|
List Of MeSH Codes (G08)
The following is a partial list of the "G" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (G07). Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (G09). For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set o2006 MeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – reproductive and urinary physiology – reproduction – clutch size – coitus – ejaculation – embryonic and fetal development * – embryonic development * – cell lineage * – embryo implantation * – embryo implantation, delayed * – embryonic induction * – twinning, monozygotic * – fetal development * – fetal movement * – fetal organ maturity * – fetal viability * – fetal weight * – gestational age * – organogenesis * – sex differentiation – estrous cycle * – anestrus * – diestrus * – estrus * � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/ PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH vocabulary is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Development
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth. In human pregnancy, prenatal development is also called antenatal development. The development of the human embryo follows fertilization, and continues as fetal development. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age the embryo has acquired its basic form and is referred to as a fetus. The next period is that of fetal development where many organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age. The very early stages of embryonic development are the same in all mammals, but later stages of development, and the length of gestation varies. Terminology In the human: Different terms are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metestrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrus Synchronization
In agriculture, estrous synchronization is used (particularly in the dairy and beef industries) to facilitate breeding by artificial insemination. Background The term “estrus” refers to the phase of the estrous cycle in which a sexually mature, non-pregnant female is receptive to sexual advances from the male³. Ovulation occurs at approximately this time. Estrous synchronisation is the process of targeting female mammals to come to heat within a short time frame (36 to 96 hours). This is achieved through the use of one or more hormones. Methods to improve our ability to synchronize the reproductive process and result in the ‘timed insemination’ without the detection of heat have been developed. These include the “Synch” protocols that involve the application of GnRH and PGF2α in various combinations. These “Synch” protocols may include: Select Synch, OvSynch, CoSynch, and Modified Select Synch The synchronization of the estrous cycle is commonly used in differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic system t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diestrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrous Cycle
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases, otherwise known as "rest" phases, or by pregnancies. Typically, estrous cycles repeat until death. These cycles are widely variable in duration and frequency depending on the species.Bronson, F. H., 1989. Mammalian Reproductive Biology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, USA. Some animals may display bloody vaginal discharge, often mistaken for menstruation. Many mammals used in commercial agriculture, such as cattle and sheep, may have their estrous cycles artificially controlled with hormonal medications for optimum productivity. The male equivalent, seen primarily in ruminants, is called rut. Differences from the menstrual cycle Mammals share the same reproductive system, including the regulatory hypothalamic sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
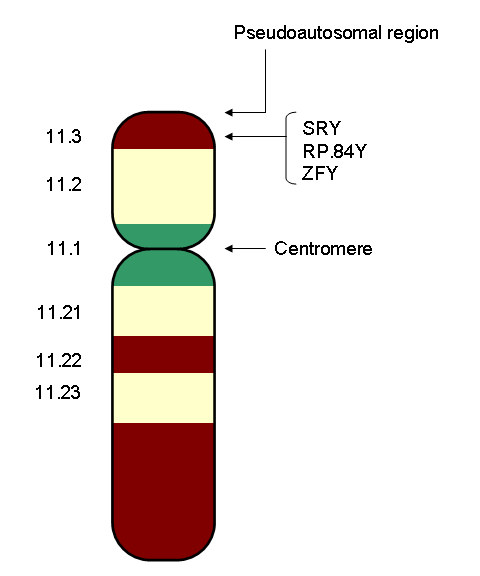
Sex Differentiation
Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation; sex determination is the designation for the development stage towards either male or female, while sex differentiation is the pathway towards the development of the phenotype. In many species, testicular or ovarian differentiation begins with appearance of Sertoli cells in males and granulosa cells in females. As male and female individuals develop from embryos into mature adults, sex differences at many levels develop, such as genes, chromosomes, gonads, hormones, anatomy, and psyche. Beginning with determination of sex by genetic and/or environmental factors, humans and other organisms proceed down different pathways of differentiation as they grow and develop. These processes are not fixed, and can change over one organism's lifetime or over many generations evolutionarily. Sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal organs of the organism. The cells of each of the three germ layers undergo differentiation, a process where less-specialized cells become more-specialized through the expression of a specific set of genes. Cell differentiation is driven by cell signaling cascades. Differentiation is influenced by extracellular signals such as growth factors that are exchanged to adjacent cells which is called juxtracrine signaling or to neighboring cells over short distances which is called paracrine signaling. Intracellular signals consist of a cell signaling itself ( autocrine signaling), also play a role in organ formation. These signaling pathways allow for cell rearrangement and ensure that organs form at specific sites within the organism. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Age (obstetrics)
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization (as is possible in in vitro fertilization), or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this definition of gestational age is that menstrual periods are essentially always noticed, while there is usually a lack of a convenient way to discern when fertilization occurred. Gestational age is contrasted with fertilization age which takes the date of fertilization as the start date of gestation. The initiation of pregnancy for the calculation of gestational age can differ from definitions of initiation of pregnancy in context of the abortion debate or beginning of human personhood. Methods According to American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Weight
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth. The average birth weight in babies of European descent is , with the normative range between . On average, babies of South Asian and Chinese descent weigh about . As far as low birth weight prevalence rates changing over time, there has been a slight decrease from 7.9% (1970) to 6.8% (1980), then a slight increase to 8.3% (2006), to the current levels of 8.2% (2016). The prevalence of low birth weights has trended slightly upward from 2012 to the present. There have been numerous studies that have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to show links between birth weight and later-life conditions, including diabetes, obesity, tobacco smoking, and intelligence. Low birth weight is associated with neonatal infection and infant mortality. Abnormalities *A low birth weight can be caused either by a preterm birth (low gestational age at birth) or of the infant being small for gestational age (slow prenatal growth rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |