|
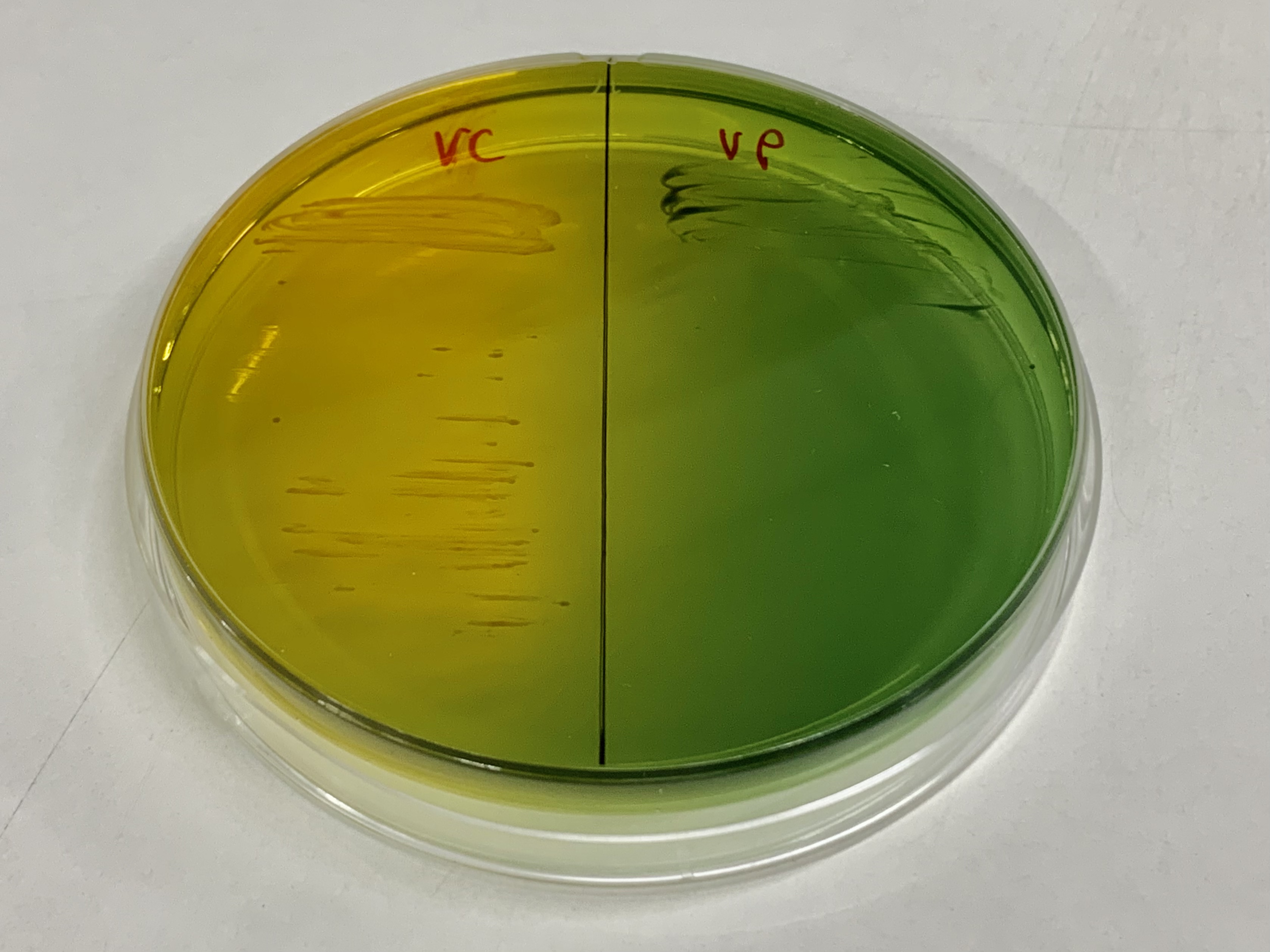
Listonella Pelagia
''Listonella'' is a genus of Gram-negative marine bacteria in the family Vibrionaceae named after the American microbiologist J. Liston. Analysis of phylogenetic, genomic and phenotypic data has shown the genus is not distinct from the genus ''Vibrio ''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, which have a characteristic curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection or soft-tissue infection called Vibriosis. Infection is commonly associated with eati ...'', so it is now considered a synonym of ''Vibrio''.(Thompson et al. 2011 doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.030015-0) References Vibrionales Bacteria genera {{Gammaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listonella Anguillarum
''Listonella anguillarum'' is a Gram-negative marine bacterium in the family Vibrionaceae The Vibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota given their own order, Vibrionales. Inhabitants of fresh or salt water, several species are pathogenic, including the type species ''Vibrio cholerae'', which is the agent responsible for cholera. Mo .... The correct nomenclature for this bacterium is Vibrio anguillarum. References Vibrionales {{gammaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listonella Pelagia
''Listonella'' is a genus of Gram-negative marine bacteria in the family Vibrionaceae named after the American microbiologist J. Liston. Analysis of phylogenetic, genomic and phenotypic data has shown the genus is not distinct from the genus ''Vibrio ''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, which have a characteristic curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection or soft-tissue infection called Vibriosis. Infection is commonly associated with eati ...'', so it is now considered a synonym of ''Vibrio''.(Thompson et al. 2011 doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.030015-0) References Vibrionales Bacteria genera {{Gammaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner ( cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Bacteria
Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain. Prokaryotes play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers recycling nutrients. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic, causing disease and even death in plants and animals. Marine prokaryotes are responsible for significant levels of the photosynthesis that occurs in the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrionaceae
The Vibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota given their own order, Vibrionales. Inhabitants of fresh or salt water, several species are pathogenic, including the type species ''Vibrio cholerae'', which is the agent responsible for cholera. Most bioluminescent bacteria belong to this family, and are typically found as symbionts of deep-sea animals. Vibrionaceae are Gram-negative organisms and facultative anaerobes, capable of fermentation. They contain oxidase and have one or more flagella, which are generally polar. Originally, these characteristics defined the family, which was divided into four genera. Two of these, ''Vibrio'' and '' Photobacterium'', correspond to the modern group, although several new genera have been defined. Genetic studies have shown the other two original members—''Aeromonas'' and '' Plesiomonas''—belong to separate families. The family Vibrionaceae currently comprises eight validly published genera: ''Aliivibrio'', ''Catenococcus'', ''En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, which have a characteristic curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection or soft-tissue infection called Vibriosis. Infection is commonly associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive in freshwater, ''Vibrio'' spp. are commonly found in various salt water environments. ''Vibrio'' spp. are facultative anaerobes that test positive for oxidase and do not form spores. All members of the genus are motile. They are able to have polar or lateral flagellum with or without sheaths. ''Vibrio'' species typically possess two chromosomes, which is unusual for bacteria. Each chromosome has a distinct and independent origin of replication, and are conserved together over time in the genus. Recent phylogenies have been constructed based on a suite of genes (multilocus sequence analysis). O. F. Müller (1773, 1786) described eight species of the genus ''Vibrio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrionales
The Vibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota given their own order, Vibrionales. Inhabitants of fresh or salt water, several species are pathogenic, including the type species ''Vibrio cholerae'', which is the agent responsible for cholera. Most bioluminescent bacteria belong to this family, and are typically found as symbionts of deep-sea animals. Vibrionaceae are Gram-negative organisms and facultative anaerobes, capable of fermentation. They contain oxidase and have one or more flagella, which are generally polar. Originally, these characteristics defined the family, which was divided into four genera. Two of these, ''Vibrio'' and '' Photobacterium'', correspond to the modern group, although several new genera have been defined. Genetic studies have shown the other two original members—''Aeromonas'' and '' Plesiomonas''—belong to separate families. The family Vibrionaceae currently comprises eight validly published genera: ''Aliivibrio'', ''Catenococcus'', ''En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |