (the cost involved in moving, insuring, or registering mail), who then affix the stamp to the face or address-side of any item of mail—an envelope or other postal cover (e.g., packet, box, mailing cylinder)—that they wish to send. The item is then processed by the postal system, where a postmark or cancellation mark—in modern usage indicating date and point of origin of mailing—is applied to the stamp and its left and right sides to prevent its reuse. The item is then delivered to its addressee. Always featuring the name of the issuing nation (with the exception of the United Kingdom), a denomination of its value, and often an illustration of persons, events, institutions, or natural realities that symbolize the nation's traditions and values, every stamp is printed on a piece of usually rectangular, but sometimes triangu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
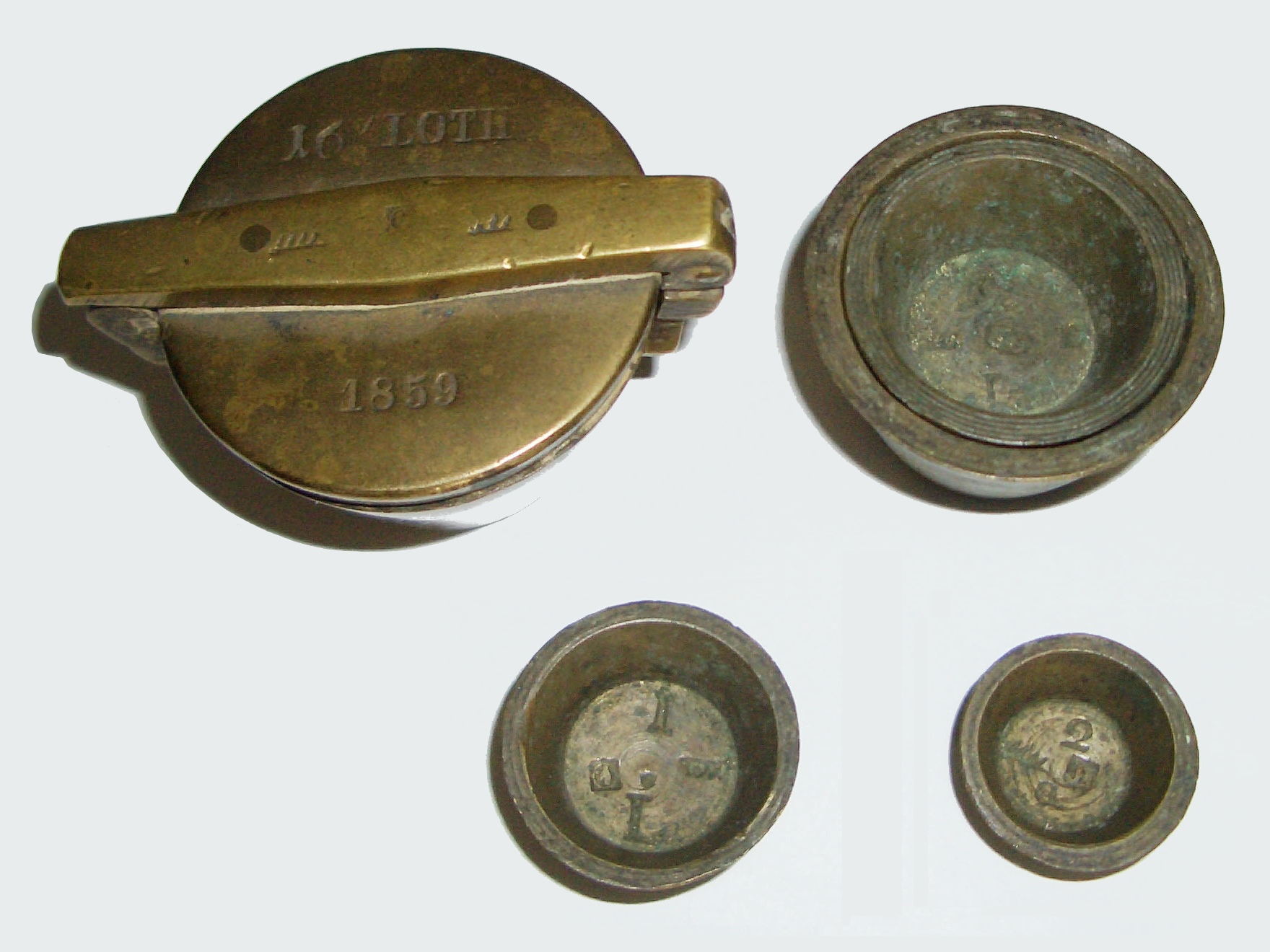
Lot (mass)
The Lot (formerly also written ''Loth'') was a unit of measurement of mass, which was mainly used in German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire and in Scandinavia. It was replaced in the German Reich in 1868/69/72, in Austria in 1871/76 and in Switzerland in 1875/77 by the metric unit of measurement, the gramme. But in the early 20th century it was still used as a popular unit of measure in cooking and baking recipes. An imprecise but clear rule of thumb is that a ''lot'' corresponds to a "spoonful". Old ''Lot'' In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, the following weight system was traditionally used: (trading) '' Pfund'' = 1 ''Lot'' = 4 ''Quents'' = 16 ''Pfennig'' weights = 32 ''Heller'' weights The ''Lot'' had different weights in the various German states depending on the definition of the ''Pfund'' ("pound"); its definition also varied over time. However it was mostly set at between 14 g and 18 g. Some examples: * 14.606 g before May 1856 in Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone ( lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146 Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 11 Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Originally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat limestone pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France ( Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland ( Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary ( Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic group, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language after English, which is also a West Germanic language. German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Coat Of Arms
The coat of arms of the Swiss Confederation shows the same white-on-red cross as the flag of Switzerland, but on a heraldic shield instead of the square field. The federal coat of arms (''eidgenössisches Wappen'') was defined by the Swiss Diet (''Tagsatzung'') in 1815, for the Restored Confederacy. A more elaborate federal seal was also defined, as the federal coat of arms surrounded by the twenty-two cantonal coats of arms. Similar heraldic arrangements representing the Thirteen Cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy are on record from the mid-16th century. The 1815 legislation remained in force in the federal state established in 1848, as was explicitly recognized by the Federal Council in 1889. While the simple coat of arms was in wide use, especially on coins, and from the early 20th century also on car number plates and passports, the full seal did not see official use beyond its representation in stained glass in the Federal Palace of Switzerland (c. 1900). The 19th-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugle
The bugle is one of the simplest brass instruments, normally having no valves or other pitch-altering devices. All pitch control is done by varying the player's embouchure. History The bugle developed from early musical or communication instruments made of animal horns, with the word "bugle" itself coming from "buculus", Latin for bullock ( castrated bull). The earliest bugles were shaped in a coil – typically a double coil, but also a single or triple coil – similar to the modern horn, and were used to communicate during hunts and as announcing instruments for coaches (somewhat akin to today's automobile horn). Predecessors and relatives of the bugle included the post horn, the Pless horn (sometimes called the "Prince Pless horn"), the bugle horn, and the shofar, among others. The ancient Roman army used the buccina. The first verifiable formal use of a brass bugle as a military signal device was the ''Halbmondbläser'', or half-moon bugle, used in Hanover in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Post Rayon III Stamp 1852
Swiss may refer to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland *Swiss people Places *Swiss, Missouri *Swiss, North Carolina * Swiss, West Virginia *Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses * Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports * Swiss International Air Lines **Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary *Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland *.swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also *Swiss made, label for Swiss products *Swiss cheese (other) *Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer Schweitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Albert Schweitzer, German theologian, musician, physician, and medical missionary, winner of the 1952 Nobel Peace Prize * Anton Schweitzer, opera composer * Brian Schweitzer, forme ..., a family name meaning Swiss in German * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Switzerland
Municipalities (german: Gemeinden, ' or '; french: communes; it , comuni; rm, vischnancas) are the lowest level of administrative division in Switzerland. Each municipality is part of one of the Swiss cantons, which form the Swiss Confederation. In most cantons, municipalities are also part of districts or other sub-cantonal administrative divisions. There are 2,136 municipalities . Their populations range between several hundred thousand (Zürich), and a few dozen people ( Kammersrohr, Bister), and their territory between 0.32 km² (Rivaz) and 439 km² ( Scuol). History The beginnings of the modern municipality system date back to the Helvetic Republic. Under the Old Swiss Confederacy, citizenship was granted by each town and village to only residents. These citizens enjoyed access to community property and in some cases additional protection under the law. Additionally, the urban towns and the rural villages had differing rights and laws. The creation of a uniform S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)