|
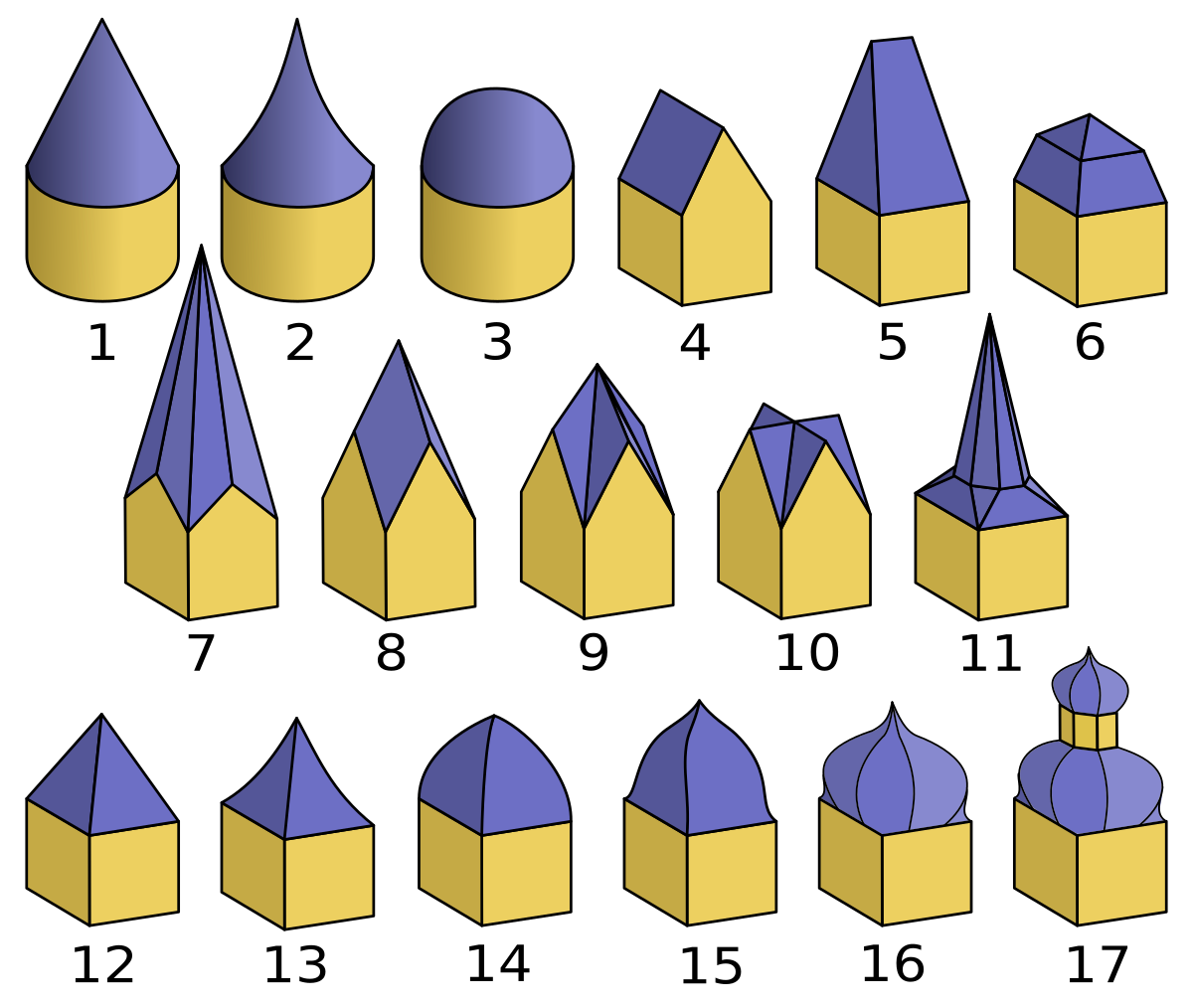
List Of Roof Shapes
Roof shapes encompass a broad range of designs, including flat (or shed roof, shed), gabled, hip roof, hipped, arched, domed, and a wide variety of other configurations An essential aspect of roof design is the roof angle or roof pitch, pitch, which can range from nearly flat to sharply steep. This angle significantly influences both the aesthetic and functional characteristics of a roof. The diversity of roof shapes across the world reflects adaptations to varying climates, locally available materials, cultural traditions, and architectural preferences. Consequently, roof design is deeply influenced by geographic and social factors. It is important to note that roof-related terminology lacks strict standardization. Definitions and naming conventions frequently differ across regions, countries, and even between individual builders or architects. Roof shapes * Flat roof, Flat: Traditionally found in buildings located in regions with low precipitation. However, modern materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
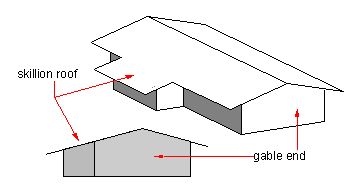
Shed Roof
A shed roof, also known variously as a pent roof, lean-to roof, outshot, catslide, skillion roof (in Australia and New Zealand), and, rarely, a mono-pitched roof,Cowan, Henry J., and Peter R. Smith. ''Dictionary of Architectural and Building Technology''. 4th ed. London: Spon Press, 2004. Print. is a single-pitched roof surface. This is in contrast to a gabled roof, dual- or list of roof shapes#Roof shapes, multiple-pitched roof. Applications A single-pitched roof can be a smaller addition to an existing roof, known in some areas as a lean-to roof, and a "outshot", "catslide", or skillion roof in others. Some Saltbox homes were expanded by the addition of such a roof, often at a shallower roof pitch, pitch than the original roof. Single-pitched roofs are used beneath clerestory windows. One or more single-pitched roofs can be used for aesthetic consideration(s). A form of single-pitched roof with multiple roof surfaces is the sawtooth roof. See also * List of roof shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow-stepped Gable
A stepped gable, crow-stepped gable, or corbie step is a stairstep type of design at the top of the triangular gable-end of a building. The top of the parapet wall projects above the roofline and the top of the brick or stone wall is stacked in a step pattern above the roof as a decoration and as a convenient way to finish the brick courses. A stepped parapet may appear on building facades with or without gable ends, and even upon a false front. Geography The oldest examples can be seen in Ghent (Flanders, Belgium) and date from the 12th century, such as the house called ''Spijker'' on the ''Graslei'', and some other Romanesque buildings in the city. From there, they spread to the whole of Northern Europe from the 13th century, in particular in cities of the Hanseatic League (with brick Gothic style), and then to Central Europe by the next century. These gables are numerous in Belgium, France (French Flanders, Eastern Normandy, Picardy and Alsace), the Netherlands, all Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Roof
A bell roof (bell-shaped roof, ogee roof, ''Philibert de l'Orme roof'') is a roof form resembling the shape of a bell.Harris, Cyril M.. "bell roof" and "bellcast eaves". ''Dictionary of architecture & construction''. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006. Print. Shapes Bell roofs may be round, multi-sided or square. A similar-sounding feature added to other roof forms at the eaves or walls is ''bell-cast'', ''sprocketed''Brett, Peter. "Bellcast eaves". ''An illustrated dictionary of building: an illustrated reference guide for practitioners and students''. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann, 1997. Print. or ''flared'' eaves, the roof flairs upward resembling the common shape of the bottom of a bell. Gallery File:Aspen Community Church.jpg, A classic, round bell roof on the round tower of Aspen Community Church in the USA File:Almond A. White House, Front.jpg, A metal bell roof on the Almond A. White House in the United States File:Vetschau Kirchturm 2.JPG, A multi-sided bell r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambrel
A gambrel or gambrel roof is a usually symmetrical two-sided roof with two slopes on each side. The upper slope is positioned at a shallow angle, while the lower slope is steep. This design provides the advantages of a sloped roof while maximizing headroom inside the building's upper level and shortening what would otherwise be a tall roof, as well as reducing the span of each set of rafters. The name comes from the Medieval Latin word ''gamba'', meaning horse's hock or leg. The term ''gambrel'' is of American origin, the older, European name being a curb (kerb, kirb) roof. Europeans historically did not distinguish between a gambrel roof and a mansard roof but called both types a mansard. In the United States, various shapes of gambrel roofs are sometimes called Dutch gambrel or Dutch Colonial gambrel with bell-cast eaves, Swedish, German, English, French, or New England gambrel. The cross-section of a gambrel roof is similar to that of a mansard roof, but a gambrel has vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansard Roof
A mansard or mansard roof (also called French roof or curb roof) is a multi-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterised by two slopes on each of its sides, with the lower slope at a steeper angle than the upper, and often punctured by dormer windows. The steep roofline and windows allow for additional floors of habitable space (a garret), and reduce the overall height of the roof for a given number of habitable storeys. The upper slope of the roof may not be visible from street level when viewed from close proximity to the building. The earliest known example of a mansard roof is credited to Pierre Lescot on part of the Louvre built around 1550. This roof design was popularised in the early 17th century by François Mansart (1598–1666), an accomplished architect of the French Baroque period. It became especially fashionable during the Second French Empire (1852–1870) of Napoléon III. ''Mansard'' in Europe (France, Germany and elsewhere) also means the attic or garret s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Roof
A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downward to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope, with variants including Tented roof, tented roofs and others. Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof. A square hip roof is shaped like a pyramid. Hip roofs on houses may have two triangular sides and two Trapezoid, trapezoidal ones. A hip roof on a rectangular plan has four faces. They are almost always at the same pitch or slope, which makes them symmetrical about the centerlines. Hip roofs often have a consistent level fascia (architecture), fascia, meaning that a gutter can be fitted all around. Hip roofs often have dormer slanted sides. Construction Hip roofs can be constructed on a wide variety of plan shapes. Each ridge is central over the rectangle of the building below it. The triangular faces of the roof are called the hip ends, and they are bounded by the hips themselves. The "hips" and hip rafters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Roof
The Also sometimes called . ''Koya'' is the technical term for the space between the roof and the ceiling. is a type of roof widely used in Japan both at Buddhist temples in Japan, Buddhist temples and Shinto shrines. It is composed of a true roof above and a second roof beneath, permitting an outer roof of steep pitch to have eaves of shallow pitch, jutting widely from the walls but without overhanging them. The second roof is visible only from under the eaves and is therefore called a "hidden roof" (giving its name to the whole structure) while the first roof is externally visible and is called an "exposed roof" in English and in Japanese. Invented in Japan during the 10th century, its earliest extant example is Hōryū-ji's Daikō-Dō (architecture), dō, rebuilt after a fire in 990. History and structure Japanese architecture continued to evolve after new techniques imported from China and Korea together with Buddhism around the 6th century. Climate in Japan being different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karahafu
is a type of curved gable found in Japanese architecture. It is used on Japanese castles, Buddhist temples, and Shinto shrines. Roofing materials such as tile and bark may be used as coverings. The face beneath the gable may be flush with the wall below, or it may terminate on a lower roof. History Although ''kara'' (唐) can be translated as meaning "China" or " Tang", this type of roof with undulating bargeboards is an invention of Japanese carpenters in the late Heian period.karahafu 唐破風 " JAANUS. Retrieved on May 30, 2009. It was named thus because the word ''kara'' could also mean "peculiar" or "elegant", and was often added to names of objects considered grand or intricate regardless of origin. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly Roof
A butterfly roof (sometimes called a V roof) is a form of roof characterised by an inversion of a standard roof form, with two roof surfaces sloping down from opposing edges to a valley near the middle of the roof. It is so called because its shape resembles a butterfly's wings.Palm Springs Modernism – The Butterfly Effect, Morris Newman in Palm Springs Life, February 2009 Retrieved 2016-04-09 History The modern butterfly roof is commonly credited to be the creation of William Krisel and Dan Palmer in the late 1950s in |
Monitor (architecture)
A monitor in architecture is a raised structure running along the ridge of a double-pitched roof, with its own roof running parallel with the main roof. The long sides of monitors usually contain clerestory windows or louvers to light or ventilate the area under the roof. A monitor roof looks like the roof of a traditional sugar house (building for boiling down maple syrup) but the purpose of the sugar house roof is to vent steam. Historically, some railroad passenger cars had monitor roofs. See also * Roof lantern A roof lantern is a Daylighting (architecture), daylighting architectural element. Architectural lanterns are part of a larger roof and provide natural light into the space or room below. In contemporary use it is an architectural skylight stru ... * Säteri roof References Roofs {{architecturalelement-stub pt:lanternim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltbox House
A saltbox house is a gable-roofed residential structure that is typically two stories in the front and one in the rear. It is a traditional New England style of home, originally timber framed, which takes its name from its resemblance to a wooden lidded box in which salt was once kept. The structure's unequal sides and long, low rear roofline are its most distinctive features. A flat front and central chimney are also recognizable traits. Origins The saltbox is an example of American colonial architecture, although it probably originated in Kent and East Anglia, coming across with the first wave of Puritans. Its shape evolved organically as an economical way to enlarge a house by adding a shed to a home's rear. Original hand-riven oak clapboards are still in place on some of the earliest New England saltboxes, such as the Comfort Starr House and Ephraim Hawley House. Once part of their exteriors, they are preserved in place in attics that were created when shed-roofed ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |