|
List Of Diagnoses Characterized As Pseudoscience
Many proposed diseases and diagnoses are rejected by mainstream medical consensus and are associated with pseudoscience due to a lack of scientific evidence for their existence, proposed mechanism or action, or manifestation that cannot be explained by something else. Definition Pseudoscientific diseases are not defined using objective criteria. Such diseases cannot achieve, and perhaps do not seek, medical recognition. Pseudoscience rejects empirical methodology. Other conditions may be rejected or contested by orthodox medicine, but are not necessarily associated with pseudoscience. Diagnostic criteria for some of these conditions may be vague, over-inclusive, or otherwise ill-defined. Although the evidence for the disease may be contested or lacking, the justification for these diagnoses is nevertheless empirical and therefore amenable to scientific investigation, at least in theory. In some cases, patients are exhibiting genuine signs and symptoms but the explanation or di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Wakefield
Andrew Jeremy Wakefield (born 3 September 1956) is a British fraudster, anti-vaccine activist, and disgraced former physician. He was struck off the medical register for "serious professional misconduct" due to his involvement in the fraudulent 1998 ''Lancet'' MMR autism study that falsely claimed a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism. The publicity surrounding the study caused a sharp decline in vaccination uptake, leading to a number of outbreaks of measles around the world and many deaths therefrom. He was a surgeon on the liver transplant programme at the Royal Free Hospital in London, and became a senior lecturer and honorary consultant in experimental gastroenterology at the Royal Free and University College School of Medicine. He resigned from his positions there in 2001 "by mutual agreement", then moved to the United States. In 2004, Wakefield co-founded and began working at the Thoughtful House research centre (later renamed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- "belly", -énteron "intestine", and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which include the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autistic Enterocolitis
On 28 February 1998, a fraudulent research paper by physician Andrew Wakefield and twelve coauthors, titled "Ileal-lymphoid-nodular hyperplasia, non-specific colitis, and pervasive developmental disorder in children", was published in the British medical journal ''The Lancet''. The paper falsely claimed causative links between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and colitis and between colitis and autism. The fraud involved data selection, data manipulation, and two undisclosed conflicts of interest. It was exposed in a lengthy ''Sunday Times'' investigation by reporter Brian Deer, resulting in the paper's retraction in February 2010 and Wakefield’s being discredited and struck off the UK medical register three months later. Wakefield reportedly stood to earn up to US$43 million per year selling diagnostic kits for a non-existent syndrome he claimed to have discovered. He also held a patent to a rival vaccine at the time, and he had been employed by a lawyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical evidence have tended to focus on epistemological questions regarding its role in theory testing ... even though empirical evidence also plays important and philosophically interesting roles in other areas including scientific discovery, the development of experimental tools and techniques, and the application of scientific theories to practical problems." Such evidence is expected to be empirical evidence and interpretable in accordance with the scientific method. Standards for scientific evidence vary according to the field of inquiry, but the strength of scientific evidence is generally based on the results of Statistics, statistical analysis and the strength of scientific controls. Principles of inference A person's assumptions or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science-Based Medicine
''Science-Based Medicine'' is a website and blog with articles covering issues in science and medicine, especially medical scams and practices. Founded in 2008, it is owned and operated by the New England Skeptical Society, and run by Steven Novella and David Gorski. History Started as a skeptical medical blog with five writers, ''Science-Based Medicine'' (SBM) launched on January 1, 2008. Steven Novella, Harriet Hall, and David Gorski were founding editors, along with Mark Crislip and Kimball Atwood. ''Science-Based Medicine'' is owned and operated by the New England Skeptical Society (NESS), where Novella, a clinical neurologist at Yale University and the executive editor of SBM, has served as president since its inception. Gorski, a surgical oncologist at Wayne State University, is the managing editor for SBM. The blog was affiliated with the former Society for Science-Based Medicine (SfSBM), an opinionated education and advocacy group, that registered in 2014 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiropractic
Chiropractic () is a form of alternative medicine concerned with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mechanical disorders of the musculoskeletal system, especially of the spine. It is based on several pseudoscientific ideas. Many chiropractors (often known informally as chiros), especially those in the field's early history, have proposed that mechanical disorders of the joints, especially of the spine, affect general health, and that regular manipulation of the spine (spinal adjustment) improves general health. The main chiropractic treatment technique involves manual therapy, especially manipulation of the spine, other joints, and soft tissues, but may also include exercises and health and lifestyle counseling. AHCPR Pub No. 98-N002. A chiropractor may have a Doctor of Chiropractic (D.C.) degree and be referred to as "doctor" but is not a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.). While many chiropractors view themselves as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
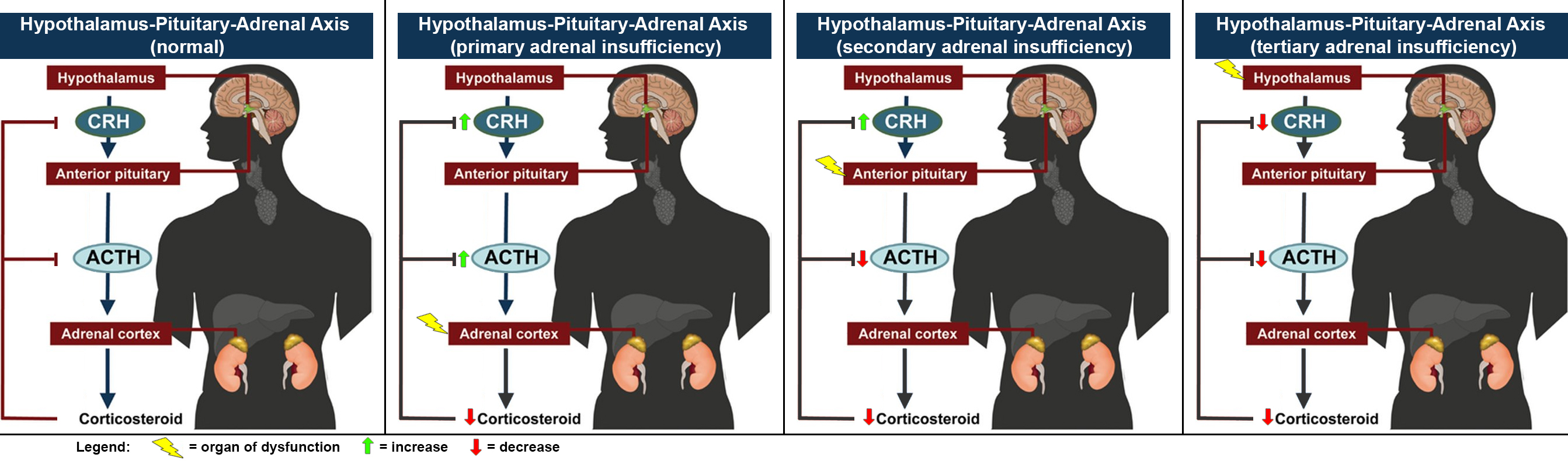
Addison's Disease
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal glands ( adrenal cortex), causing adrenal insufficiency. Symptoms generally develop slowly and insidiously and may include abdominal pain and gastrointestinal abnormalities, weakness, and weight loss. Darkening of the skin in certain areas may also occur. Under certain circumstances, an adrenal crisis may occur with low blood pressure, vomiting, lower back pain, and loss of consciousness. Mood changes may also occur. Rapid onset of symptoms indicates acute adrenal failure, which is a clinical emergency. An adrenal crisis can be triggered by stress, such as from an injury, surgery, or infection. Addison's disease arises when the adrenal gland does not produce sufficient amounts of the steroid hormones cortisol and (sometimes) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone. Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in an adrenal gland. In other tissues, it is produced in lower quantities. By a Circadian rhythm, diurnal cycle, cortisol is released and increases in response to Stress (biology), stress and a low Blood sugar, blood-glucose concentration. It functions to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, suppress the immune system, and aid in the metabolism of calories. It also decreases bone formation. These stated functions are carried out by cortisol binding to glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptors inside a cell, which then bind to DNA to affect gene expression. Health effects Metabolic response Metabolism of glucose Cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis (glucose synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau of "glucose", "cortex", and "steroid" and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an Autoimmunity, overactive immune system, such as Allergy, allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many Side effect, diverse effects such as pleiotropy (drugs), pleiotropy, including Adverse drug reaction, potentially harmful side effects. They also interfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |