|
Little Switzerland (landscape)
A little Switzerland or ''Schweiz'' is a landscape, often of wooded hills. This Romantic aesthetic term is not a geographic category, but was widely used in the 19th century to connote dramatic natural scenic features that would be of interest to tourists. Since it was ambiguous from the very beginning, it was flexibly used in travel writing to imply that a landscape had some features, though on a much smaller scale, that might remind a visitor of Switzerland. Rock outcrops The original generic term was applied to dozens of locations in Europe, the bulk of them German-speaking, as well as to other parts of the world, to direct attention to rock outcrops that stand out, usually amid steep forest. The original, 18th-century comparison was usually with the fissured crags of the Jura Mountains on the Franco-Swiss border which hardly rise higher than 1700 metres. Histories of Saxon Switzerland (''Sächsische Schweiz'') in Saxony, Germany, assert that the landscape description ''sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the physical elements of geophysically defined landforms such as (ice-capped) mountains, hills, water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and the sea, living elements of land cover including indigenous vegetation, human elements including different forms of land use, buildings, and structures, and transitory elements such as lighting and weather conditions. Combining both their physical origins and the cultural overlay of human presence, often created over millennia, landscapes reflect a living synthesis of people and place that is vital to local and national identity. The character of a landscape helps define the self-image of the people who inhabit it and a sense of place that differentiates one region from other regions. It is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrad Malte-Brun
Conrad Malte-Brun (12 August 177514 December 1826), born Malthe Conrad Bruun, and sometimes referred to simply as Malte-Brun, was a Dano-French geographer and journalist. His second son, Victor Adolphe Malte-Brun, was also a geographer. Today he is perhaps best remembered for coining the name for the geographic region Oceania (French ''Océanie'') around 1812, he also coined the name Indo-China. Biography Born in Thisted to an administrator of Danish crown lands, Malte-Brun was originally destined for a career as a pastor, but chose instead to attend classes at the University of Copenhagen, and became a supporter of the French Revolution and an activist in favor of freedom of the press. Following the harsh censorship laws instituted by the Danish ruler crown prince Frederick in September 1799, he was indicted because of his many pamphlets which contained outright criticism of the government, which the new censorship laws forbade. A particular cause for offence was a pamphlet he p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohburg Switzerland
The Hohburg Hills (german: Hohburger Berge), also called Hohburg Switzerland (''Hohburger Schweiz''), are located in the district of Nordsachsen near the eponymous village of Hohburg in the municipality of Lossatal in the German state of Saxony. Geography These quartz-porphyry hills rise prominently up to 120 metres out of the surround plain of the Leipzig Bay, east of the River Mulde. Their highest point is the Löbenberg at (). Other high points are the Gaudlitzberg (), the Burzelberg () and the Galgenberg ("Gallows Hill", ). South of Hohburg is the Kleine Berg ("Little Hill") with a height of . In the valley lying amongst the Hohburg Hills, the stream of the Lossabach flows through Müglenz, Hohburg, Klein- and Großzschepa to empty into the Mulde near Thallwitz. History The Hohburg Hills were shaped by decades of intensive stone quarrying. This produced steep rock faces and several lakes in the hollows that were left behind. The rock faces, up to forty meters high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
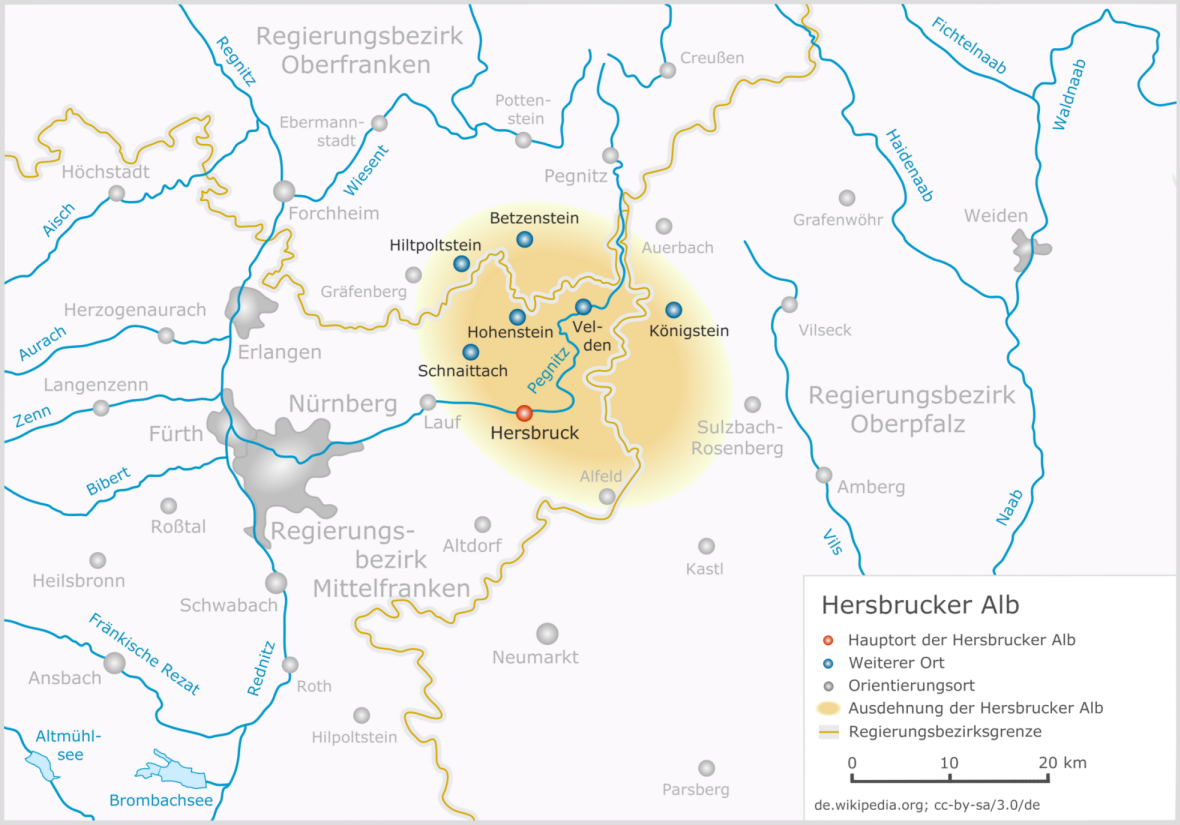
Hersbruck Switzerland
The Hersbrucker Alb ("Hersbruck Jura") – also called ''Hersbrucker Schweiz'' ("Hersbruck Switzerland") or ''Pegnitz-Alb'' ("Pegnitz Jura") – is the northeastern part of the Franconian Jura near the town of Hersbruck. The River Pegnitz and its tributaries flow through the region. Location In the west the Hersbrucker Alb reaches the valley of the Schnaittach. It is bounded by the course of the Pegnitz and Hiltpoltstein to the west, Betzenstein to the north, Auerbach in der Oberpfalz and Sulzbach-Rosenberg to the east and Alfeld (Mittelfranken) to the south. Much of it lies within the Bavarian provinces of Middle Franconia and the Upper Palatinate; a small part is in Upper Franconia. The Hersbrucker Alb is formed from the White Jura platform of hard, brittle and karstified massive and Corallian Limestones and the Franconian dolomite together with their more recent depositions. Numerous cave A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geest
Geest is a type of landform, slightly raised above the surrounding countryside, that occurs on the plains of Northern Germany, the Northern Netherlands and Denmark. It is a landscape of sandy and gravelly soils formed as a glacial outwash plain and now usually mantled by a heathland vegetation on the glacial deposits left behind after the last ice age during the Pleistocene epoch.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, p. 214. . The term ''geest'' is a substantivisation of the Low German adjective ''güst'', which means "dry and infertile". It is an Old Drift landscape, characterised by the sandy depositions of the Ice Age. In the depressions between the raised flats are wet meadows and, where drainage is poor, bogs. Geest lands are made up of moraines and sandurs. They are almost always next to flat marshlands, the geest being higher and better protected against flood but, compared to the marsh, with poor soil for agriculture. Where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen Switzerland
Bremen Switzerland (german: Bremer Schweiz; Northern Low Saxon: ''Bremer Swiez'') is an undulating geest landscape in the north of Bremen (Bremen Nord) and the adjacent district of Osterholz, and forms the western portion of the Osterholz Geest. In comparison to the rather flat land on which the city of Bremen is built and its surrounding area which is built on marsh and bog, Bremen Switzerland reaches heights of up to about . The region of the ''Bremen Switzerland'' is framed by the Weser tributary of Lesum to the south, the Weser to the west, the marsh region of Osterstade to the northwest, the forest of ''Düngel'' to the north ( Garlstedt-Meyenburg line), the former B 6 federal route to Bremerhaven (now the L135) to the east and the adjoining heath of ''Lange Heide''. Bremen Switzerland is divided into nature reserves, meadows, woods, heathland and depressions like the Ihle valley and the valleys of the Schönebecker Aue, the Blumenthaler Aue and the Beckedorfer Beeke. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Switzerland
Bohemian Switzerland ( cs, České Švýcarsko; german: Böhmische Schweiz), also known as Czech Switzerland, is a picturesque region in the north-western Czech Republic. It has been a protected area (as Elbe Sandstone Mountains Protected Landscape Area) since 1972. The region along the right side of the Elbe became a national park on 1 January 2000, the Bohemian Switzerland National Park. The National Park is adjacent to the Saxon Switzerland National Park in Germany. Etymology The concept of Bohemian Switzerland developed in the 18th century as an extension of the Saxon Switzerland, the part of the Elbe Sandstone Mountains in Germany. The name was inspired by the Swiss artists Adrian Zingg and Anton Graff, who were reminded of their homeland by the geography of northern Bohemia. Geography Bohemian Switzerland lies on the Czech side of the Elbe Sandstone Mountains north of Děčín, on both banks of the Elbe River. It extends eastward into the Lusatian Mountains and westward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlaken
, neighboring_municipalities= Bönigen, Därligen, Matten bei Interlaken, Ringgenberg, Unterseen , twintowns = Scottsdale (USA), Ōtsu (Japan), Třeboň (Czech Republic) Interlaken (; lit.: ''between lakes'') is a Swiss town and municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Bern. It is an important and well-known tourist destination in the Bernese Oberland region of the Swiss Alps, and the main transport gateway to the mountains and lakes of that region. The town is located on flat alluvial land called Bödeli between two lakes, Brienz to the east and Thun to the west, and alongside the river Aare, which flows between them. Transport routes to the east and west alongside the lakes are complemented by a route southwards into the near mountain resorts and high mountains, e.g. the famous high Alpine peaks of Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau, following upwards the Lütschine. Interlaken is the central town of a Small Agglomeration with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburgische Schweiz
Mecklenburgische Schweiz is an ''Amt'' in the district of Rostock, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. The seat of the ''Amt'' is in Teterow Teterow () is a town of Germany, in the district of Rostock, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. It is the geographical center of this federal state. It had a population of 8,852 in 2011. History The ''Stadtkirche St. Peter und Paul'' (St. Pete ..., itself not part of the ''Amt''. The ''Amt'' Mecklenburgische Schweiz consists of the following municipalities: References Ämter in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania Rostock (district) {{LandkreisRostock-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holstein Switzerland
Holstein Switzerland (german: Holsteinische Schweiz) is a hilly area with a patchwork of lakes and forest in Schleswig Holstein, Germany, reminiscent of Swiss landscape. Its highest point is the Bungsberg (168 metres above sea level).Carl Ingwer Johannsen & Eckardt Opitz: ''Das grosse Schleswig-Holstein-Buch.'' Hamburg 1996 It is a designated nature park as well as an important tourist destination in Northern Germany situated between the cities of Kiel and Lübeck. Geography Holstein Switzerland lies in eastern Schleswig-Holstein. This picturesque region in the historical county of Wagria has no precise political or geographic boundaries. Most of the area falls within the districts of Ostholstein and Plön, roughly between the cities of Lübeck and Kiel and extends as far north as the Baltic coast. Its major towns include Bad Malente-Gremsmühlen, Lütjenburg, Oldenburg in Holstein, Preetz and the old ''Residenz'' seats of Eutin and Plön. The charm of this region is its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plön Panorama Ploener See
Plön (; Holsatian: ''Plöön'') is the district seat of the Plön district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, and has about 8,700 inhabitants. It lies right on the shores of Schleswig-Holstein's biggest lake, the Great Plön Lake, as well as on several smaller lakes, touching the town on virtually all sides. The town's landmark is Plön Castle, a chateau built in the 17th century on a hill overlooking the town. Plön has a grammar school with a 300-year history, and is home to a German Navy non-commissioned officer school and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology. The town, nestled as it is in the hilly, wooded lake district of Holstein Switzerland (''Holsteinische Schweiz''), also has importance in the tourism industry. History In the course of the Migration Period, Slavic tribes entered the region of Plön during the early 7th century following the withdrawal of the original Germanic population. On the large island opposite Plön, which was later called ''Olsbor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Mountain Art
White Mountain art is the body of work created during the 19th century by over four hundred artists who painted landscape scenes of the White Mountains of New Hampshire in order to promote the region and, consequently, sell their works of art. In the early part of the 19th century, artists ventured to the White Mountains of New Hampshire to sketch and paint. Many of the first artists were attracted to the region because of the 1826 tragedy of the Willey family, in which nine people lost their lives in a mudslide. These early works portrayed a dramatic and untamed mountain wilderness. Dr. Robert McGrath describes a Thomas Cole (1801–1848) painting titled ''Distant View of the Slide that Destroyed the Willey Family'' thus: "... an array of broken stumps and errant rocks, together with a gathering storm, suggest the wildness of the site while evoking an appropriate ambient of darkness and desolation". The images stirred the imagination of Americans, primarily from the large ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |