|
Lobau Bombing
The Lobau bombing was a bomb attack in Paris, France, carried out on 15 March 1892, by the anarchist militant Théodule Meunier against the Lobau barracks. Organized four days after the Saint-Germain bombing, it was one of the first attacks of the Ère des attentats (1892–1894). The explosion caused material damage in the surrounding area but killed or injured no one. Meunier managed to carry out the Véry bombing a month later before fleeing to the United Kingdom. He was subsequently extradited to France, sentenced to life imprisonment with hard labor, and deported to the penal colony of Cayenne, where he died. This bombing, along with other attacks during the Ère des attentats, marked an early shift in terrorist strategy: instead of targeting specific individuals, it focused on symbolic locations—in this case, the Lobau barracks as a stand-in for a precise human target. This shift became a hallmark of modern terrorism but was poorly understood by contemporaries. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ère Des Attentats
The (), or the French anarchist campaign of attacks from 1892 to 1894, was a period in the history of France and the broader Propaganda of the deed, history of propaganda of the deed (1880–1914), marked by a significant wave of political violence—both from the French authorities and Anarchism, anarchist terrorists. Its chronological boundaries extend from the Saint-Germain bombing (11 March 1892) to the Revolt of Saint-Joseph, massacre of the anarchist convicts (22 October 1894). During this period, the French press largely shaped political discourse and public opinion, presenting these acts as interconnected events forming a progressive logic rather than isolated incidents. In response to the significant repression anarchists had suffered in France since the Paris Commune (1871), a number of them came to consider terrorism as a legitimate means of avenging this repression, targeting symbols of power, state institutions, and emblematic places of bourgeois life. During the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravachol
François Claudius Ravachol (; born Koenigstein; 14 October 1859 – 11 July 1892) was a French illegalist anarchist mainly known for his terrorist activism, impact, the myths developed around his figure and his influence on the anarchist movement in France. Born in 1859 in Saint-Chamond, in the Saint-Étienne area, Ravachol grew up in poverty and domestic violence. Later, he began a life of crime marked by the murder and robbery of a rich hermit. In this city, Ravachol gradually adopted anarchist ideas and met other activists, such as Rosalie Soubère and Joseph Jas-Béala. He managed to escape from arrest and with these two accomplices, the militant moved to Paris in 1891. There, joined by the young anarchist militant Charles Simon, they carried out the Saint-Germain and Clichy bombings (1892), targeting the judge and prosecutor responsible for the judicial persecution of anarchists arrested during the Clichy Affair (1891). Quickly arrested after the second attack, he s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Pierre François (anarchist)
Jean-Pierre François, nicknamed 'Francis', (3 December 1855, in Reims-after 1907) was a carpenter and individualist- illegalist anarchist terrorist. After a youth marked by poverty and repeated criminal convictions, he was sent to a disciplinary battalion in French Algeria, where he was again imprisoned for theft. Upon his return to the ''métropole'', he married the anarchist activist Victorine Delanoy, and together they became involved in Parisian anarchist circles. Close to figures such as Théodule Meunier and Pierre Martinet—one of the leading theorists of individualist anarchism—François became active in several anarchist movements and groups, including the Pieds plats group. He is best known for his participation during the Ère des attentats (1892–1894). In this context, he took part in the Véry bombing, which targeted its owner, Jean-Marie Véry, an informant for the police and the denouncer of Ravachol. Arrested shortly thereafter, he managed to be freed and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieds Plats
The Pieds plats () were an Individualist anarchism, individualist and Illegalism, illegalist Anarchism, anarchist group founded in the 1880s in Paris. Bringing together workers from the Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in the carpentry trade, some of its members participated in the Era of Attacks (1892–1894), such as Théodule Meunier, Jean-Pierre François (anarchist), Jean-Pierre François, and Fernand Bricout, who carried out the Véry bombing or the Lobau bombing in the first half of 1892. Through their extensive use of Propaganda of the deed, propaganda by the deed during this period, they positioned themselves as counter-powers to the authority of prominent anarchist figures like Charles Malato, Errico Malatesta, or Peter Kropotkin, whom the Pieds plats and broader individualist anarchists openly opposed. The group also gained influence through its combination of direct action, illegalism, and propaganda by the deed. Its members are thus credited with pioneering and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mort Aux Vaches
''Mort'' is a fantasy novel by British writer Terry Pratchett. Published in 1987, it is the fourth ''Discworld'' novel and the first to focus on the character Death, who only appeared as a side character in the previous novels. The title is the name of its main character, and is also a play on words: in French and Catalan, ''mort'' means "death", while in Romanian it means "dead". The French language edition is titled ''Mortimer'', and the Catalan language edition is titled ''Morth''. In 2004, Pratchett stated that ''Mort'' was the first Discworld novel with which he was "pleased", stating that in previous books, the plot had existed to support the jokes, but that in ''Mort'', the plot was integral. Plot summary As a teenager, Mort has a personality and temperament that makes him unsuited to the family farming business. Mort's father Lezek takes him to a local hiring fair in the hope that Mort will land an apprenticeship. Just before the last stroke of midnight, Death arrives an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
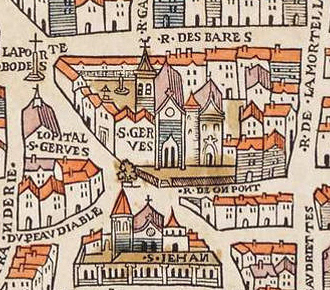
Saint-Gervais-Saint-Protais
Saint-Gervais-Saint-Protais () is a Roman Catholic parish church located in the 4th arrondissement of Paris, 4th arrondissement of Paris, on Place Saint-Gervais in the Le Marais (Paris), Marais district, east of Hôtel de Ville, Paris, City Hall (Hôtel de Ville). The current church was built between 1494 and 1657, on the site of two earlier churches; the facade, completed last, was the first example of the French Baroque, French baroque style in Paris. The organists of the church included Louis Couperin and his nephew François Couperin, two of the most celebrated composers and musicians of the Baroque period; the organ they used can still be seen today. The church contains remarkable examples of medieval carved choir stalls, stained glass from the 16th century, 17th century sculpture, and modern stained glass by Sylvie Gaudin and Claude Courageux. Saint-Gervais was a parish church until 1975, when it became the headquarters of the Monastic Fraternities of Jerusalem. History A c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rue De Rivoli
The Rue de Rivoli (; English: "Rivoli Street") is a street in central Paris, France. It is a commercial street whose shops include leading fashionable brands. It bears the name of Napoleon's early victory against the Austrian army, at the Battle of Rivoli, fought on 14–15 January 1797. Developed by Napoleon through the heart of the city, it includes on one side the north wing of the Louvre Palace and the Tuileries Gardens. History The Rue de Rivoli is an example of a transitional compromise between an environment of prestigious monuments and aristocratic squares, and the results of modern town-planning by municipal authorities. The new street that Napoleon developed through the heart of Paris includes on one side the north wing of the Louvre Palace, (which Napoleon extended) and the Tuileries Gardens. Upon completion, it was the first time that a wide, well designed and aesthetically pleasing street bound the north wing of the Louvre Palace. Napoleon's original section of the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (, ) was a French revolutionary government that seized power in Paris on 18 March 1871 and controlled parts of the city until 28 May 1871. During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard (France), National Guard had defended Paris, and working-class radicalism grew among its soldiers. Following the establishment of the French Third Republic in September 1870 (under French chief-executive Adolphe Thiers from February 1871) and the complete defeat of the French Army by the Germans by March 1871, soldiers of the National Guard seized control of the city on 18 March. The Communards killed two French Army generals and refused to accept the authority of the Third Republic; instead, the radicals set about establishing their own independent government. The Commune governed Paris for two months, promoting policies that tended toward a Progressivism, progressive, anti-clericalism , anti-religious system, which was an eclectic mix of many 19th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semaine Sanglante
The ''Semaine sanglante'' ("") was a weeklong battle in Paris from 21 to 28 May 1871, during which the French Army recaptured the city from the Paris Commune. This was the final battle of the Paris Commune. Following the Treaty of Frankfurt (1871), Treaty of Frankfurt and France's loss in the Franco-Prussian War, on 18 March the new French government under Prime Minister Adolphe Thiers attempted to remove a large number of cannon from a park in Montmartre, to keep them out of the hands of the more radical soldiers of the Paris National Guard (France), National Guard. In the confrontation that followed, two French generals were seized and executed by the National Guard. Thiers, the army commander Patrice de MacMahon and the French government hurriedly left the city, and established their headquarters in Palace of Versailles, Versailles, and prepared plans to recapture the city. The Paris Commune made an unsuccessful attack on Versailles under the leadership of Louis Charles De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Guard (France)
The Republican Guard (, ) is part of the French National Gendarmerie. It is responsible for special security duties in the Paris area and for providing guards of honour at official ceremonies of the French Republic. Its missions include guarding important public buildings in Paris, such as the Élysée Palace (the residence of the President of the French Republic), the Hôtel Matignon (the residence of the Prime Minister of France), the Luxembourg Palace (the Senate), the Palais Bourbon (the National Assembly) and the Palais de Justice, as well as keeping public order in Paris. Ceremonial and security services for the highest national personalities and important foreign guests, military ceremonies and guards of honour for fallen soldiers, support of other law enforcement forces with intervention teams, as well as staffing horseback patrol stations (particularly for the forests of the Île-de-France region) are also part of its duties. The close physical protection of the Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |