|
LivK RNA Motif
The ''livK'' RNA motif describes a conserved RNA structure that was discovered using bioinformatics. The ''livK'' motif is detected only in the species ''Pseudomonas syringae''. It is found in the potential 5' untranslated regions (5' UTRs) of ''livK'' genes and downstream ''livM'' and ''livH'' genes, as well as the 5' UTRs of amidase genes. The ''liv'' genes are predicted to be transporters of branched-chain amino acids, i.e., leucine, isoleucine or valine Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deproton .... The specific reaction catalyzed the amidase genes is not predicted. References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, data science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term ''computational biology'' refers to building and using models of biological systems. Computational, statistical, and computer programming techniques have been used for In silico, computer simulation analyses of biological queries. They include reused specific analysis "pipelines", particularly in the field of genomics, such as by the identification of genes and single nucleotide polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Syringae
''Pseudomonas syringae'' is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathology, plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from international culture collections such as the NCPPB, International Collection of Microorganisms from Plants, ICMP, and others. ''Pseudomonas syringae'' is a member of the genus ''Pseudomonas'', and based on 16S rRNA analysis, it has been placed in the ''P. syringae'' group. It is named after the lilac tree (''Syringa vulgaris''), from which it was first isolated. A phylogenomic analysis of 494 complete genomes from the entire ''Pseudomonas'' genus showed that ''P. syringae'' does not form a monophyletic species in the strict sense, but a wider evolutionary group that also included other species as well, such as ''P. avellanae'', ''P. savastanoi'', ''P. amygdali'', and ''P. cerasi''. ''Pseudomonas syringae'' tests negative for Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5' Untranslated Region
The 5′ untranslated region (also known as 5′ UTR, leader sequence, transcript leader, or leader RNA) is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Despite its name, the 5′ UTR, or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product may involve in regulation of transcription, and translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA, such as the sex-lethal gene in ''Drosophila''. Regulatory elements within 5′ UTRs have also been linked to mRNA export. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming a complex secondary structure to regulate translation. General structure Length The 5′ UTR begins at the transcription start site and ends one nucleotide (nt) before the initiation sequence (usually AUG) of the coding region. In pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
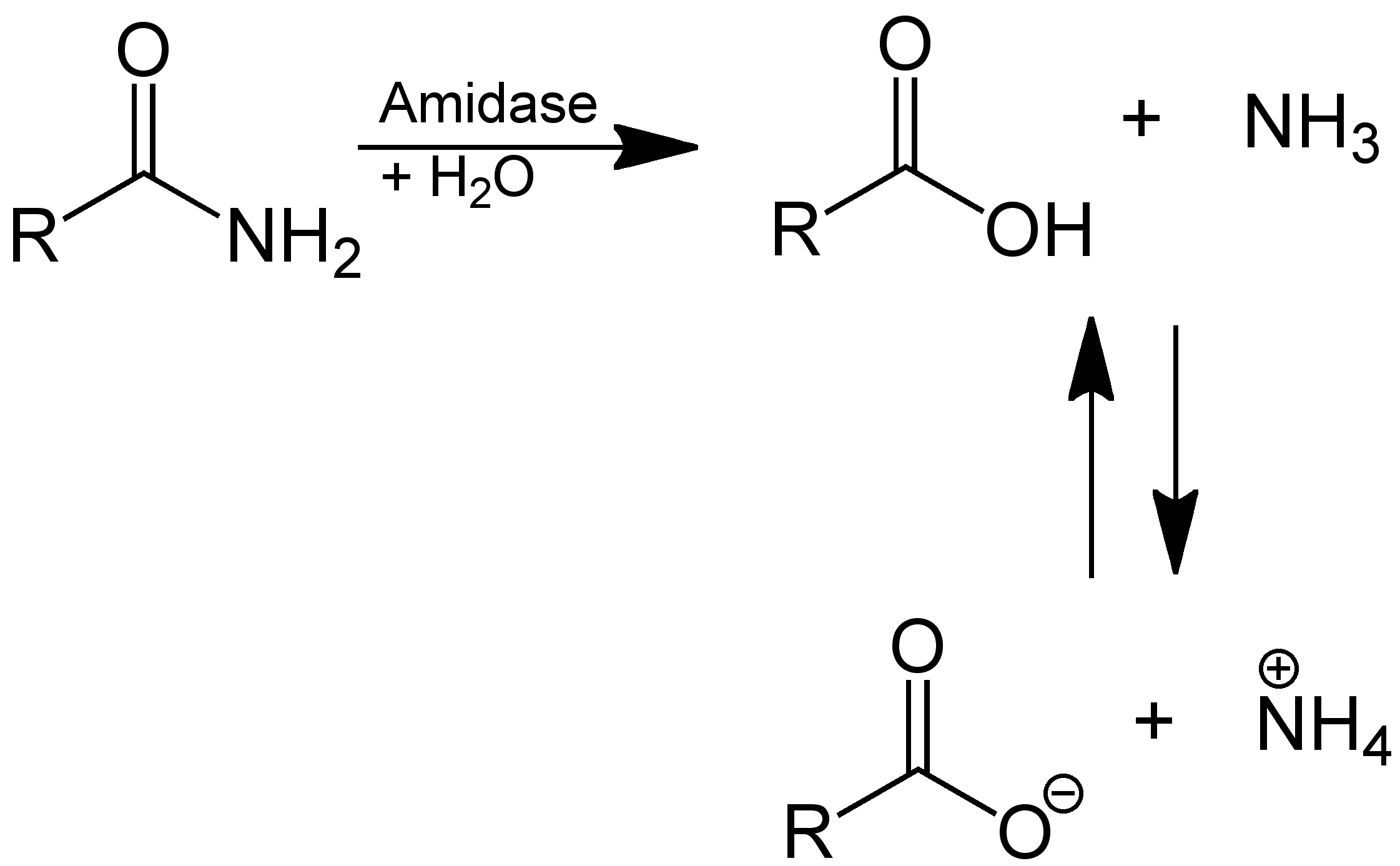
Amidase
In enzymology, an amidase (, ''acylamidase'', ''acylase (misleading)'', ''amidohydrolase (ambiguous)'', ''deaminase (ambiguous)'', ''fatty acylamidase'', ''N-acetylaminohydrolase (ambiguous)'') is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of an amide. In this way, the two substrate (biochemistry), substrates of this enzyme are an amide and water, H2O, whereas its two product (chemistry), products are monocarboxylate and ammonia, NH3. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The List of enzymes, systematic name of this enzyme class is acylamide amidohydrolase. Other names in common use include acylamidase, acylase, amidohydrolase, deaminase, fatty acylamidase, and N-acetylaminohydrolase. This enzyme participates in 6 metabolism, metabolic pathways: urea cycle and metabolism of amino groups, phenylalanine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, cyanoamino acid metabolism, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Transport Protein
A membrane transport protein is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Transport proteins are integral membrane proteins, integral transmembrane proteins; that is they exist permanently within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion, active transport, osmosis, or reverse diffusion. The two main types of proteins involved in such transport are broadly categorized as either ''channels'' or ''carriers'' (a.k.a. transporters, or permeases). Examples of channel/carrier proteins include the GLUT1, GLUT 1 uniporter, sodium channels, and potassium channels. The Solute carrier family, solute carriers and atypical SLCs are secondary active or facilitative transporters in humans. Collectively membrane transporters and channels are known as the transportome. Transportomes govern cellular i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-Carboxylic acid, carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain Isobutyl, isobutyl group, making it a Chemical polarity, non-polar Aliphatic compound, aliphatic amino acid. It is Essential amino acid, essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is genetic code, encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Leucine is named after the Greek language, Greek word for "white": ''λευκός'' (''leukós'', "white"), after its common appearance as a white powder, a property it shares with many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three other carbon atoms). It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it. Essential amino acids are necessary in the human diet. In plants isoleucine can be synthesized from threonine and methionine. In plants and bacteria, isoleucine is synthesized from a pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA. Metabolism Biosynthesis In plants and microorganisms, isoleucine is synthesized from pyruvate and alpha-ketobutyrate. This pathway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. Valine is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from dietary sources which are foods that contain proteins, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from its structural similarity to valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |