|
Listeria
''Listeria'' is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. As of 2024, 28 species have been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pioneer of sterile surgery Joseph Lister. ''Listeria'' species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, and do not produce endospores. The major human pathogen in the genus is '' L. monocytogenes''. Although ''L. monocytogenes'' has low infectivity, it is hardy and can grow in a refrigerator temperature of 4 °C (39.2 °F) up to the human body temperature of 37 °C (98.6 °F). [No longer accessible. Archived version availablhere] It is the usual cause of the relatively rare bacterial disease listeriosis, an infection caused by eating foodborne illness, food contaminated with the bacteria. The overt form of the disease has a case-fatality rate of around 20–30%. Listeriosis can cause serious illness in pregnant women, newborns, adults with weakened immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
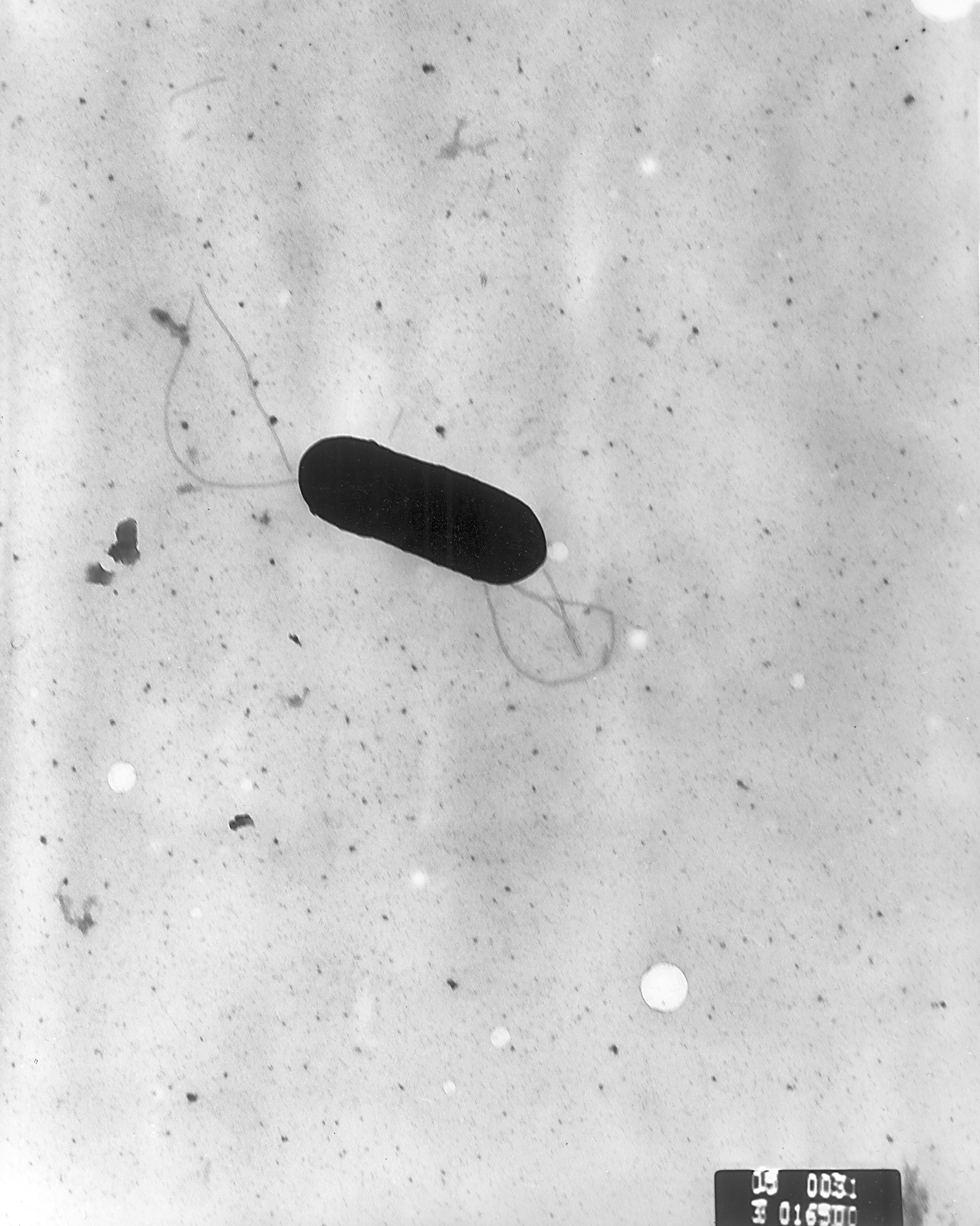
Listeria Monocytogenes PHIL 2287 Lores
''Listeria'' is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. As of 2024, 28 species have been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pioneer of sterile surgery Joseph Lister. ''Listeria'' species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, and do not produce endospores. The major human pathogen in the genus is '' L. monocytogenes''. Although ''L. monocytogenes'' has low infectivity, it is hardy and can grow in a refrigerator temperature of 4 °C (39.2 °F) up to the human body temperature of 37 °C (98.6 °F). [No longer accessible. Archived version availablhere] It is the usual cause of the relatively rare bacterial disease listeriosis, an infection caused by eating foodborne illness, food contaminated with the bacteria. The overt form of the disease has a case-fatality rate of around 20–30%. Listeriosis can cause serious illness in pregnant women, newborns, adults with weakened immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listeria Monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host's cells and is one of the most virulent foodborne pathogens. Twenty to thirty percent of foodborne listeriosis infections in high-risk individuals may be fatal. In the European Union, listeriosis continues an upward trend that began in 2008, causing 2,161 confirmed cases and 210 reported deaths in 2014, 16% more than in 2013. In the EU, listeriosis mortality rates also are higher than those of other foodborne pathogens. Responsible for an estimated 1,600 illnesses and 260 deaths in the United States annually, listeriosis ranks third in total number of deaths among foodborne bacterial pathogens, with fatality rates exceeding even ''Salmonella'' spp. and ''Clostridium botulinum''. Named for Joseph Lister, ''Listeria monocytogenes'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listeriosis
Listeriosis is a bacterial infection most commonly caused by '' Listeria monocytogenes'', although '' L. ivanovii'' and '' L. grayi'' have been reported in certain cases. Listeriosis can cause severe illness, including severe sepsis, meningitis, or encephalitis, sometimes resulting in lifelong harm and even death. Those at risk of severe illness are the elderly, fetuses, newborns, and those who are immunocompromised. In pregnant women, it may cause stillbirth or spontaneous abortion, and preterm birth is common. Listeriosis may cause mild, self-limiting gastroenteritis and fever in anyone. ''Listeria'' is ubiquitous and is primarily transmitted via the oral route after ingestion of contaminated food products, after which the bacteria penetrates the intestinal tract to cause systemic infections. The diagnosis of listeriosis requires the isolation of the causative bacteria from the blood or the cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment includes prolonged administration of antibioti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Lister
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, (5 April 1827 – 10 February 1912) was a British surgeon, medical scientist, experimental pathologist and pioneer of aseptic, antiseptic surgery and preventive healthcare. Joseph Lister revolutionised the Surgical technique, craft of surgery in the same manner that John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter revolutionised the science of surgery. From a technical viewpoint, Lister was not an exceptional surgeon, but his research into bacteriology and infection in wounds revolutionised surgery throughout the world. Lister's contributions were four-fold. Firstly, as a surgeon at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary, he introduced carbolic acid (modern-day phenol) as a sterilization (microbiology), steriliser for surgical instruments, patients' skins, surgical suture, sutures, surgeons' hands, and wards, promoting the principle of antiseptics. Secondly, he researched the role of inflammation and tissue perfusion in the healing of wounds. Thirdly, he advanced diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, and an inability to tolerate loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid hemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease ( sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, (5 April 1827 – 10 February 1912) was a British surgeon, medical scientist, experimental pathologist and pioneer of aseptic, antiseptic surgery and preventive healthcare. Joseph Lister revolutionised the Surgical technique, craft of surgery in the same manner that John Hunter (surgeon), John Hunter revolutionised the science of surgery. From a technical viewpoint, Lister was not an exceptional surgeon, but his research into bacteriology and infection in wounds revolutionised surgery throughout the world. Lister's contributions were four-fold. Firstly, as a surgeon at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary, he introduced carbolic acid (modern-day phenol) as a sterilization (microbiology), steriliser for surgical instruments, patients' skins, surgical suture, sutures, surgeons' hands, and wards, promoting the principle of antiseptics. Secondly, he researched the role of inflammation and tissue perfusion in the healing of wounds. Thirdly, he advanced diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foodborne Illness
Foodborne illness (also known as foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the contamination of food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites, as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease), and toxins such as aflatoxins in peanuts, poisonous mushrooms, and various species of beans that have not been boiled for at least 10 minutes. While contaminants directly cause some symptoms, many effects of foodborne illness result from the body's immune response to these agents, which can vary significantly between individuals and populations based on prior exposure. Symptoms vary depending on the cause. They often include vomiting, fever, aches, and diarrhea. Bouts of vomiting can be repeated with an extended delay in between. This is because even if infected food was eliminated from the stomach in the first bout, microbes, like bacteria (if applicable), can pass through the stomach into the intestine and begin to multiply. Some types of microbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvey Pirie
Dr James Hunter Harvey Pirie FRSE FRCPE (10 December 1878 – 27 September 1965"Dr. J.H. Harvey Pirie" in ''The London Philatelist'', Vol. 74, No. 876, December 1965, p. 223.) was a 20th-century British medical doctor, philatelist, orchid-grower and bacteriologist. Pirie named the bacterial genus ''Listeria'' in honor of Joseph Lister and the Pirie Peninsula is named after him. Cape Mabel was named after his wife. In authorship he is known as J. H. H. Pirie. Life He was born in Glasgow the son of Dr John Pirie of 26 Elmbank Crescent. Pirie was commissioned into the Royal Field Artillery as a second lieutenant on 28 March 1900, but resigned from the military later the same year. He earned his first medical degree at Glasgow University graduating MB ChB in 1902. From 1902 until 1904 he participated in the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition on the ex-whaling ship ''Scotia'', under William Speirs Bruce, Pirie acting as both surgeon and geologist. This involved spending th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facultative Anaerobic Organism
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent. Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are '' Staphylococcus'' spp., ''Escherichia coli'', ''Salmonella'', '' Listeria'' spp., '' Shewanella oneidensis'' and '' Yersinia pestis''. Certain eukaryotes are also facultative anaerobes, including pupfish, fungi such as ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and many aquatic invertebrates such as nereid polychaetes. It has been observed that in mutants of '' Salmonella typhimurium'' that underwent mutations to be either obligate aerobes or anaerobes, there were varying levels of chromatin-remodeling proteins. The obligate aerobes were later found to have a defective DNA gyrase subunit A gene ('' gyrA''), while obligate anaerobes were defective in topoisomerase I (''topI''). This indicates that topoisomerase I and its associated relaxation of chromosomal DNA is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the Stain (biology), stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |