|
List Of Soviet Tanks
Below is a list of tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles of the Russian empire, Soviet Union, the Russian Federation, and Ukraine. Imperial Russia, World War I Armored tractors *Gulkevich's armored tractor *F. Blinov armored tractor *Walter armored vehicle Tanks *Vezdekhod *Vezdekhod No.2 *Tsar tank *Mendeleev tank (project) *Rybinsk tank *Ground Battleship (''Земной броненосец'') - project Self-propelled guns *Drizhenko self-propelled gun *Turtle (Navrotsky Self-propelled gun) After World War I to early World War II (1918-1940) Armored cars * FAI armoured car, FAI * FAI-2 *''Broneavtomobil''-series armored cars: ** BA-I ** BA-3 ** BA-5 ** BA-6 ** BA-64, BA-6S - half-tracked version of BA-6 ** BA-9 ** BA-10 ** BA-11 ** BA-20 ** BA-21 ** BA-23 ** BA-27 ** BA-30 * BAD-1 * BAD-2 * BDT * BKhM-1000/800 * D-8 Armored Car * D-9 * D-8 Armored Car, D-12 * D-13 * D-18/37 * DSh * DTR * FVV * GAZ-TK * KS-18 * PB-4 * PB-7 * ''Matval'' Tankettes *T-17 tank, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIAN Archive 1274 Tanks Going To The Front
RIA Novosti (), sometimes referred to as RIAN () or RIA (), is a Russian State media, state-owned domestic news agency. On 9 December 2013, by a decree of Vladimir Putin, it was liquidated and its assets and workforce were transferred to the newly created Rossiya Segodnya agency. On 8 April 2014, RIA Novosti was registered as part of the new agency. RIA Novosti is headquartered in Moscow. The chief editor is Anna Gavrilova. Content RIA Novosti was scheduled to be closed down in 2014; starting in March 2014, staff were informed that they had the option of transferring their contracts to Rossiya Segodnya or sign a Voluntary redundancy, redundancy contract. On 10 November 2014, Rossiya Segodnya launched the Sputnik (news agency), Sputnik multimedia platform as the international replacement of RIA Novosti and Voice of Russia. Within Russia itself, however, Rossiya Segodnya continues to operate its Russian language news service under the name RIA Novosti with itria.ruwebsite. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BA-6
The BA-3 () was a heavy armored car developed in the Soviet Union in 1933, followed by a slightly changed model BA-6 in 1936. Both were based mostly on BA-I, the most important development being the new turret, same as in the T-26 m 1933 and BT-5 tanks, and also equipped with the 45 mm main gun. 221 BA-3 cars were built at the Izhorskij and Vyksunskij factories, until production ended in 1935. BA-6 followed with 386 cars produced between 1936 and 1938 in Izhorskij factory. Most BA-3 production was based on the Ford-Timken chassis, a 6×4 modification of the US Ford AA 4×2 truck, but the last batch was built on the Russian version of the same chassis - GAZ-AAA, and continued to be used in the BA-6. The biggest limitation of the BA-3 was the mobility, limited to roads or very hard ground, the result of unnecessarily large weight. The innovation that slightly improved mobility was the auxiliary ("Overall") tracks that could be fitted onto the rear tandem wheels, convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-27
The T-27 was a tankette produced in the 1930s by the Soviet Union. It was based on the design of the Carden Loyd tankette, bought under license from the United Kingdom in 1930. Design The Soviets were not fully satisfied with the Carden Loyd design and made a number of changes before putting it into mass production under the designation of T-27. Compared with the British original, the hull was larger, the running gear was improved and the weapon mount was modified to take a Soviet 7.62 mm DT machine gun. A number of other changes were made by Chief Engineer N. Kozyrev and Lead Engineer K. Sirken to improve the tankette's ability to cope with the Russian climate and terrain. It lacked any communication devices, as communication between vehicles was intended to be carried out using signal flags. Service The tankette was accepted into service on February 13, 1931. It was manufactured in two factories simultaneously, the Bolshevik factory in Leningrad and what would later bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-17 Tank
The T-17 tank was a one-man "mechanized support" tankette designed and developed by the Soviet Union during the Interwar period. Development In 1926, the design bureau КБ Orudiyno-Arsenalny Trest, OAT (later OKMO) began work on a "Liliput" single man light reconnaissance tank. The development team faced several problems, including finding a new chassis and engine. The project was stalled continuously. On March 3, 1928, under the leadership of the head motor lab, AP Kushka involving LY Lalmena, as well as engineers, Semyon Ginzburg and Edward Grote undertook the production of a new draft. As part of a three-year plan to produce a force structure capable of conducting operational maneuver and infantry support, a mechanized and armored force was to be established by December 1930. In 1929 the Field Regulation (''Polevoi Ustav''), declared that future war would be one of maneuver, developing the theory of successive operations by injecting the idea of motorization and mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAD-2
BAD-2 was a Soviet experimental amphibious armored car, that could be also converted to run on railroad tracks (see '' draisine''). The changing for rail mode took 30 minutes. Only one prototype was built in 1932, designed by engineer P. N. Syachentov. Dimensions The BAD-2 armored vehicle, weighs 4.6 tons, and is about 5.5 meters long, about 2 meters wide, and about 2.2 meters high. Conversion The BAD-2 had a set of special rail road wheels used on the railway. It takes about half an hour to replace all the wheels. After completion, the BAD-2 can be used as a light rail armored vehicle. Rubber tracks can also be installed on the rear wheels of the armored vehicle to transform into a half-track A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with wheels at the front for steering and continuous tracks at the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. A half-track combines the soft-ground traction of a tank with the Car handl ... vehicle to enhance its off-road cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BA-30
The BA-30 was a Soviet half-track armored car developed in 1937. Only a small number were built. Developments Developed at the NATI Institute, it was hoped that the BA-30 would be an improvement on the off-road performance of the previous BA series and was based on the chassis of the NATI-3 half-tracked transporter, whereas its armored hull was fully welded like the BA-20. The tracks on the BA-30 used 4 small and two large wheels, along with one return roller which was also incorporated on the NATI-3 and GAZ-60. When used in snowy environments two skis could be added to the front wheels. The BA-30 was noted for having good performance over varying terrains. It was fitted with a 71-TK-1 radio with its antenna on the hull, armed with a 7.62 DT machine gun, while the vehicle needed manning by a crew of three. Unapproved Only a few BA-30s were built and tested, with some taking part in the Winter War The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BA-27
The BA-27 was a Soviet The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ... first series-produced armoured car, manufactured from 1928 to 1931, and used for scouting and infantry support duties early in the Second World War. The BA-27 was a heavy armoured car, having the same turret and armament as the first Soviet tank, T-18, manufactured at the same time: the main gun was a modified copy of the French 37 mm Puteaux SA 18 cannon, and it was supported by an additional machine gun. The production of the first Soviet truck, '' AMO-F-15 truck'' (a copy of the Fiat 15), started in 1924. Using the chassis of this truck, the Izhorsky Factory design team developed BA-27 heavy armoured car in 1927. There was no significant production of AFVs in Russia since 1918, and the indigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BA-21
The BA-21 was an experimental Soviet armored car from 1938. It was a major modification of the BA-20, using a triaxial truck chassis instead of biaxial. The next year, the design was further developed into the LB-23, which had a better engine. Both vehicles were not accepted for production.United States Air Force (1978), p. 189. Specifications The BA-21 had a weight of , while having a length of , a width of , and a height of . It was powered by a GAZ M1 water-cooled four-cylinder engine with a speed of . It had 11 mm (0.43 in) of armor Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ..., with a 7.62 in (0.3 in) DT machine gun. The vehicle was manned by a crew of two, consisting of a commander and a driver. Development The BA-21 was designed in 1938, as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
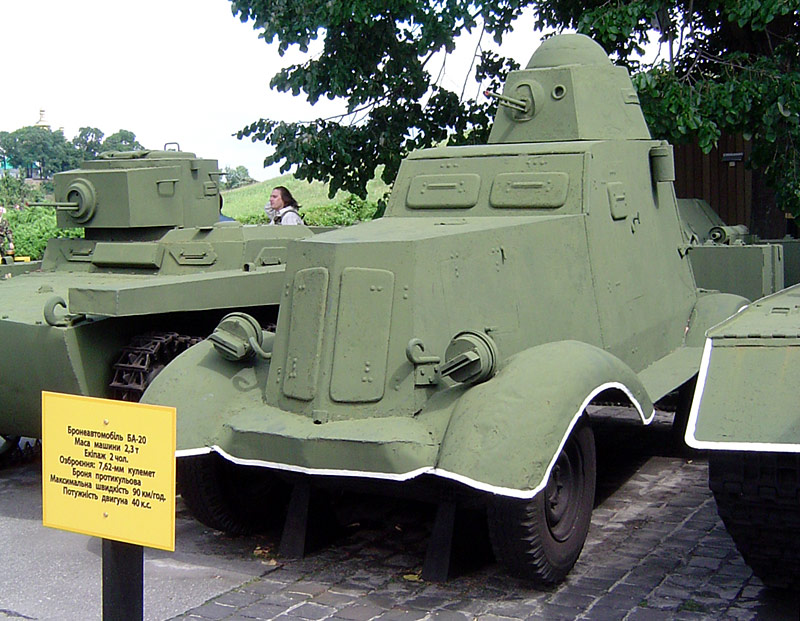
BA-20
The BA-20 () was an armored car developed in the Soviet Union in 1934. It was intended to replace the FAI and its field trials were completed in 1935. The BA-20 was then used in the early stages of World War II. Design and production The BA-20 armored car was developed in 1934 for use by HQ staffs, reconnaissance and communications units. It was derived from the civilian GAZ-M1 car using its chassis, which was itself a modified version of a Ford design, produced by the Nizhny Novgorod-based vehicle manufacturer GAZ. Full production of the BA-20 started in 1935. The chassis was built at the Nizhny Novgorod factory; the body was built at the Vyksinskiy plant, where final assembly of the BA-20 occurred as well. Service The principal use of the BA-20 was as a scout vehicle. The BA-20's tires were designed to be resistant to bullets and shrapnel by the simple expedient of filling them with spongey rubber. A variant, the BA-20ZhD, could travel on railway lines by replacing the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |