|
Livingston L. Holder, Jr.
Livingston L. Holder Jr. (born 29 September 1956) is a former USAF astronaut in the Manned Spaceflight Engineer Program during the mid-1980s. He was assigned to fly as a military payload specialist on the Space Shuttle, but could not fly in space due to the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, ''Challenger'' accident in 1986. Biography Holder was born in Detroit, Michigan, United States and now resides in Seattle, Washington. He has three sons (Jonathan, Nathan, and Christopher). He holds a B.S. in Astronautical Engineering from the United States Air Force Academy, and an M.S. in Systems Management from University of Southern California. While serving in the Air Force, Holder was a Titan III launch crew member at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Vandenberg AFB, California. He also served in the Office of the Secretary of the Air Force, Special Projects organization, Los Angeles AFS, California, on a classified satellite program. Holder trained and qualified as a Manned Spaceflight Enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps (United States Army), Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, airlift, rapid global mobility, Strategic bombing, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the United States Department of the Air Force, De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Hudson (engineer)
Gary Hudson (born 1949/1950) has been involved in private spaceflight development since 1970, for over 40 years. Biography Gary Hudson is currently Co-Founder and Chief Architect of Gravitics, Inc. a space station manufacturing company. Mr. hudson is also Executive Chairman of Oisin Biotechnologies, Inc. & President/Truste of the Space Studies Institute. is Previously, Hudson was the founder of Rotary Rocket Company, which in spending ~$30 Million attempted to build a unique single stage to orbit launch vehicle known as the Roton. Rotary Rocket built a landing test simulator (the Roton ATV) which flew three successful test flights in 1999. The book "They All Laughed at Christopher Columbus - An Incurable Dreamer Builds the First Civilian Spaceship" by Elizabeth Weil is about the Roton project and Gary Hudson. He also helped found Transformational Space T/Space in 2004. He also helped found AirLaunch LLC which was awarded the DARPA/USAF FALCON project in 2003. Previous proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AirLaunch LLC
AirLaunch was an aerospace design and development company headquartered in Kirkland, Washington. They had hoped to provide launch services for launching payloads into orbits around the Earth. This was to be realized through a method called air launch where a rocket is carried to high altitude by an aircraft and then released for launch. The rocket engine is then ignited to launch the rocket (with its payload) into a low Earth orbit (LEO). The principal advantage of a rocket being launched by a high flying airplane is that it need not fly through the low, dense atmosphere, the drag of which requires a considerable amount of extra work and thus mass of propellant. Another advantage is to precisely launch a payload into any orbital inclination at any time, and from a much wider variety of geographic launch locations. Falcon Small Launch Vehicle On June 14, 2006, the firm, in a DARPA sponsored test, dropped a dummy payload from the back of a C-17 The McDonnell Douglas/B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop Grumman Corporation
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military technology providers. The firm ranks on the 2022 ''Fortune'' 500 list of America's largest corporations. Northrop Grumman and its industry partners have won the Collier Trophy eight times, most recently for developing the X-47B, the first unmanned, autonomous air system to operate from an aircraft carrier. Northrop Grumman currently leads the development of the B-21 Raider, a long-range, stealth strategic bomber that can drop conventional and nuclear weapons; it will replace Northrop's own B-2 Spirit, the world's only known stealth bomber. Among its other current projects are development and production of the James Webb Space Telescope, an orbiting observatory launched in 2021, and production of the solid rocket boosters for NASA's Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), the agency was created on February 7, 1958, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in response to the Soviet launching of Sputnik 1 in 1957. By collaborating with academia, industry, and government partners, DARPA formulates and executes research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, often beyond immediate U.S. military requirements.Dwight D. Eisenhower and Science & Technology, (2008). Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial CommissionSource '' The Economist'' has called DARPA the agency "that shaped the modern world," and pointed out that " Moderna's COVID-19 vaccine sits alongside weather satellites, GPS, drones, stealth technology, voice interfaces, the personal comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA FALCON
The DARPA Falcon Project (Force Application and Launch from Continental United States) is a two-part joint project between the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and the United States Air Force (USAF) and is part of Prompt Global Strike. One part of the program aims to develop a reusable, rapid-strike ''Hypersonic Weapon System'' (HWS), now retitled the ''Hypersonic Cruise Vehicle'' (HCV), and the other is for the development of a launch system capable of accelerating an HCV to cruise speeds, as well as launching small satellites into Earth orbit. This two-part program was announced in 2003 and continued into 2006.FALCON Force Application and Launch from CONUS Broad Agency Announcement (BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrews Space
Andrews Space was founded in 1999 by Jason Andrews and Marian Joh to be a catalyst in the commercialization, exploration and development of space. Originally named Andrews Space & Technology, the company shortened its name in 2003 to Andrews Space. Over its life the company developed many unique technologies and space transportation architectures for the US Government (NASA, DARPA, others) and commercial customers. The company is now Spaceflight Systems, a subsidiary of Spaceflight Industries, Inc. Projects and products Andrews Space developed a number of innovative technologies and space transportation concepts including: * Mini-mag Orion * Alchemist Air Collection and Enrichment System * Gryphon fully reusable horizontal take / horizontal landing space plane * Peregrine small launch system * SHERPA space tug * Cubesat/Nanosat recovery system Andrews Space worked for most branches of the US Government. Noteworthy efforts include: * NASA Space Launch Initiative * NASA Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Department Of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The department's mission is "to develop and coordinate policies that will provide an efficient and economical national transportation system, with due regard for need, the environment, and the national defense." History Prior to the creation of the Department of Transportation, its functions were administered by the under secretary of commerce for transportation. In 1965, Najeeb Halaby, administrator of the Federal Aviation Agency (predecessor to the Federal Aviation Administration, FAA), suggested to President Lyndon B. Johnson that transportation be elevated to a cabinet-level post, and that the FAA be folded into the DOT. It was established by Congress in the Department of Transportation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COMSTAC
The Commercial Space Transportation Advisory Committee (COMSTAC) is an advisory board within the US Federal Aviation Administration The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ... (FAA). COMSTAC was established in 1984 and provides information, advice, and recommendations to the FAA administrator within the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) on issues regarding the U.S. commercial space transportation industry. Goals and objectives According to the FAA website, the primary goals of COMSTAC are to: FAA COMSTAC website * Evaluate economic, technological and institutional developments within to the U.S. commercial spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-33
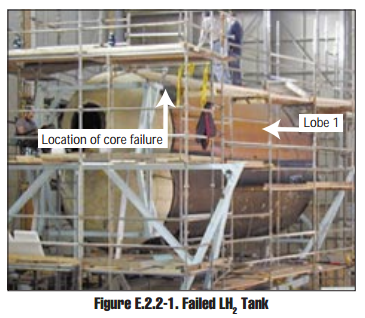
The Lockheed Martin X-33 was a proposed uncrewed, sub-scale technology demonstrator suborbital spaceplane that was developed for a period in the 1990s. The X-33 was a technology demonstrator for the VentureStar orbital spaceplane, which was planned to be a next-generation, commercially operated reusable launch vehicle. The X-33 would flight-test a range of technologies that NASA believed it needed for single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch vehicles (SSTO RLVs), such as metallic thermal protection systems, composite cryogenic fuel tanks for liquid hydrogen, the aerospike engine, autonomous (uncrewed) flight control, rapid flight turn-around times through streamlined operations, and its lifting body aerodynamics. Failures of its 21-meter wingspan and multi-lobed, composite-material fuel tank during pressure testing ultimately led to the withdrawal of federal support for the program in early 2001. Lockheed Martin has conducted unrelated testing, and has had a single success afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
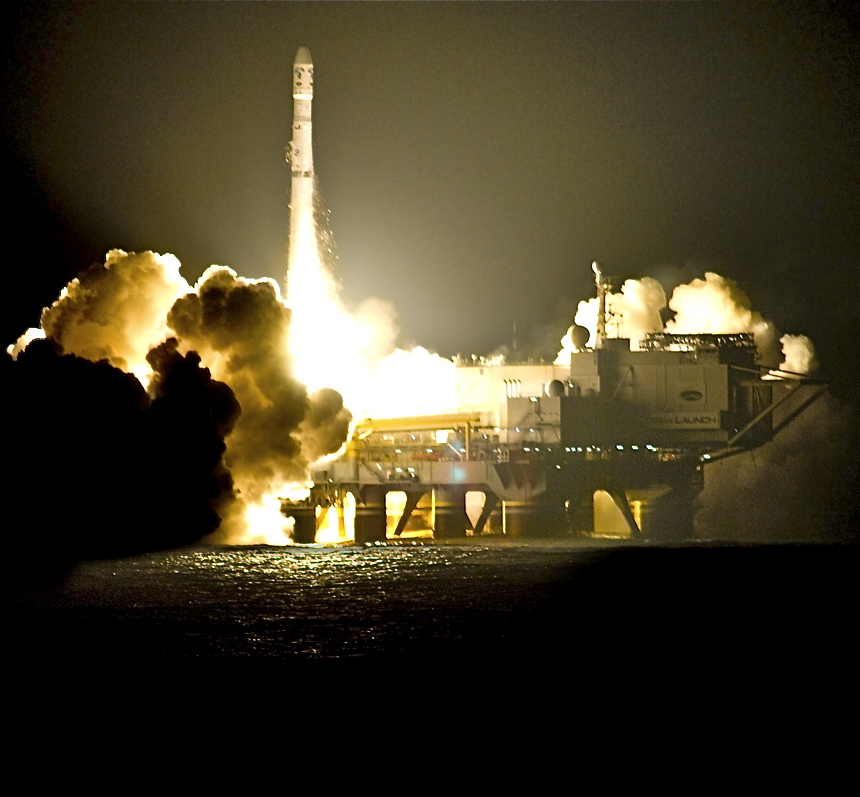
Sea Launch
Sea Launch was a multinational—Norway, Russia, Ukraine, United States—spacecraft launch company founded in 1995 that provided orbital launch services from 1999–2014. The company used a mobile maritime launch platform for equatorial launches of commercial payloads on specialized Zenit-3SL rockets from a former mobile/floating oil drilling rig renamed ''Odyssey''. By 2014, it had assembled and launched thirty-two rockets, with an additional three failures and one partial failure. All commercial payloads were communications satellites intended for geostationary transfer orbit with such customers as EchoStar, DirecTV, XM Satellite Radio, PanAmSat, and Thuraya. The approach Sea Launch LLC used was to assemble the launcher on a purpose-built ship '' Sea Launch Commander'' in Nimitz Rd., Long Beach, California, USA. The assembled spacecraft was then positioned on top of the self-propelled ''Odyssey'' floating launch platform and moved to the equatorial Pacific Ocean for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |