|
Llan (placename Element)
Llan () and its variants (; ; ; Irish and ) are a common element of Celtic placenames in the British Isles and Brittany, especially of Welsh toponymy. In Welsh the (often mutated) name of a local saint or a geomorphological description follows the ''Llan'' morpheme to form a single word: for example Llanfair is the parish or settlement around the church of (Welsh for " Mary"). Goidelic toponyms end in ''-lann''. The various forms of the word are distantly cognate with English ''land'' and ''lawn'' and presumably initially denoted a specially cleared and enclosed area of land. In late antiquity it came to be applied particularly to the sanctified land occupied by communities of Christian converts. It is part of the name of more than 630 locations in Wales and nearly all have some connection with a local patron saint. These were usually the founding saints of the parish,Baring-Gould, Sabine''The Lives of the Saints'', Vol. 16, "The Celtic Church and its Saints", p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous language, indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was the majority of the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century, in what is sometimes characterised as a result of linguistic imperialism. Today, Irish is still commonly spoken as a first language in Ireland's Gaeltacht regions, in which 2% of Ireland's population lived in 2022. The total number of people (aged 3 and over) in Ireland who declared they could speak Irish in April 2022 was 1,873,997, representing 40% of respondents, but of these, 472,887 said they never spoke it and a further 551,993 said they only spoke it within the education system. Linguistic analyses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of Wales
Representing 43.6% of the Welsh population in 2021, Christianity is the largest religion in Wales. Wales has a strong tradition of Nonconformist (Protestantism), nonconformism, particularly Methodism. From 1534 until 1920 the established church was the Church of England, but this was Separation of church and state#United Kingdom, disestablished in Wales in 1920, becoming the still Anglicanism, Anglican but self-governing Church in Wales. Most adherents to organised religion in Wales follow the Church in Wales, Anglican Church in Wales, Presbyterian Church of Wales, Baptist Union of Wales, Union of Welsh Independents, Methodist Church of Great Britain, Methodist, Catholic Church in England and Wales, Catholic and Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox churches. History Celtic Christianity Nearly 200 years before Constantine the Great, Constantine, Lucius of Britain, Saint Lucius, a legendary 2nd-century King of the Britons (or Silures) is traditionally credited with introducing C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
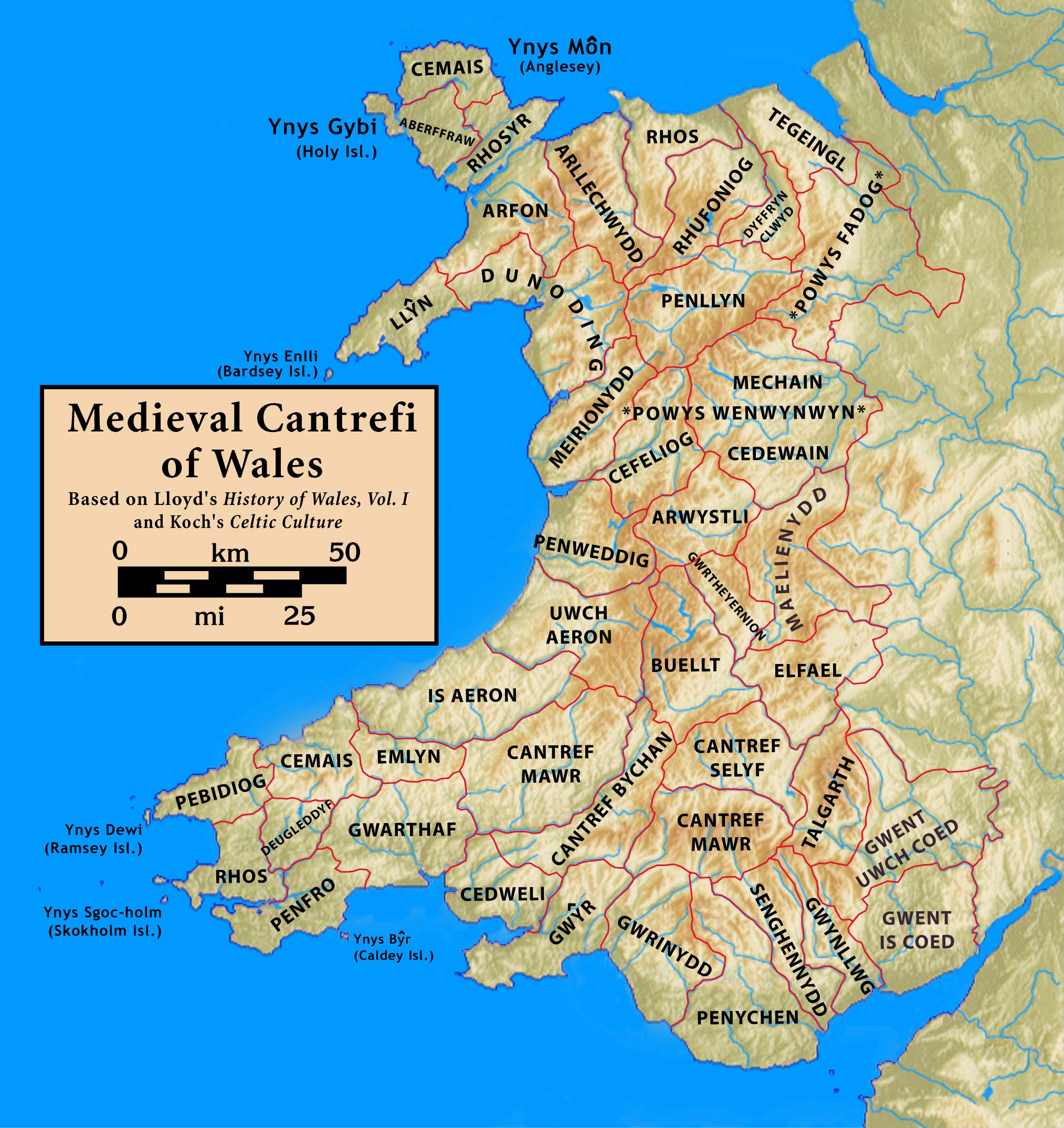
Llanafan Fawr
Llanafan Fawr is a village, community and ecclesiastical parish in Powys, Wales. Located in the former cantref of Buellt (Builth) and historic county of Brecknockshire, the community includes the former parish of Llanfihangel Bryn Pabuan. The parish has an area of slightly over (about twenty square miles) and a scattered rural population of more than a thousand. It is named after Saint Afan and was the centre of Cantref Buallt in ancient times, before the building of Builth Wells about away. The former spa town of Llandrindod Wells lies about to the north east. An electoral ward of the same name exists. The population of this ward at the 2011 census was 1,386. Name The village is also known simply as Llanafan or variantly spelled Llanafan-Fawr. In Welsh placenames, many smaller communities are named for their parish ('), having grown up around the local church. This name of the village honours its patron saint Afan. "" is the mutated form of the Welsh ', meaning "big" or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aelhaiarn
Saint Aelhaiarn or Aelhaearn (Welsh language, Welsh for "Iron Brow";Baring-Gould, Sabine & al''The Lives of the British Saints: The Saints of Wales and Cornwall and Such Irish Saints as Have Dedications in Britain'', Vol. I, pp. 101 ff Chas. Clark (London), 1908. Hosted at Archive.org. Accessed 18 November 2014. early 7th century) was a Welsh people, Welsh Confessor of the Faith, confessor and list of Welsh saints, saint of the Celtic Church, British Church. He was a disciple of Saint Beuno. His Gŵyl Mabsant, feast day was usually observed on 2 November, although it is sometimes recorded as the 1st and is no longer observed by either the Church in Wales, Anglican or Catholic Church in England and Wales, Catholic church in Wales. Life Saint Aelhaiarn is listed among the ''Bonedd y Seint'' (Genealogies of the Saints). He was the brother of saints Llwchaiarn and Cynhaiarn and son of Hygarfael or Cerfael, son of Cyndrwyn, a prince of the Kingdom of Powys, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanaelhaearn
Llanaelhaearn is a village on the Llŷn Peninsula in the Local government in Wales, county of Gwynedd, Wales. Located in the community of (prior to 2024 called just "Llanaelhaearn") which also includes the larger village of Trefor, Gwynedd, Trefor and has a population of 1,067, increasing to 1,117 at the 2011 Census. Name The town's name honours its patron saint and supposed founder Aelhaiarn ( "Iron Brow"), although it was long known by the corrupted name Llanhaiarn, leading locals to suppose there had once been a "Saint Elern" instead. (A nearby estate known as Elernion—i.e., "St. Elern's"—is thought to have a similar origin.Baring-Gould, Sabine & al''The Lives of the British Saints: The Saints of Wales and Cornwall and Such Irish Saints as Have Dedications in Britain'', Vol. I, pp. 101 ff Chas. Clark (London), 1908. Hosted at Archive.org. Accessed 18 Nov 2014.) The official spelling of the parish's name was Llanaelhaiarn until 1957 when i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a Barony (Ireland), barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commote
A commote (, sometimes spelt in older documents as , plural , less frequently )'' Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru'' (University of Wales Dictionary), p. 643 was a secular division of land in Medieval Wales. The word derives from the prefix ("together", "with") and the noun ("home, abode"). The English word "commote" is derived from the Middle Welsh . The basic unit of land was the , a small basic village or settlement. In theory, 100 made up a (literally, "one hundred settlements"; plural: ), and half or a third of a was a , although in practice the actual numbers varied greatly. Together with the , commotes were the geographical divisions through which defence and justice were organised. In charge of a commote would be a chieftain probably related to the ruling Prince of the Kingdom. His court would have been situated in a special , referred to as a . Here, the bonded villagers who farmed the chieftain's estate lived, together with the court officials and servants. Commotes were f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or more curates, and who operates from a parish church. Historically, a parish often covered the same geographical area as a Manorialism, manor. Its association with the parish church remains paramount. By extension the term ''parish'' refers not only to the territorial entity but to the people of its community or congregation as well as to church property within it. In England this church property was technically in ownership of the parish priest ''Ex officio member, ex officio'', vested in him on his institution to that parish. Etymology and use First attested in English in the late 13th century, the word ''parish'' comes from the Old French , in turn from , the Romanization of Greek, Romanisation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laity
In religious organizations, the laity () — individually a layperson, layman or laywoman — consists of all Church membership, members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-Ordination, ordained members of religious orders, e.g. a nun or a lay brother. In secular usage, by extension, a layperson is a person who is not qualified in a given profession or is not an expert in a particular field. The phrase "layman's terms" is used to refer to plain language that is understandable to the everyday person, as opposed to specialised terminology understood only by a professional. Terms such as ''lay priest'', ''lay clergy'' and ''lay nun'' were once used in certain Buddhist cultures, especially Japanese, to indicate ordained persons who continued to live in the wider community instead of retiring to a monastery. Some Christian churches utilise lay preachers, who sermon, preach but are not clergy. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints uses the term ''lay pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clas (ecclesiastical Settlement)
A clas ( Welsh ''clasau'') was a native Christian church in early medieval Wales. Unlike later Norman monasteries, which were made up of a main religious building supported by several smaller buildings, such as cloisters and kitchens, a clas was normally a single building. The building was run by a community of clergy and headed by an abod. Clasau were autonomous and were administered locally. Following the Norman invasion of Wales in the late 11th century, many of the clasau of south Wales became dependencies of religious houses in England. This resulted in several sites becoming part of the Benedictine or Augustinian orders, or built upon in the following centuries by Norman churches. Clas locations in Wales A map of ''clasau'' that can be recognised from Welsh documentary sources was provided by William Rees in 1951. Wendy Davies, in her study of the Llandaff Charters, has identified 36 monasteries or ''clasau'' from the 7th to 9th centuries, mainly in the Diocese of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caer
Caer (; or ') is a placename element in Welsh meaning "stronghold", "fortress", or "citadel", roughly equivalent to an Old English suffix (''-ceaster'') now variously written as , , and .Allen, Grant"Casters and Chesters" in ''The Cornhill Magazine'', Vol. XLV, pp. 419 ff.Smith, Elder, & Co. (London), 1882. In modern Welsh orthography, caer is usually written as a prefix, although it was formerly—particularly in Latin—written as a separate word. The Breton equivalent is ''kêr'', which is present in many Breton placenames as the prefix ''Ker-''. Etymology The term is thought to have derived from the Brittonic *''kagro-'' and to be cognate with ''cae'' ("field, enclosed piece of land"). Although stone castles were largely introduced to Wales by the invading Normans, "caer" was and remains used to describe the settlements around some of them as well. An example is the Roman fort at Caernarfon, formerly known in Welsh as ' from its position on the Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of England
The Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England was the process starting in the late 6th century by which population of England formerly adhering to the Anglo-Saxon, and later Nordic, forms of Germanic paganism converted to Christianity and adopted Christian worldviews. The process of Christianisation and timing of the adoption of Christianity varied by region and was not necessarily a one-way process, with the traditional religion regaining dominance in most kingdoms at least once after their first Christian king. Kings likely often converted for political reasons such as the imposition by a more powerful king, to gain legitimacy, and to access book-writing traditions; however, there were also significant drawbacks to the conversion that may explain the reluctance of many kings to be baptised. The first major step was the Gregorian mission that landed in the Kingdom of Kent in 597, and within the Heptarchy, Æthelberht of Kent became the first Anglo-Saxon king to be baptised, aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |