|
Liverpool Central Railway Station
Liverpool Central railway station in Liverpool, England, forms a central hub of the Merseyrail network, being on both the Northern Line and the Wirral Line. The station is located underground on two levels, below the site of a former mainline terminus. It is the busiest station in Liverpool, though considerably smaller than Lime Street station, the mainline terminus, and the busiest station to operate solely on the Merseyrail network. The station is the busiest underground station outside London serving 40,000 people daily. The station in passengers per platform is the busiest underground railway station in the United Kingdom outside of London at 3,979,547 per platform per annum and coming tenth out of all stations outside the capital, underground or overground. Liverpool Central is one of nine stations on the Merseyrail network to incorporate automatic ticket gates. The main concourse is part of a shopping centre, and includes a closed subway link to the former Lewis's d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population of (in ), Liverpool is the administrative, cultural and economic centre of the Liverpool City Region, a combined authority, combined authority area with a population of over 1.5 million. Established as a borough in Lancashire in 1207, Liverpool became significant in the late 17th century when the Port of Liverpool was heavily involved in the Atlantic slave trade. The port also imported cotton for the Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution, Lancashire textile mills, and became a major departure point for English and Irish emigrants to North America. Liverpool rose to global economic importance at the forefront of the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century and was home to the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
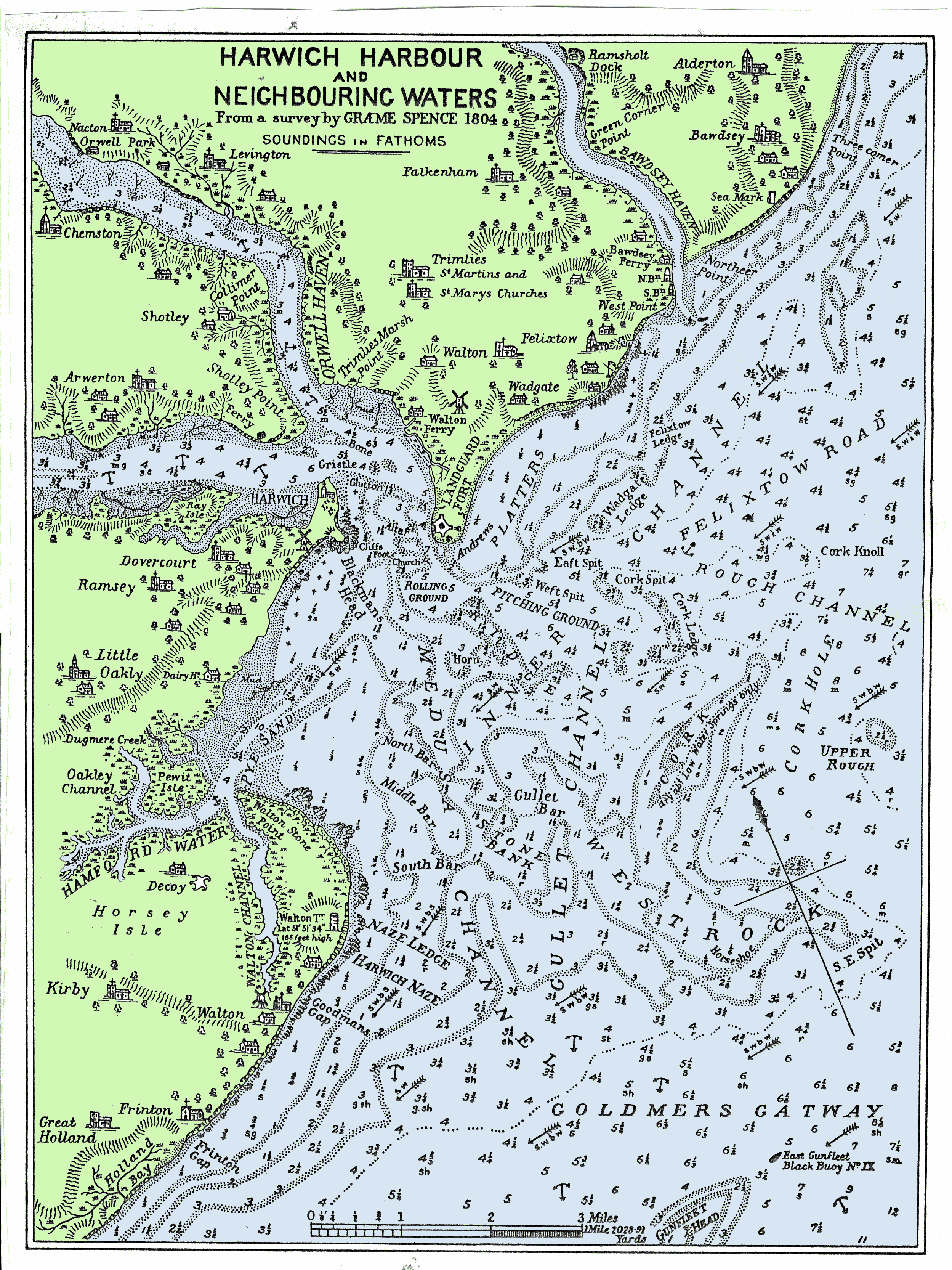
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the ''Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorfields Railway Station
Moorfields railway station is an underground railway station in the city centre of Liverpool, England. The station is situated on both the Northern and Wirral Lines of the Merseyrail network. It is the third-busiest station on the Merseyrail network, and the largest underground station. It is also the only station on the network having services to all other Merseyrail stations. History The station was built in the 1970s, as a replacement for Liverpool Exchange railway station, opening on 2 May 1977. The station was opened by British Rail and is accessed via entrances at Moorfields and on the corner of Old Hall Street and Tithebarn Street. The Old Hall Street entrance is open from only 5:30 am until 7 pm on weekdays. Services from the north had previously terminated at nearby Liverpool Exchange terminus station. The newly created north–south crossrail Northern Line runs through Moorfields. Liverpool Exchange was closed and the line extended underground to the new Moor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Line (Merseyrail)
The Northern line is one of two Commuter rail in the United Kingdom, commuter rail routes operated by Merseyrail and centred on Merseyside, England, the other being the Wirral line. The Cross-city route, cross-city route runs from in south Liverpool then (by way of an underground section through Liverpool's city centre) branches in the north to terminate at , (both Merseyside) and (Lancashire). Passenger interchange to the Wirral line is available at Moorfields railway station, Moorfields and Liverpool Central railway station, Liverpool Central, and to the separately-owned City line (Merseytravel), City line at Hunts Cross railway station, Hunts Cross and Liverpool South Parkway railway station, Liverpool South Parkway. Liverpool South Parkway also allows interchange with regional and long-distance services, while connections to services operated by Northern Trains are possible at Headbolt Lane, Ormskirk and Southport. Description The line runs from Hunts Cross railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool James Street Railway Station
Liverpool James Street (or simply James Street) is a railway station located in the centre of Liverpool, England; it is situated on the Wirral Line of the Merseyrail network. James Street is an underground station, with access to the platforms via lifts from the booking hall. At certain times, the platforms are accessed via a pedestrian tunnel from the India Buildings on Water Street, Liverpool, Water Street. As of 2013/14, James Street was the fifth-busiest station on the Merseyrail network. History The station opened as the original Liverpool terminus of the Mersey Railway Tunnel in 1886. It is accessed by lifts, and these were initially hydraulically operated. There were originally two platforms, either side of a twin-track tunnel. The Mersey railway tunnel was extended under dry land to Liverpool Central railway station, Liverpool Central station in 1892, changing James Street's status to a through station. By this time, there were trains from Liverpool branching from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkenhead
Birkenhead () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. The town is on the Wirral Peninsula, along the west bank of the River Mersey, opposite Liverpool. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic county boundaries of Cheshire, and became part of Merseyside in 1974. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the built up area as defined by the Office for National Statistics had a population of 109,835. Birkenhead Priory and the Mersey Ferry were established in the 12th century. In the 19th century, Birkenhead expanded greatly as a consequence of the Industrial Revolution, leading to a shipbuilding firm which became Cammell Laird. A Great Float, seaport was established. As the town grew, Birkenhead Park and Hamilton Square were laid out. The first street tramway in Britain was built, followed by the Mersey Railway which connected Birkenhead and Liverpool through the world's first railway tunnel beneath a tidal estuary. In the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersey Railway Tunnel
The Mersey Railway was the passenger railway connecting the communities of Liverpool and Birkenhead, England. It is currently a part of the Merseyrail network. It was extended further into the Wirral Peninsula, which lies on the opposite bank of the River Mersey to Liverpool. Both sides of the river were connected via the Mersey Railway Tunnel. The railway opened in 1886 with four stations using steam locomotives hauling unheated wooden carriages; in the next six years the line was extended with the opening of three more stations. Using the first tunnel under the Mersey, the line is the world's oldest underground railway outside London. Because the steam locomotives created a polluted atmosphere in the tunnel despite the forced ventilation system, many passengers reverted back to using the river ferries making the railway bankrupt by 1900. Recovery came after the railway adopted electric traction in 1903. The Mersey Railway remained independent after the railway grouping of 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool RJD 42
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population of (in ), Liverpool is the administrative, cultural and economic centre of the Liverpool City Region, a combined authority, combined authority area with a population of over 1.5 million. Established as a borough in Lancashire in 1207, Liverpool became significant in the late 17th century when the Port of Liverpool was heavily involved in the Atlantic slave trade. The port also imported cotton for the Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution, Lancashire textile mills, and became a major departure point for English and Irish emigrants to North America. Liverpool rose to global economic importance at the forefront of the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century and was home to the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Village, Liverpool
Central Village was a proposed shopping, leisure, commercial and residential development in Liverpool, England, United Kingdom. The complex was to cover the site of Liverpool Central railway station, and the former Lewis's department store. Planning permission was granted for the project by Liverpool City Council in May 2009, and final approval was given for construction of the entire complex to commence in February 2010. The project was never completed and the Lewis's building is now being used as offices, a hotel and a gym. Project timeline * June 2006 - Planning permission is obtained for the development. * October 2006 - The largely run-down site on which Central Village will be built is acquired by Merepark. * October 2006 - In the same month as site acquisition, funding for the project is received. * Early 2007 - Projected start date for construction, however some decisions were pending and more focus was given to the L1 development; it was delayed for a number of year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunts Cross Chord
Hunts Cross chord is a section of railway track in Liverpool that was built by the Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) to connect the LNWR's Edge Hill to Ditton Junction line with the CLC's Liverpool to Manchester Line. Mainline services between Manchester and Liverpool were diverted to Lime Street from their previous terminus at Central High Level over this connection from 5 September 1966. Train operating companies using the chord are East Midlands Railway and Northern for services between and along the CLC route. TransPennine Express TransPennine Trains Limited, trading as TransPennine Express (TPE), is a British train operating company that has operated passenger services in the TransPennine Express franchise area since May 2023. It runs regional and inter-city rail ser ... used this route until May 2018, when trains were rerouted via Newton-le-Willows. References Rail transport in Liverpool Rail junctions in England {{England-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts, also colloquially referred to as the Beeching Axe, were a major series of route closures and service changes made as part of the restructuring of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain in the 1960s. They are named for Dr. Richard Beeching, then-chair of the British Railways Board and the author of two reports''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965) that set out proposals for restructuring the railway network, with the stated aim of improving economic efficiency. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and the loss of 67,700 British Rail jobs, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |