|
Liubovichi
Lyubavichi ( be, Любаві́чы; russian: Люба́вичи; yi, ליובאַװיטש, ''Lyubavitsh''; pl, Lubawicze) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a village#Russia, village) in Rudnyansky District, Smolensk Oblast, Rudnyansky District of Smolensk Oblast, Russia. History The village existed in what was the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since at least 1654. In 1784, it was mentioned as a small town,''Geographical Dictionary of the Kingdom of Poland, 1880–1914''Słownik Geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego tom V, s. 392 then a possession of the Princely Houses of Poland, Polish princely family the Lubomirski family, Lubomirski. After the Partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the village was annexed by the Russian Empire. During the French invasion of Russia in 1812, the village was occupied by Napoleonic troops for two weeks. During the reign of the Russian Empire, the village was in Orshansky Uyezd of Mogi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
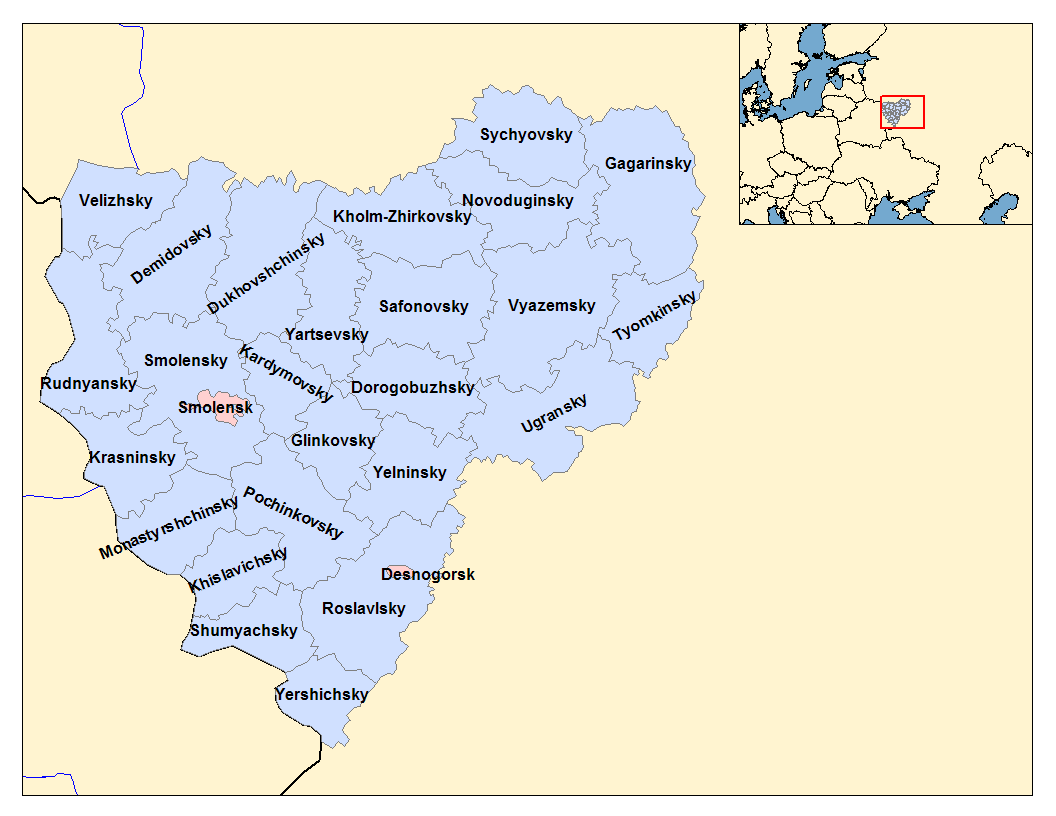
Smolensk Oblast
Smolensk Oblast (russian: Смоле́нская о́бласть, ''Smolenskaya oblast''; informal name — ''Smolenschina'' (russian: Смоле́нщина)) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative centre is the city of Smolensk. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 985,537. Geography The oblast was founded on 27 September 1937.Исполнительный комитет Смоленского областного совета народных депутатов. Государственный архив Смоленской области. "Административно-территориальное устройство Смоленской области. Справочник", изд. "Московский рабочий", Москва 1981. Стр. 8 It borders Pskov Oblast in the north, Tver Oblast in the northeast, Moscow Oblast in the east, Kaluga Oblast in south, Bryansk Oblast in the southwest, and Mogilev and Vitebsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Weddings, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display. Synagogues are consecrated spaces used for the purpose of Jewish prayer, study, assembly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of the North Caucasus. The southwestern suburbs of the city lie above the Don river delta. Rostov-on-Don has a population of over one million people, and is an important cultural centre of Southern Russia. History Early history From ancient times, the area around the mouth of the Don River has held cultural and commercial importance. Ancient indigenous inhabitants included the Scythian and Sarmatian tribes. It was the site of Tanais, an ancient Greek colony, Fort Tana under the Genoese, and Fort Azak in the time of the Ottoman Empire. In 1749, a custom house was established on the Temernik River, a tributary of the Don, by edict of the Empress Elizabeth, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
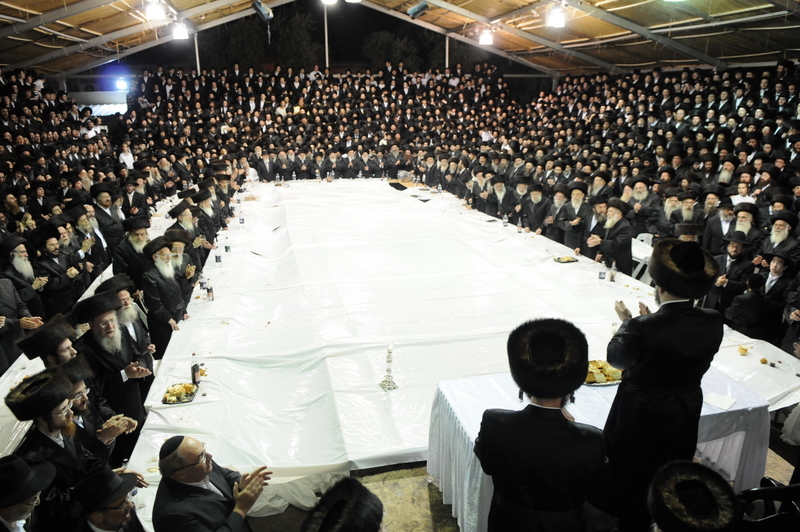
Tomchei Temimim
Tomchei Tmimim ( he, תומכי תמימים, "supporters of the complete-wholesome ones") is the central Yeshiva (Talmudical academy) of the Chabad-Lubavitch Hasidic movement. Founded in 1897 in the town of Lubavitch by Rabbi Sholom Dovber Schneersohn, it is now an international network of institutions of advanced Torah study, the United Lubavitcher Yeshivoth. History As above, Tomechei Tmimim was founded in 1897 in Lubavitch, by Rabbi Sholom DovBer Schneersohn for the study of Hasidic philosophy according to the Chabad tradition, in parallel with the traditional Yeshiva curriculum. Here, Rabbi Schneersohn authore''Kuntres Eitz HaChayim'' guidelines and standards for a student's learning goals and schedule, personal conduct, prayer, and appearance. Correspondingly, he called the students of this yeshiva "''tmimim''" (sing. "''tomim''" תמים = pure, perfect). When Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn left the Soviet Union in 1927, the yeshiva reestablished itse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sholom Dovber Schneersohn
Sholom Dovber Schneersohn ( he, שלום דובער שניאורסאהן) was the fifth Rebbe (spiritual leader) of the Chabad Lubavitch chasidic movement. He is known as "the Rebbe Rashab" (for Reb Sholom Ber). His teachings represent the emergence of an emphasis on outreach that later Chabad Rebbes developed into a major theme. Life Early life Schneersohn was born in Lubavitch, on 20 Cheshvan 5621 (24 October, 1860), the second son of Shmuel Schneersohn, the fourth Chabad ''Rebbe''.''Encyclopedia of Hasidim, entry: Schneersohn, Shalom Dovber''. Naftali Lowenthal. Aronson, London 1996. In 1882, when his father died, he was not quite 22 years old, and his brother Reb Zalman Aharon was not much older. A period followed, during which both brothers fulfilled some of the tasks of a rebbe, but neither felt ready to take on the title and responsibilities. Over this period he gradually took on more responsibilities, particularly in dealing with the impact of the May Laws regarding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shmuel Schneersohn
Shmuel Schneersohn (or Rabbi Shmuel of Lubavitch or The Rebbe Maharash) (29 April 1834 – 14 September 1882 OS) was an Orthodox rabbi and the fourth Rebbe (spiritual leader) of the Chabad Lubavitch Chasidic movement. Biography Shmuel Schneersohn was born in Lyubavichi, on 2 Iyar 5594 (1834), the seventh son of Menachem Mendel Schneersohn. He faced competition from three of his brothers, primarily from Yehuda Leib Schneersohn who established a dynasty in Kapust upon their father's death. Other brothers also established dynasties in Lyady, Nizhyn, and Ovruch. In 1848, Schneersohn was married to the daughter of his brother, Chaim Shneur Zalman Schneersohn. After several months she died, and he then married Rivkah, a granddaughter of his own grandfather Dovber Schneuri. He had three sons, Zalman Aharon, Shalom Dovber, and Menachem Mendel, as well as one daughter, Devorah Leah. Schneersohn was said to have had chariots on call for the evacuation of books in time of fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menachem Mendel Schneersohn
Menachem Mendel Schneersohn (September 9, 1789 – March 17, 1866) also known as the Tzemach Tzedek (Hebrew: "Righteous Sprout" or "Righteous Scion") was an Orthodox rebbe, leading 19th-century posek, and the third rebbe (spiritual leader) of the Chabad Lubavitch Hasidic movement. Biography Menachem Mendel Schneersohn was born in Liozna, on September 9, 1789. His mother Devorah Leah died just three years later, and her father Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi raised him as his own son. He married his first cousin Chaya Mushka Schneersohn, daughter of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri. After his father-in-law/uncle's death, and a three-year interregnum during which he tried to persuade the Hasidim to accept his brother-in-law Menachem-Nachum Schneuri or his uncle Chaim-Avraham as their leader, he assumed the leadership of Lubavitch on the eve of Shavuot 5591 (May 5, 1831 OS). He was known as the Tzemach Tzedek after the title of a voluminous compendium of Halakha (Jewish law) that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyady, Vitebsk Region
Lyady ( be, Ляды́, russian: Ляды) is a hamlet in the Dubrovna District of Vitebsk Region, Belarus adjacent to the Belarus–Russia border. History Lyady was founded in the 17th century. It was located on the road connecting Moscow and Warsaw. It is located near the Mereya River, once the border between Russia and Poland and later between the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. Jewish population Lyady used to have a predominantly Jewish population. It was the center of Chabad chasidism for over a decade. The first rebbe Shneur Zalman of Liadi settled there at the invitation of Prince Stanisław Lubomirski, voivode of the town, after his second imprisonment in 1800. He left the town in 1812, fleeing the French Invasion under Napoleon. After the German occupation of Belarus in the Second World War, the town's Jews were gathered into a ghetto. On April 2, 1942, the Germans and collaborators killed more than 2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovber Schneuri
Dovber Schneuri (13 November 1773 – 16 November 1827 OS) was the second Rebbe (spiritual leader) of the Chabad Lubavitch Chasidic movement. Rabbi Dovber was the first Chabad rebbe to live in the town of Lyubavichi (in present-day Belarus), the town for which this Hasidic dynasty is named. He is also known as the Mitteler Rebbe ("Middle Rebbe" in Yiddish), being the second of the first three generations of Chabad leaders. Biography Rabbi Schneuri was born in Liozna, modern day Belarus, on 9 Kislev 5534. His father, Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi, was Rebbe of the community there, and of many Chassidim in White Russia and Lithuania, and other parts of Russia. His father named him after his own teacher, Rabbi Dov Ber of Mezeritch, a disciple and successor of the Baal Shem Tov, the founder of the Chassidic movement. The Yiddish first name דוב-בער ''Dov-Ber'' literally means "bear-bear", traceable back to the Hebrew word דב ''dov'' "bear" and the German word ''Bär'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebbe
A Rebbe ( yi, רבי, translit=rebe) or Admor ( he, אדמו״ר) is the spiritual leader in the Hasidic movement, and the personalities of its dynasties.Heilman, Samuel"The Rebbe and the Resurgence of Orthodox Judaism."''Religion and Spirituality (Audio)''. UCTV, 20 Oct 2011. web. 31 Jul 2013. The titles of Rebbe and Admor, which used to be a general honor title even before the beginning of the movement, became, over time, almost exclusively identified with its Tzaddikim. Terminology and origin Usage Today, ''rebbe'' is used in the following ways: # Rabbi, a teacher of Torah – Yeshiva students or '' cheder'' (elementary school) students, when talking to their teacher, would address him with the honorific ''Rebbe'', as the Yiddish-German equivalent to the Hebrew word ''rabbi'' ( ' ). # Personal mentor and teacher—A person's main Rosh Yeshiva, Yeshiva teacher, or mentor, who teaches him or her Talmud and Torah and gives religious guidance, is referred to as ''rebbe' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contemporary Western Ukraine during the 18th century, and spread rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most affiliates reside in Israel and the United States. Israel Ben Eliezer, the " Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members adhere closely both to Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the traditions of Eastern European Jews. Many of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Hasidic thought draws heavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chabad-Lubavitch
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (), is an Orthodox Jewish Hasidic dynasty. Chabad is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, particularly for its outreach activities. It is one of the largest Hasidic groups and Jewish religious organizations in the world. Unlike most Haredi groups, which are self-segregating, Chabad operates mainly in the wider world and caters to secularized Jews. Founded in 1775 by Rabbi Schneur Zalman of Liadi, the name "Chabad" () is an acronym formed from three Hebrew words— (the first three sephirot of the kabbalistic Tree of Life) (): "Wisdom, Understanding, and Knowledge"—which represent the intellectual and kabbalistic underpinnings of the movement. The name Lubavitch derives from the town in which the now-dominant line of leaders resided from 1813 to 1915. Other, non-Lubavitch scions of Chabad either disappeared or merged into the Lubavitch line. In the 1930s, the sixth Rebbe of Chabad, Rabbi Yosef Yitzcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
2.jpg)






