|
Listed Buildings In Greasley
Greasley is a civil parish in the Borough of Broxtowe, Nottinghamshire, England. The parish contains 30 Listed building#England and Wales, listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. Of these, two are listed at Grade II*, the middle of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The parish contains the settlements of Beauvale, Moorgreen and Watnall and the surrounding area. Most of the listed buildings are houses, cottages and associated structures, farmhouses and farm buildings. The others include the remains of a fortified manor house, a church and a former chapel, and a school. __NOTOC__ Key Buildings References Citations Sources * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Greasley Lists of listed buildings in Nottinghamshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greasley
Greasley is a civil parish north west of Nottingham in Nottinghamshire, England. Although it is thought there was once a village called Greasley, there is no settlement of that name today as it was destroyed by the Earl of Rutland. The built up areas in the parish are Beauvale, Giltbrook, Moorgreen (often confused with Greasley), Newthorpe, Watnall and parts of Eastwood, Kimberley and Nuthall. There is also a small hamlet known as Bog-End. The parish is one of the largest in Nottinghamshire at , and the 2001 UK Census reported it had a total population of 10,467, increasing to 11,014 at the 2011 Census. History Greasley (then ''Griseleia'') is mentioned in the Domesday book as belonging to William PeverelWilliam was given a large number of manors in Nottinghamshire including Chilwell, Toton, Colwick and Kimberley. and being worth ten shillings. The book includes reference to a church, a priest and woodland pasture.''Domesday Book: A Complete Translation''. London: Penguin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Church, Greasley
St Mary's Church, Greasley is a parish church in the Church of England in Greasley, Nottinghamshire. The church is Grade II listed by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport as it is a building of special architectural or historic interest. History The church is medieval, built in the mid-15th century and was restored in 1882. It had previously been restored in 1753, 1772 and 1832. However, mining subsidence caused the tower to separate from the chancel and the nave, and in 1896 the church was virtually rebuilt at a cost of £2,000. The font pre-dates the church, being 14th century. Stained glass The church contains some fragments of stained glass from Beauvale Charterhouse. Organ The church has a pipe organ by Charles Lloyd of Nottingham dating from 1910. It was the gift of Major Thomas Philip Barber. The specification of the organ can be found on thNational Pipe Organ Register Memorials *Peniston Lamb, 1st Viscount Melbourne North West corner of the tower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lintel (architecture)
A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. In the case of windows, the bottom span is instead referred to as a sill, but, unlike a lintel, does not serve to bear a load to ensure the integrity of the wall. Modern day lintels are made using prestressed concrete and are also referred to as beams in beam and block slabs or ribs in rib and block slabs. These prestressed concrete lintels and blocks are components that are packed together and propped to form a suspended floor concrete slab. Structural uses In worldwide architecture of different eras and many cultures, a lintel has been an element of post and lintel construction. Many different building materials have been used for lintels. In classical Western architecture and construction methods, by ''Merriam-Webster'' definition, a lintel is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauvale Priory From The East - Geograph
Beauvale, or Beauvale Newthorpe, is a village in Nottinghamshire, England. It is located 1 mile to the east of Eastwood. It is in Greasley parish. Beauvale Priory is the remains of a Carthusian monastery, or Charterhouse, founded in 1343 by Nicholas de Cantilupe. The extant remains include part of the church and a three-storey tower house, which may have been the Prior's lodging.Pevsner, Nikolaus. 1979. ''The Buildings of England: Nottinghamshire''. Harmondsworth, Middx. Penguin. Gallery File:Beauvale Priory Remains.jpg, The structural remains of Beauvale Priory Beauvale Priory (also known as Beauvale Charterhouse) was a Carthusian monastery in Beauvale, Nottinghamshire. It is a scheduled ancient monument. History The priory was founded in 1343 by Nicholas de Cantelupe (d.1355), in honour of the Bless ... in 2007 References External links Villages in Nottinghamshire Places in the Borough of Broxtowe {{Nottinghamshire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
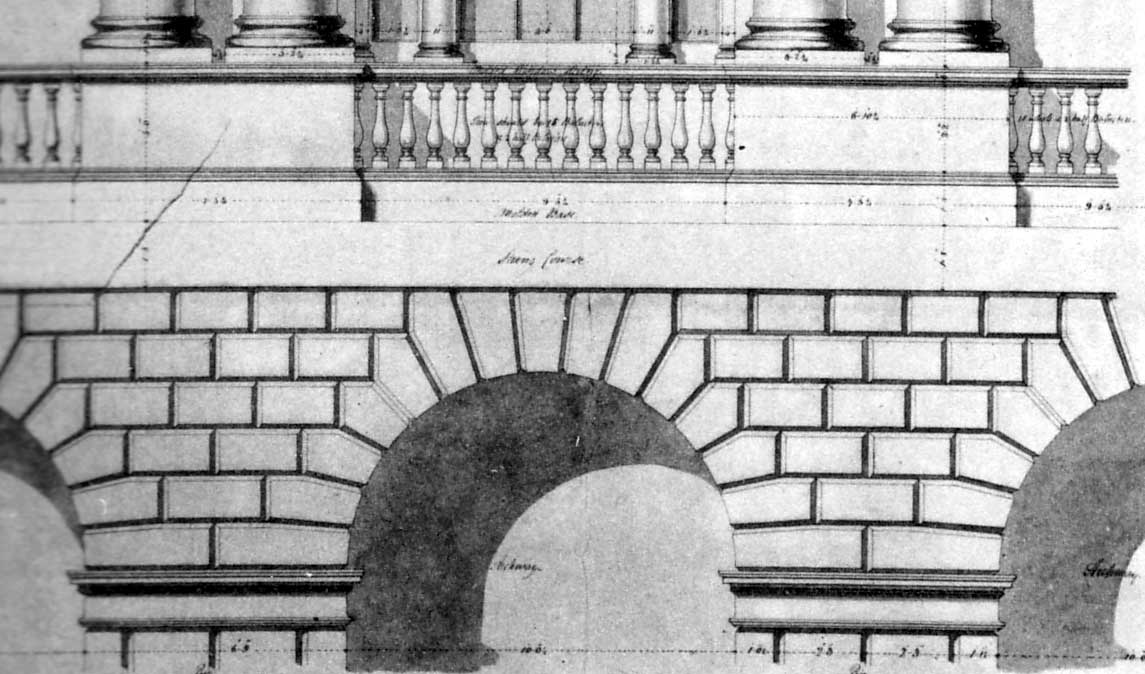
Voussoir
A voussoir () is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault. Although each unit in an arch or vault is a voussoir, two units are of distinct functional importance: the keystone and the springer. The keystone is the centre stone or masonry unit at the apex of an arch. The springer is the lowest voussoir on each side, located where the curve of the arch springs from the vertical support or abutment of the wall or pier. The keystone is often decorated or enlarged. An enlarged and sometimes slightly dropped keystone is often found in Mannerist arches of the 16th century, beginning with the works of Giulio Romano, who also began the fashion for using voussoirs above rectangular openings, rather than a lintel (Palazzo Stati Maccarani, Rome, circa 1522). The word is a stonemason's term borrowed in Middle English from French verbs connoting a "turn" ('' OED''). Each wedge-shaped voussoir ''turns aside'' the thrust of the mass above, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hood Mould
In architecture, a hood mould, hood, label mould (from Latin ''labia'', lip), drip mould or dripstone, is an external moulded projection from a wall over an opening to throw off rainwater, historically often in form of a ''pediment''. This moulding can be terminated at the side by ornamentation called a ''label stop''. The hood mould was introduced into architecture in the Romanesque period, though they became much more common in the Gothic period. Later, with the increase in rectangular windows they became more prevalent in domestic architecture. Styles of hood moulding File:IMG 0817 - Perugia - Finestra - Foto G. Dall'Orto - 6 ago 2006 - 01.jpg, Circular hood moulding File:StBeesSchoolMusicBlock.JPG, Rectangular hood mouldings on a rendered Victorian building File:Mercer House 2017.jpg, Every window of the Mercer House in Savannah, Georgia, is crowned with a cast-iron hood moulding File:Magdalene College SCR Window.jpg, Tudor-style Tudor Revival architecture (also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impost (architecture)
In architecture, an impost or impost block is a projecting block resting on top of a column or embedded in a wall, serving as the base for the springer (architecture), springer or lowest voussoir of an arch. Ornamental training The imposts are left smooth or profiled, and "then express a certain separation between abutment and arch." The Byzantine fighters are high blocks, which are sometimes referred to as pulvino. The Romanesque designed the impost ornamentally or figuratively, similar to the capitals. In the Gothic period, the fighter almost completely disappeared from the calyx bud capital. The architecture of the Renaissance returns to the formation of the imposts of the ancient column orders. See also * Capital (architecture) * Abacus (architecture) * Pulvino References Architectural elements {{architecturalelement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamfer
A chamfer or is a transitional edge between two faces of an object. Sometimes defined as a form of bevel, it is often created at a 45° angle between two adjoining right-angled faces. Chamfers are frequently used in machining, carpentry, furniture, concrete formwork, mirrors, and to facilitate assembly of many mechanical engineering designs. Terminology In machining the word ''bevel'' is not used to refer to a chamfer. Machinists use chamfers to "ease" otherwise sharp edges, both for safety and to prevent damage to the edges. A ''chamfer'' may sometimes be regarded as a type of bevel, and the terms are often used interchangeably. In furniture-making, a lark's tongue is a chamfer which ends short of a piece in a gradual outward curve, leaving the remainder of the edge as a right angle. Chamfers may be formed in either inside or outside adjoining faces of an object or room. By comparison, a '' fillet'' is the rounding-off of an interior corner, and a ''round'' (or ''radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undercroft
An undercroft is traditionally a cellar or storage room, often brick-lined and vaulted, and used for storage in buildings since medieval times. In modern usage, an undercroft is generally a ground (street-level) area which is relatively open to the sides, but covered by the building above. History While some were used as simple storerooms, others were rented out as shops. For example, the undercroft rooms at Myres Castle in Fife, Scotland of circa 1300 were used as the medieval kitchen and a range of stores. Many of these early medieval undercrofts were vaulted or groined, such as the vaulted chamber at Beverston Castle in Gloucestershire or the groined stores at Myres Castle. The term is sometimes used to describe a crypt beneath a church, used for burial purposes. For example, there is a 14th-century undercroft or crypt extant at Muchalls Castle in Aberdeenshire in Scotland, even though the original chapel above it was destroyed in an act of war in 1746. Undercrof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quoin (architecture)
Quoins ( or ) are masonry blocks at the corner of a wall. Some are structural, providing strength for a wall made with inferior stone or rubble, while others merely add aesthetic detail to a corner. According to one 19th century encyclopedia, these imply strength, permanence, and expense, all reinforcing the onlooker's sense of a structure's presence. Stone quoins are used on stone or brick buildings. Brick quoins may appear on brick buildings, extending from the facing brickwork in such a way as to give the appearance of generally uniformly cut ashlar blocks of stone larger than the bricks. Where quoins are decorative and non-load-bearing a wider variety of materials is used, including timber, stucco Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ..., or other cement rend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
