|
List Of MeSH Codes (C04)
The following is a partial list of the "C" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (C03). Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (C05). For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set o2006 MeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – neoplasms – cysts – arachnoid cysts – bone cysts * – bone cysts, aneurysmal * – jaw cysts * – nonodontogenic cysts * – odontogenic cysts * – basal cell nevus syndrome * – dentigerous cyst * – odontogenic cyst, calcifying * – periodontal cyst * – radicular cyst – branchioma – breast cyst – bronchogenic cyst – chalazion – choledochal cyst – dermoid cyst – epidermal cyst – esophageal cyst – follicular cyst (other), follicular cyst – ganglion cysts – lymphocele – mediastinal cyst – mesenteric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/ PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH vocabulary is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicular Cyst
Radicular pain, or radiculitis, is pain "radiated" along the dermatome (sensory distribution) of a nerve due to inflammation or other irritation of the nerve root (radiculopathy) at its connection to the spinal column. A common form of radiculitis is sciatica – radicular pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve from the lower spine to the lower back, gluteal muscles, back of the upper thigh, calf, and foot as often secondary to nerve root irritation from a spinal disc herniation or from osteophytes in the lumbar region of the spine. Friday, 20 January 2017 Radiculitis indicates inflammation of the spinal nerve root, which may lead to pain in that nerve's distribution without weakness as opposed to radiculopathy. When the radiating pain is associated with numbness or weakness, the diagnosis is radiculopathy if the lesion is at the nerve root and myelopathy if at the spinal cord itself. See also * Intervertebral disc * Sciatica * Spinal disc herniation * Arachnoiditis Arac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
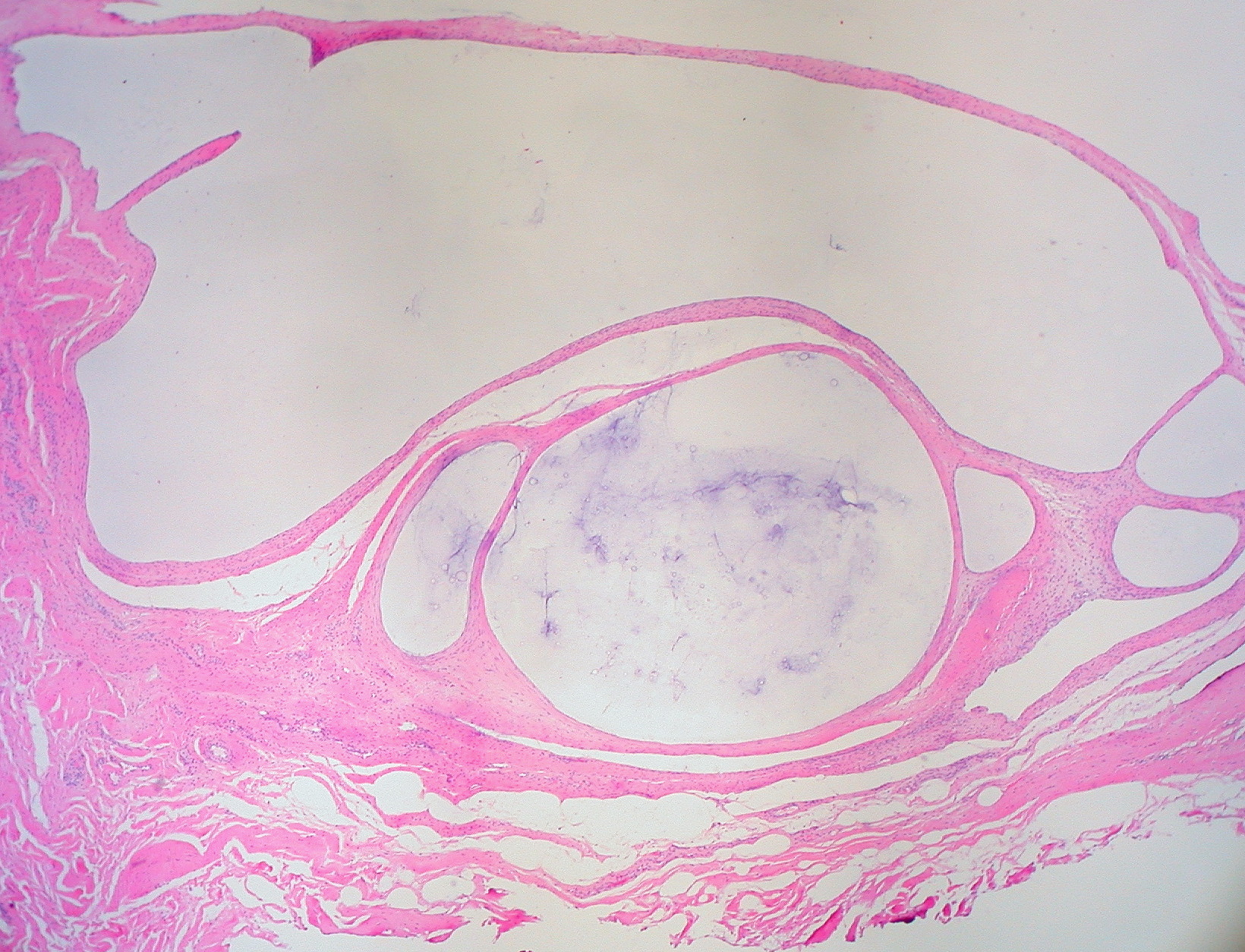
Mesenteric Cyst
A mesenteric cyst () is a cyst in the mesenterium, and is one of the rarest abdominal tumors, with approximately 822 cases reported since 1507. The incidence is between 1 per 100,000 to 1 per 250,000 hospital admissions. Tillaux's triad named after the French surgeon Paul Jules Tillaux Paul Jules Tillaux (8 December 1834 – 20 October 1904) was a French physician who was a native of Aunay-sur-Odon, département Calvados. Tillaux was a surgeon and professor of surgery in Paris, and in 1879 became a member of the ''Académie d ... can be seen in cases of mesenteric cyst. It consists of the following signs: *a fluctuating swelling near the umbilicus, *freely mobile in the direction perpendicular to the attachment of mesentry, *On Percussion :- zone of resonance ,ie Band of bowel resonance (due to loop of bowel infront of cyst) and dull note behind due to fluid inside the cyst It is basically of two types : 1. Chylolymphatic most common type, thin wall, lined by flat endothelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinal Cyst
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane. * The inferior mediastinum from this level to the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocele
A lymphocele is a collection of lymphatic fluid within the body not bordered by epithelial lining. It is usually a surgical complication seen after extensive pelvic surgery (such as cancer surgery) and is most commonly found in the retroperitoneal space. Spontaneous development is rare. Signs and symptoms Many lymphoceles are asymptomatic. Larger lymphoceles may cause symptoms related to compression of adjacent structures leading to lower abdominal pain, abdominal fullness, constipation, urinary frequency, and edema of the genitals and/or legs. Serious sequelae could develop and include infection of the lymphocele, obstruction and infection of the urinary tract, intestinal obstruction, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, chylous ascites and lymphatic fistula formation. On clinical examination the skin may be reddened and swollen and a mass felt. Ultrasonography or CT scan will help to establish a diagnosis. Other fluid collections to be considered in the differential diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganglion Cysts
A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled bump associated with a joint or tendon sheath. It most often occurs at the back of the wrist, followed by the front of the wrist. Onset is often over several months, typically with no further symptoms. Occasionally, pain or numbness may occur. Complications may include carpal tunnel syndrome. The cause is unknown. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve an outpouching of the synovial membrane. Risk factors include gymnastics activity. Diagnosis is typically based on examination with light shining through the lesion being supportive. Medical imaging may be done to rule out other potential causes. Treatment options include watchful waiting, splinting the affected joint, needle aspiration, or surgery. About half the time, they resolve on their own. About three per 10,000 people newly develop ganglion of the wrist or hand a year. They most commonly occur in young and middle-aged females. Presentation The average size of these cysts is 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicular Cyst (other)
{{disambiguation ...
Follicular Cyst may refer to: * Dentigerous cyst * Follicular cyst of ovary The follicular cyst of the ovary is a type of functional simple cyst, and is the most common type of ovarian cyst. Signs and symptoms Its rupture can create sharp, severe pain on the side of the ovary on which the cyst appears. This sharp pain ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Cyst
Esophageal can refer to: * The esophagus * Esophageal arteries * Esophageal glands * Esophageal cancer Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse vo ... {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Cyst
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermoid Cyst
A dermoid cyst is a teratoma of a cystic nature that contains an array of developmentally mature, solid tissues. It frequently consists of skin, hair follicles, and sweat glands, while other commonly found components include clumps of long hair, pockets of sebum, blood, fat, bone, nail, teeth, eyes, cartilage, and thyroid tissue. As dermoid cysts grow slowly and contain mature tissue, this type of cystic teratoma is nearly always benign. In those rare cases wherein the dermoid cyst is malignant, a squamous cell carcinoma usually develops in adults, while infants and children usually present with an endodermal sinus tumor.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Location Due to its classification, a dermoid cyst can occur wherever a teratoma can occur. Vaginal and ovarian dermoid cysts Ovaries normally grow cyst-like structures called follicles each month. Once an egg is released from its follicle during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choledochal Cyst
Choledochal cysts (a.k.a. bile duct cyst) are congenital conditions involving cystic dilatation of bile ducts. They are uncommon in western countries but not as rare in East Asian nations like Japan and China. Signs and symptoms Most patients have symptoms in the first year of life. It is rare for symptoms to be undetected until adulthood, and usually adults have associated complications. The classic triad of intermittent abdominal pain, jaundice, and a right upper quadrant abdominal mass is found only in minority of patients. In infants, choledochal cysts usually lead to obstruction of the bile ducts and retention of bile. This leads to jaundice and an enlarged liver. If the obstruction is not relieved, permanent damage may occur to the liver - scarring and cirrhosis - with the signs of portal hypertension (obstruction to the flow of blood through the liver) and ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen). There is an increased risk of cancer in the wall of the cyst. In older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalazion
A chalazion (; plural chalazia or chalazions) or meibomian cyst is a cyst in the eyelid usually due to a blocked meibomian gland, typically in the middle of the eyelid, red, and not painful. They tend to come on gradually over a few weeks. A chalazion may occur following a stye or from hardened oils blocking the gland. The blocked gland is usually the meibomian gland, but can also be the gland of Zeis. A stye and cellulitis may appear similar. A stye, however, is usually more sudden in onset, painful, and occurs at the edge of the eyelid. Cellulitis is also typically painful. Treatment is initiated with warm compresses. In addition, antibiotic/corticosteroid eyedrops or ointment may be used. If this is not effective, injecting corticosteroids into the lesion may be tried. If large, incision and drainage may be recommended. While relatively common, the frequency of the condition is unknown. It is most common in people 30–50 years of age, and equally common in males and fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)