|
Liu Xuan (Three Kingdoms)
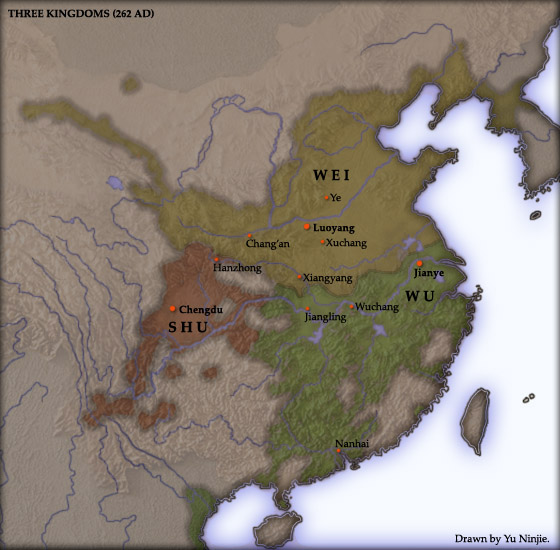
Liu Xuan (224–264), courtesy name Wenheng, was a prince of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. He was the eldest son of Liu Shan, the second and last ruler of Shu. His mother was Consort Wang (王貴人), a former servant of Liu Shan's first wife Empress Jing'ai; Lady Wang later became one of Liu Shan's concubines. Liu Xuan became crown prince in 238. After the fall of Shu to the rival state of Wei, Liu Xuan and his surviving brothers returned to the capital, Chengdu. In 264, Liu Xuan was killed in Chengdu by rebelling soldiers during Zhong Hui's rebellion.''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', chapter 34, p. 908. See also * Lists of people of the Three Kingdoms The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of ... * Shu Han family trees Notes Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife of the person styled crown prince. ''Crown prince'' as a descriptive term has been used throughout history for the prince who is first-in-line to a throne and is expected to succeed (i.e. the heir apparent), barring any unforeseen future event preventing this. In certain monarchies, a more specific substantive title may be accorded and become associated with the position of ''heir apparent'' (e.g. Prince of Wales in the United Kingdom or Prince of Asturias in the Spain, Kingdom of Spain). In these monarchies, the term crown prince may be used less often than the substantive title (or never). Until the late twentieth century, no modern monarchy adopted a system whereby females would be guaranteed to succeed to the throne (i.e. absolute pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The '' Records of the Grand Historian'', '' Book of Han'' and ''Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
224 Births
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han Imperial Princes
Shu may refer to: China * Sichuan, China, officially abbreviated as Shu (蜀) * Shu (state) (conquered by Qin in 316 BC), an ancient state in modern Sichuan * Shu Han (221–263) during the Three Kingdoms Period * Western Shu (405–413), also known as Qiao Shu, a state founded by Qiao Zong during the Eastern Jin Dynasty * Former Shu (907–925) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Later Shu (934–965) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shū'' 書) People * Shu, the guitarist in the Japanese rock band, BACK-ON * Shu (surname), Chinese surname 舒 * Frank Shu (born 1943), Chinese-American professor of astronomy * Quan-Sheng Shu, American physicist *, Japanese footballer * Will Shu (born 1979), American businessman, the co-founder and CEO of Deliveroo Fictional characters * Shu, in the Xbox 360 game ''Blue Dragon'' * Shu, in the '' Dragon Ball'' franchise * Shu (''Suikoden''), in the video game ''Suikoden II'' * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han Family Trees
This article contains the family trees of members of the Liu clan, who ruled the state of Shu Han (221-263) in the Three Kingdoms period (220-280) in China. They were related to the House of Liu, the imperial clan of the Han dynasty. Liu Bei's ancestors Liu Bei's biography in the ''Sanguozhi'' stated that Liu Bei was a descendant of Liu Sheng (Prince of Zhongshan), who was a son of Emperor Jing. Liu Sheng's son was Liu Zhen. However, the ''Dianlue'' claimed that Liu Bei descended from the Marquis of Linyi. Based on historical records in the ''Han Shu'' and the ''Houhanshu'', there were two Marquis of Linyi lineages which could be traced to Emperor Jing's sons, hence there were another two lines from which Liu Bei could have possibly descended. The central line in the family tree below shows the Liu Sheng lineage, while the other two show the Marquis of Linyi lineages. Liu Bei Liu Bei's father was Liu Hong. Liu Hong's father was Liu Xion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Notes The states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu were officially established in 220, 221, and 229 respectively. Therefore, certain people in the list who died before these years have their respective lords' names, in place of either of the three states, listed in the allegiance column. Take Guan Yu for example — he died before Liu Bei Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhong Hui's Rebellion
Zhong Hui's Rebellion was a rebellion in March 264 led by Zhong Hui, a general of the state of Cao Wei, against the Wei regent, Sima Zhao. Zhong Hui had support from Jiang Wei, a general from the former state of Shu Han, which was conquered by Wei forces just before the rebellion started. Zhong Hui, as one of the Wei commanders in the Conquest of Shu by Wei, had considered himself capable enough to overcome the Wei regime and establish his own kingdom in the newly conquered Shu territory.Alan Kam-Leung Chan, National University of Singapore. http://www.iep.utm.edu/zhonghui/#H1 The rebellion ended when some Wei officers and soldiers, who were unwilling to join Zhong Hui, started a mutiny against him and killed him and Jiang Wei. Background Initially, when Sima Zhao wanted to put Zhong Hui in charge of leading the Wei army to conquer Shu, Shao Ti warned him that Zhong Hui might rebel against Wei because he was in command of an army of thousands, was single, and had no family to wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhong Hui
Zhong Hui (225 – 3 March 264), courtesy name Shiji, was a Chinese calligrapher, essayist, military general, and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was the younger son of Zhang Changpu with Zhong Yao, who served as the Grand Tutor in the Wei imperial court. He was already known for being insightful, intelligent and knowledgeable since he was young. Zhong Hui rose to prominence in the 250s when he became a close aide to Sima Zhao, the regent and ''de facto'' ruler of Wei. He advised Sima Zhao on how to deal with the Third Rebellion in Shouchun from 257–258 and was highly regarded by the latter. With Sima Zhao's help, Zhong Hui steadily moved up the ranks and became one of the key figures in the Wei government. In 263, the Wei imperial court ordered Zhong Hui, Deng Ai and Zhuge Xu to lead separate armies to attack and conquer Wei's rival state, Shu Han. During and after the campaign against Shu, Zhong Hui framed Zhuge Xu and De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei (Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < Middle Chinese: *''ŋjweiC'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter Luoyang, the state was established by [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Shu By Wei
The Conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the dynastic state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in late 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu Han and the tripartite equilibrium maintained in China proper for over 40 years since the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty in 220. The conquest laid the foundation for an eventual reunified China proper under the Jin dynasty (266–420)#Western Jin (266–316), Western Jin dynasty in 280. Background Following the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Eastern Han dynasty in 220, three contending states emerged in China and fought for control over the territories of the former Han Empire. Among the three, Cao Wei, Wei was the most powerful one in terms of military prowess, economic resources, manpower and geographical size. The other two, Shu Han, Shu and Eastern Wu, Wu, reestablished their alliance against Wei in 223. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife of the person styled crown prince. ''Crown prince'' as a descriptive term has been used throughout history for the prince who is first-in-line to a throne and is expected to succeed (i.e. the heir apparent), barring any unforeseen future event preventing this. In certain monarchies, a more specific substantive title may be accorded and become associated with the position of ''heir apparent'' (e.g. Prince of Wales in the United Kingdom or Prince of Asturias in the Spain, Kingdom of Spain). In these monarchies, the term crown prince may be used less often than the substantive title (or never). Until the late twentieth century, no modern monarchy adopted a system whereby females would be guaranteed to succeed to the throne (i.e. absolute pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period (220–280). The state was based in the area around present-day Hanzhong, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou, and north Guangxi, an area historically referred to as "Shu" based on the name of the past Shu (state), ancient state of Shu, which also occupied this approximate geographical area. Its core territory also coincided with Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang's Emperor Gaozu of Han#King of Han, Kingdom of Han, the precursor of the Han dynasty. Shu Han's founder, Liu Bei, had named his state "Han", as he considered it a rump state of the Han dynasty and thus the legitimate successor to the Han throne, while the prefix "Shu" was first used by the rival state of Cao Wei to delegitimize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)