|
List Of Mountains In Scotland
Scotland is the most mountainous country in the United Kingdom. Scotland's mountain ranges can be divided in a roughly north to south direction into: the Scottish Highlands, the Central Belt and the Southern Uplands, the latter two primarily belonging to the Scottish Lowlands. The highlands eponymously contains the country's main mountain ranges, but hills and mountains are to be found south of these as well. The below lists are not exhaustive; there are countless subranges throughout the country. Ben Nevis (Beinn Nibheis), the highest mountain in Scotland and the United Kingdom at , is in the Highland region at the western end of the Grampian Mountains. A Scottish mountain over is referred to as a Munro, of which there are 282. As of 2019, hundreds of thousands of people visit mountains in Scotland every winter and about 130,000 climb to the summit of Ben Nevis every year. Highlands Scotland's main mountainous region can be broadly further split into the Northwest High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Highlands
The Northwest Highlands are located in the northern third of Scotland that is separated from the Grampian Mountains by the Great Glen (Glen More). The region comprises Wester Ross, Assynt, Sutherland and part of Caithness. The Caledonian Canal, which extends from Loch Linnhe in the south-west, via Loch Ness to the Moray Firth in the north-east splits this area from the rest of the country. The city of Inverness and the town of Fort William serve as gateways to the region from the south. Geology The geology of the Highlands is complex. Along the western coastal margin it is characterised by Lewisian gneiss, the oldest rock in Scotland. Liathach, Beinn Alligin, Suilven, Cùl Mòr, Cùl Beag, and Quinag are just some of the impressive rock islands of the significantly younger rich brown-coloured Torridonian sandstone which rests on the gneiss. Some of the peaks, such as Beinn Eighe and Canisp, are topped with later light grey or white Cambrian quartzite. Cambro-Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stac Pollaidh
Stac Pollaidh () is a mountain in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. The peak displays a rocky crest of Torridonian sandstone, with many pinnacles and steep gully, gullies. The ridge was exposed to weathering as a nunatak above the ice sheet during the last Ice age, Ice Age, while the ice flow carved and scoured the smooth sides of the mountain. The modern Gaelic name is a recent invention. The peak is named on the first edition Ordnance Survey maps simply as "An Stac" (the pinnacle) and on later maps as "Stac Polly". The "Polly" element is of Norse origin, derived from "Pollå" meaning "pool river". Due to its relatively low height of just over , fine views and ease of access from a road it has become a very popular peak to climb. It also provides some fine scrambling in the traverse of the summit ridge, including one ''bad step'' near the final summit. Consequentially it has suffered from a great deal of erosion, leading to Scottish Natural Heritage constructing a large Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutherland
Sutherland () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. The name dates from the Scandinavian Scotland, Viking era when the area was ruled by the Jarl of Orkney; although Sutherland includes some of the northernmost land on the island of Great Britain, it was called ' ("southern land") from the standpoint of Orkney and Caithness. From the 13th century, Sutherland was a provincial lordship, being an earldom controlled by the Earl of Sutherland. The earldom just covered the south-eastern part of the later county. A Shires of Scotland, shire called Sutherland was created in 1633, covering the earldom of Sutherland and the neighbouring provinces of Assynt to the west and Strathnaver to the north. Shires gradually eclipsed the old provinces in administrative importance, and also become known as counties. The county is generally rural and sparsely populated. Suth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assynt
Assynt ( or ) is a sparsely populated area in the south-west of Sutherland, lying north of Ullapool on the west coast of Scotland. Assynt is known for its landscape and its remarkable mountains, which have led to the area, along with neighbouring Coigach, being designated as the Assynt-Coigach National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland. The western part of Assynt has many distinctively shaped mountains, including Quinag, Canisp, Suilven and Ben More Assynt, that rise steeply from the surrounding "cnoc and lochan" scenery. These can often appear higher than their actual height would indicate due to their steep sides and the contrast with the moorland from which they rise. Many of the most distinctive peaks such as Suilven were formed during the last Ice Age, when they were left exposed above the ice sheet as nunataks, and they now remain as inselbergs of highly eroded Torridonian sandstone sitting on a bedrock of much older Lewisian gneiss. The Moine Thrust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
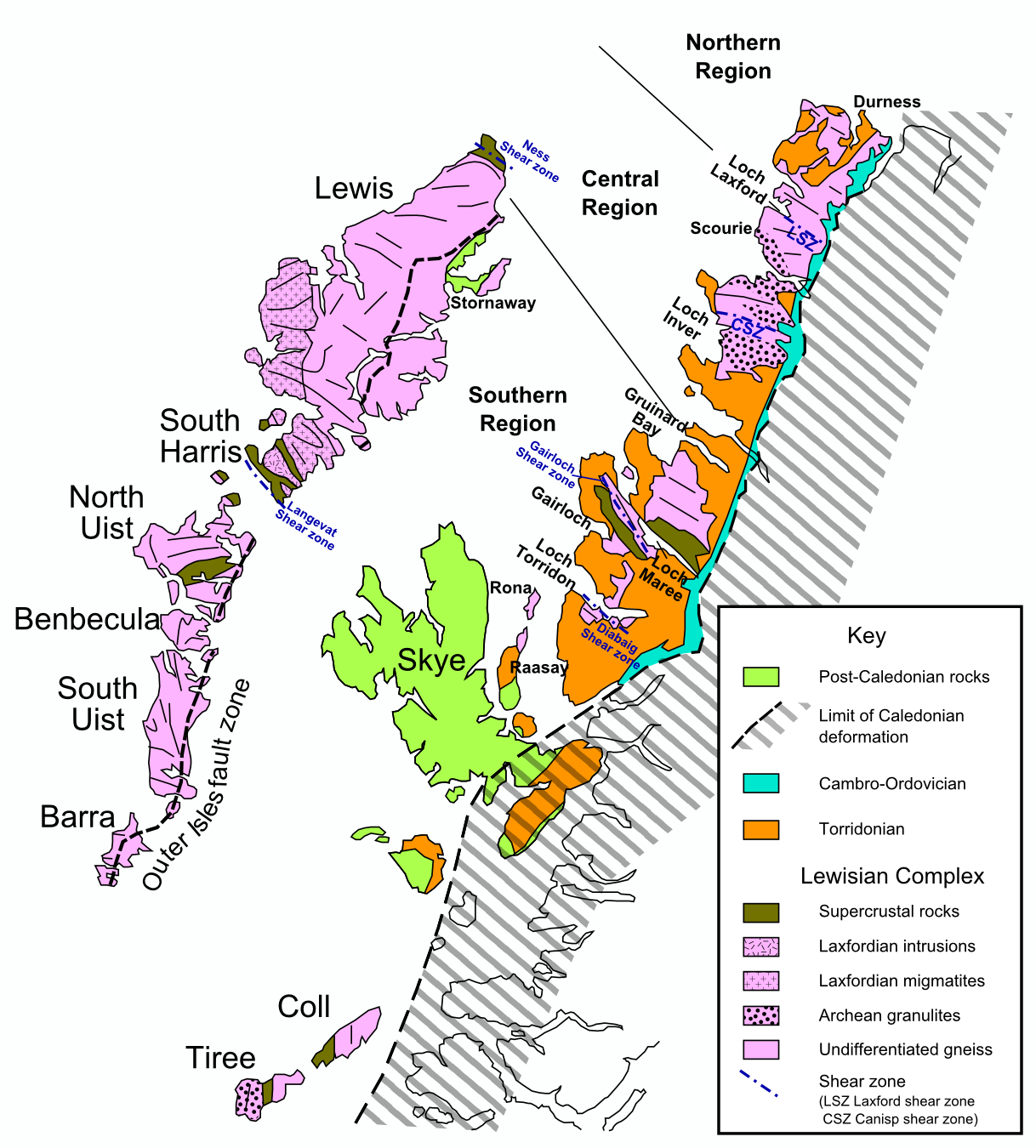
Lewisian Complex
The Lewisian complex or Lewisian gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean terrane and the North Atlantic craton, North Atlantic Craton. These rocks are of Archean, Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age, ranging from 3.0–1.7 billion years (Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ga). They form the Basement (geology), basement on which the Stoer Group, Wester Ross Supergroup and probably the Loch Ness Supergroup sediments were deposited. The Lewisian consists mainly of Granite, granitic gneisses with a minor amount of supracrustal rocks. Rocks of the Lewisian complex were caught up in the Caledonian orogeny, appearing in the hanging walls of many of the thrust faults formed during the late stages of this tectonic event. Distribution The main outcrops of the Lewisian complex are on the islands of the Outer Hebrides, including Isle of Lewis, Lewis, from which the complex takes its name. It is also exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkle (hill)
Arkle () is a mountain in Sutherland, in the far north-west corner of the Scottish Highlands. Like its sister Foinaven, the mountain is made up of glistening white Cambrian quartzite, laid down around 530 million years ago on an uneven basement of much older Lewisian complex, Lewisian gneiss. The quartzite, and the Torridonian sandstone which makes up many of the other mountains in the area, have been dissected by rivers and glaciers, leaving a series of isolated peaks, such as Suilven, Quinag and Stac Pollaidh, standing above the "knock and lochan" landscape of small hills and lakes that is typical of the Lewisian gneiss. 'Ben Arkle' was the subject of a painting by Charles, Prince of Wales. This painting was reproduced by the British Post Office as one of a set of five stamps (SG 1810–1814, issued 1 March 1994) showing paintings by Prince Charles and also, as a commemorative label, in a stamp book (SG HB16) issued 14 November 1994 to celebrate the Prince's 50th birthday. Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foinaven
Foinaven () is a mountain in Scotland, situated in the far northwest corner of the Scottish Highlands. Like many of the monolithic mountains that surround it, the mountain is within the Moine Thrust Belt and is made up of imbricated layers of Cambrian quartzite which overlie the older Lewisian gneiss basement. The quartzite, being tougher, stood firm when all the surrounding rock was eroded away, leaving the huge mountain isolated. Its highest point is named Ganu Mòr. Foinaven's smaller neighbour is Arkle. Foinaven was formerly thought by some to qualify as a Munro A Munro (; ) is defined as a mountain in Scotland with a height over , and which is on the Scottish Mountaineering Club (SMC) official list of Munros; there is no explicit topographical prominence requirement. The best known Munro is Ben Nevi ..., but an accurate survey in 2007 confirmed that it falls short of the required References {{coord, 58.41210, N, 4.88603, W, region:GB_source:enwiki-osgb36(NC315507), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beinn Eighe
is a mountain massif in the Torridon area of Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. Lying south of Loch Maree, it forms a long ridge with many spurs and summits, two of which are classified as Munros: Ruadh-stac Mòr at and Spidean Coire nan Clach at . Unlike most other hills in the area it has a cap of Cambrian basal quartzite which gives the peaks of Beinn Eighe a distinctive light colour. Its complex topography has made it popular with both hillwalkers and climbers and the National nature reserve (Scotland), national nature reserve on its northern side makes it an accessible mountain for all visitors. Geography Located between Loch Maree and Glen Torridon on the west coast of Scotland, Beinn Eighe is a complex mountain. The main ridge runs on a line extending from close to the village of Kinlochewe in the north-east to the narrow glen of the Coire Dubh Mòr, which separates it from the neighbouring mountain of Liathach to the south-west. The slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torridon Hills
The Torridon Hills surround Torridon village in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. The name is usually applied to the mountains to the north of Glen Torridon. They are among the most dramatic and spectacular peaks in the British Isles and made of some of the oldest rocks in the world. Many are over high, so are considered Munros. Rock types These are mainly made of a type of sandstone, known as Torridonian sandstone (see Geology of Great Britain), which over time has become eroded to produce the unique characteristics of the Torridon Hills. In geology, Torridonian describes a series of proterozoic arenaceous sedimentary rocks of Precambrian age. They are amongst the oldest rocks in Britain, and sit on yet older rocks, Lewisian gneiss. Some of the highest peaks, such as Beinn Eighe are crowned by white Cambrian quartzite, which gives those peaks a distinctive appearance. Some of the quartzite contains fossilized worm burrows and known as pipe rock. It is circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintail
Kintail () is a mountainous area sitting at the head of Loch Duich in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland, located in the Highland Council area. Name The area is called ''Cinn t-Sàile'' in Scottish Gaelic – which, since the "s" is silent, is anglicised as Kintail – and literally translates as the Head (ie end) of the Salt Water/Sea, describing very literally the area sitting at the head/end of Loch Duich (a long fjord-like sea loch). Area Overview Kintail is the area inland (east) from the head (end) of Loch Duich. It consists of the mountains to the north of Glen Shiel and the A87 road between the heads of Loch Duich and Loch Cluanie; its boundaries, other than Glen Shiel, are generally taken to be the valleys of Strath Croe and Gleann Gaorsaic to the north and An Caorann Mòr to the east. Although close to the west coast the mountains lie on the main east–west watershed of Scotland, as the northern side of Kintail drains via Glen AffricOrdnance Survey. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |