|
List Of MeSH Codes (A07)
The following is a partial list of the "A" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list continues the information at List of MeSH codes (A06). Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (A08). For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set oMeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – cardiovascular system – blood-air barrier – blood-aqueous barrier – blood–brain barrier – blood-nerve barrier – blood-retinal barrier – blood-testis barrier – blood vessels – adventitia – arteries * – aorta * – aorta, abdominal * – aorta, thoracic * – sinus of valsalva * – arterioles * – axillary artery * – basilar artery * – brachial artery * – brachiocephalic trunk * – bronchial arteries * – carotid arteries * – carotid artery, common * – carotid artery, external * – carotid artery, internal * – carotid si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing Academic journal, journal articles and books in the Life science, life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus of index terms that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries. This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure In a healthy vascular system, the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the endothelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
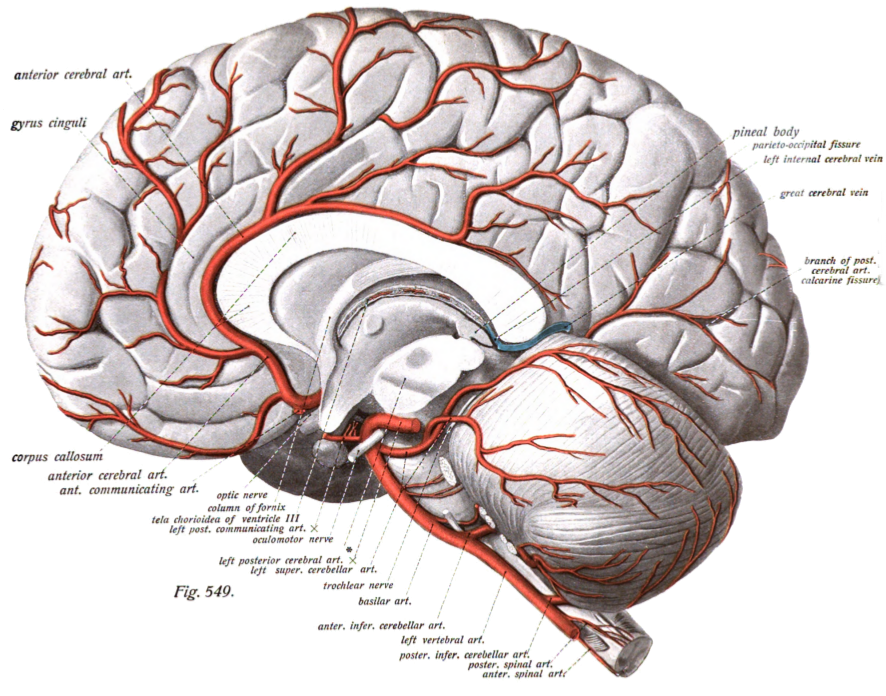
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by Paresis, weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. * A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Arteries
The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of artery, arteries and their branches, which perfusion, perfuse the cerebrum of the brain. The three main arteries are the: * ''Anterior cerebral artery'' (ACA), which supplies blood to the medial portion of the brain, including the superior parts of the Frontal lobe, frontal and anterior Parietal lobe, parietal lobes * ''Middle cerebral artery'' (MCA), which supplies blood to the majority of the lateral portion of the brain, including the Temporal lobe, temporal and lateral-parietal lobes. It is the largest of the cerebral arteries and is often affected in strokes * ''Posterior cerebral artery'' (PCA), which supplies blood to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobe, thalamus, and midbrain Both the ACA and MCA originate from the cerebral portion of internal carotid artery, while PCA branches from the intersection of the posterior communicating artery and the anterior portion of the basilar artery. The three p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled coeliac in British English), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Sinus
In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a dilated area at the base of the internal carotid artery just superior to the bifurcation of the internal carotid and external carotid at the level of the superior border of thyroid cartilage. The carotid sinus extends from the bifurcation to the "true" internal carotid artery. The carotid sinuses are sensitive to pressure changes in the arterial blood at this level. They are two out of the four baroreception sites in humans and most mammals. Structure The carotid sinus is the reflex area of the carotid artery, consisting of baroreceptors which monitor blood pressure. Function The carotid sinus contains numerous baroreceptors which function as a "sampling area" for many homeostatic mechanisms for maintaining blood pressure. The carotid sinus baroreceptors are innervated by the carotid sinus nerve, which is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX). The neurons which innervate the carotid sinus centrally project to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery, Internal
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid arise from the common carotid artery, where it bifurcates at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". In clinical settings, however, usually the classification system of the internal carotid artery follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier: C1 cervical; C2 petrous; C3 lacerum; C4 cavernous; C5 clinoid; C6 ophthalmic; and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclature remains in widespread u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery, External
The external carotid artery is the major artery of the head and upper neck. It arises from the common carotid artery. It terminates by splitting into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. Structure Origin The external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery just inferior to the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle. Course and fate It curves to pass anterosuperiorly before inclining posterior-ward to reach the space posterior the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches. Relations At the origin, external carotid artery is more medial than internal carotid artery. When external carotid artery ascends the neck, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery, Common
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries. Structure The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck and contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering literature that have looked into characterizing the geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries. Structure The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck and contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering literature that have looked into characterizing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchial Arteries
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with oxygenated blood, and nutrition. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung, and are a vital part of the respiratory system. Structure There are typically two left and one right bronchial arteries. The ''left bronchial arteries'' (superior and inferior) usually arise directly from the thoracic aorta. The single ''right bronchial artery'' may arise from one of the following: * 1) in typical anatomy, the thoracic aorta at a common trunk with the right 3rd posterior intercostal artery (known as the ''intercostobronchial trunk''). * 2) the superior bronchial artery on the left side. * 3) any number of the right intercostal arteries mostly the third right posterior. Function The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs. They travel with and branch with the bronchi, ending about at the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Trunk
The brachiocephalic artery, brachiocephalic trunk, or innominate artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm, head, and neck. It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic artery divides into the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. There is no brachiocephalic artery for the left side of the body. The left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery come directly off the aortic arch. Despite this, there are two brachiocephalic veins. Structure The brachiocephalic artery arises on a level with the upper border of the second right costal cartilage from the start of the aortic arch on a plane anterior to the origin of the left carotid artery. It ascends obliquely upward, backward, and to the right to the level of the upper border of the right sternoclavicular articulation, where it divides into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian arteries. The artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |