|
List Of Hindu Texts
Hinduism is an ancient religion, with denominations such as Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism, among others. Each tradition has a long list of Hindu texts, with subgenre based on syncretization of ideas from Samkhya, Nyaya, Yoga, Vedanta and other schools of Hindu philosophy. Of these some called ''Sruti'' are broadly considered as core scriptures of Hinduism, but beyond the ''Sruti'', the list of scriptures vary by the scholar.Dominic Goodall (1996), Hindu Scriptures, University of California Press, , page ix-xi, xx-xxi Several lists include only the Vedas, the Principal Upanishads, the Āgama (Hinduism), Agamas and the Bhagavad Gita as scriptures broadly accepted by Hindus. Goodall adds regional texts such as Bhagavata Purana and Yajnavalkya Smriti to the list. Beyond the ''Sruti'', Hindu texts include Smritis, Shastras, Sutras, Tantras, Puranas, Itihasas, Stotras, Subhashitas and others. Most of these texts exist in Sanskrit, and Old Tamil, and also later in other Languages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in South India, Southern India), Sri Lanka, and Nepal.Keay, p.xxvii. The followers of Shaivism are called Shaivas or Shaivites. According to Chakravarti, Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Aryan religions and traditions, Vedic Rudra, and post-Vedic traditions, accommodating local traditions and Yoga, puja and bhakti. According to Bisschop, early shaivism is rooted in the worship of vedic deity Rudra. The earliest evidence for sectarian Rudra-Shiva worship appears with the Pasupata (early CE), possibly owing to the Origins of Hinduism, Hindu synthesis, when many local traditions were aligned with the Brahmanism, Vedic-Brahmanical fold. The Pāśupata movement rapidly expanded through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yajnavalkya Smriti
Yajnavalkya or Yagyavalkya (, IAST:) is a Hindu Vedic sage prominently mentioned in the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad (c. 700 BCE) and ''Tattiriya Upanishad''., Quote: "Yajnavalkya, a Vedic sage, taught..."Ben-Ami Scharfstein (1998), ''A comparative history of world philosophy: from the Upanishads to Kant'', Albany: State University of New York Press, pp. 9-11 Yajnavalkya proposes and debates metaphysical questions about the nature of existence, consciousness and impermanence, and expounds the epistemic doctrine of neti neti ("not this, not this") to discover the universal Self and Ātman. Texts attributed to him include the '' Yajnavalkya Smriti'', '' Yoga Yajnavalkya'' and some texts of the Vedanta school. He is also mentioned in the ''Mahabharata'' as well as various Puranas, Brahmanas and Aranyakas. Name The name Yajnavalkya is derived from ''yajna'', which connotes ritual. Depiction in texts Yajnavalkya was a pupil of Vaisampayana and the compiler of the ''Shukla Yajurveda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achyuta Shataka
The ''Achyuta Shataka'' () is a Prakrit hymn written by the Hindu philosopher Vedanta Desika. Comprising 100 verses, the ''Achyuta Shataka'' extols Krishna, an avatar of the deity Vishnu. The hymn is composed in the arya metre. It is regarded to have been inspired by the '' Tiruvaymoli'' of Nammalvar. Etymology '' Achyuta'' is an epithet of Krishna and Vishnu, literally meaning, "the infallible one", and ''shataka'' means "hundred", referring to a genre of literature containing one hundred verses. Description Vedanta Desika is regarded to have composed the ''Achyuta Shataka'' when he visited the Devanathaswamy temple located at Tiruvahindrapuram, addressing it to the deity. He is regarded to employ the theme of ''nāyikā-bhāva'' in the hymn, the mysticism of a heroine, owing to the prevailing dramatic convention of heroines speaking in Prakrit in Sanskrit dramas. In the verses of this work, the poet asks Krishna to accept him as he would accept a bride. Hymn In the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
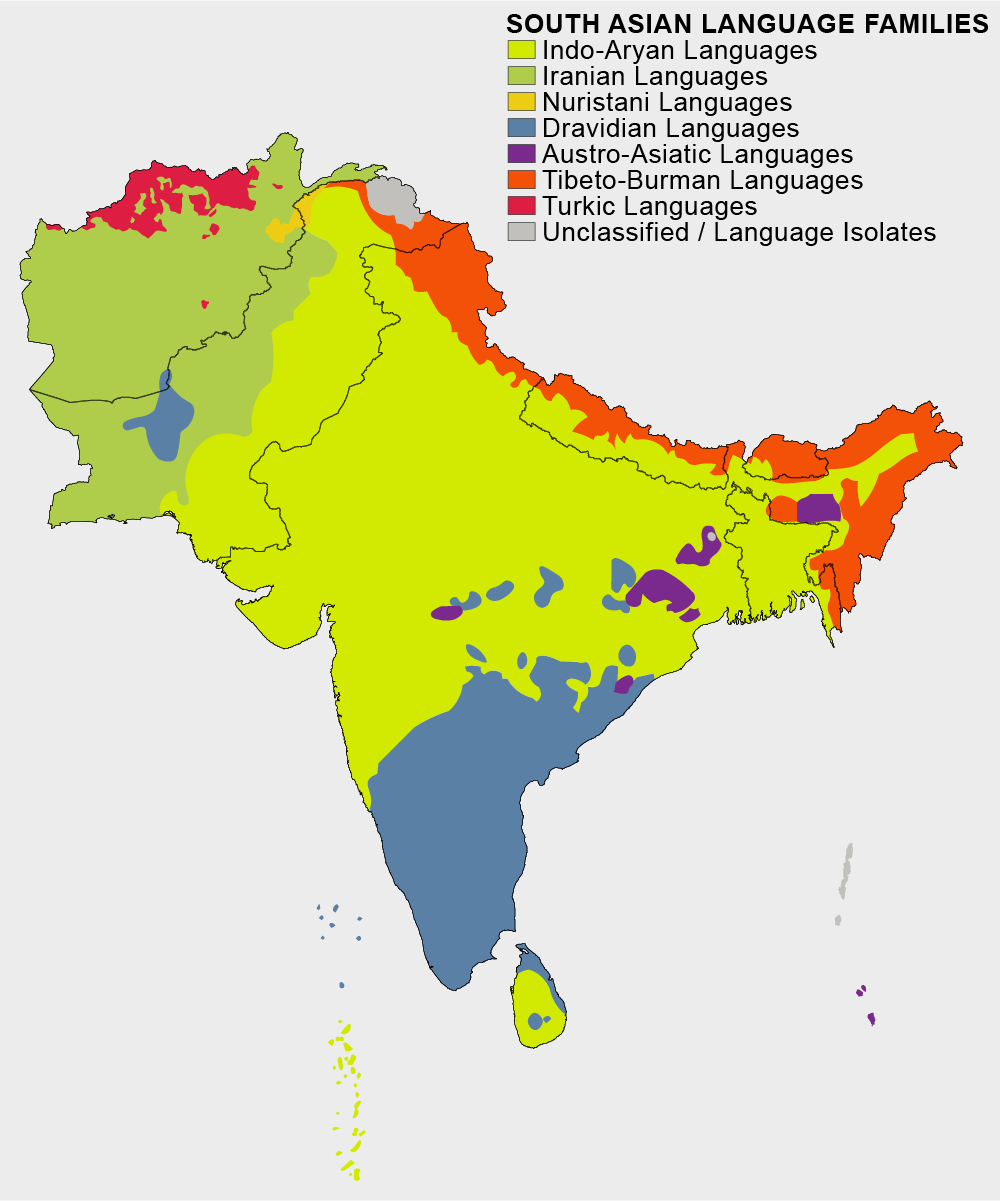
Languages Of India
Languages of India belong to several list of language families, language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indian people, Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as languages of South Asia, Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic languages, Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino–Tibetan, Kra–Dai languages, Tai–Kadai, Andamanese languages, Andamanese, and a few other minor language families and language isolate, isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the Number of languages by country, second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (Languages of Papua New Guinea, 840). ''Ethnologue'' lists a lower number of 456. Article 343 of the Constitution of India stated that the official language of the Union is Hindi in Devanagari script, with officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Indian Subcontinent
South Asia is home to several hundred languages, spanning the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It is home to the fourth most spoken language in the world, Hindi–Urdu; the seventh most spoken language, Bengali; and thirteenth most spoken language, Punjabi. Languages like Bengali, Tamil and Nepali have official/national status in more than one country of this region. The languages in the region mostly comprise Indo-Iranic and Dravidian languages, and further members of other language families like Austroasiatic, and Tibeto-Burman languages. Geographical distribution Geolinguistically, the Indo-Aryan, Dravidian and Munda language groups are predominantly distributed across the Indian subcontinent. The term Indic languages is also used to refer to these languages, though it may be narrowed to refer only to Indo-Aryan and Dravidian languages. The subcontinent is also home to a few language isolates, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tamil
Old Tamil is the period of the Tamil language spanning from the 3rd century BCE to the seventh century CE. Prior to Old Tamil, the period of Tamil linguistic development is termed as Proto-Tamil. After the Old Tamil period, Tamil becomes Middle Tamil. The earliest records in Old Tamil are inscriptions from between the 3rd and 1st century BCE in caves and on pottery. These inscriptions are written in a variant of the Brahmi script called Tamil-Brahmi. The earliest long text in Old Tamil is the ''Tolkāppiyam'', an early work on Tamil grammar and poetics, whose oldest layers could be as old as the mid-2nd century BCE.Zvelebil, K. ''The Smile of Murugan: On Tamil Literature of South '' p. xx Old Tamil preserved many features of Proto-Dravidian, the reconstructed common ancestor of the Dravidian languages, including inventory of consonants, the syllable structure, and various grammatical features. History According to Bhadriraju Krishnamurti, Tamil, as a Dravidian language, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhashita
A subhashita (, subhāṣita) is a literary genre of Sanskrit epigrammatic poems and their message is an aphorism, maxim, advice, fact, truth, lesson or riddle. ''Su'' in Sanskrit means good; ''bhashita'' means spoken; which together literally means well spoken or eloquent saying. Subhashitas in Sanskrit are short memorable verses, typically in four ''padas'' (verses) but sometimes just two; but their structure follows a meter. Subhashitas are one of many forms of creative works that have survived from ancient and medieval era of India, and sometimes known as ''Suktis''. Ancient and medieval Indian literature created tens of thousands of subhashitas covering a vast range of subjects. These epigrammatic verses and their anthologies are also referred to as ''Subhashitavali'' or ''Subhashitani''. Philosophy Subhashitas are known for their inherent moral and ethical advice, instructions in worldly wisdom and guidance in making righteous deeds. Subhashitas create an appeal as the inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stotra
''Stotra'' (Sanskrit: स्तोत्र) is a Sanskrit word that means "ode, eulogy or a hymn of praise."Monier Williams, Monier Williams' Sanskrit-English Dictionary, Oxford University Press, Article on 'Stotra'' It is a literary genre of Indian religious texts designed to be melodically sung, in contrast to a ''shastra'' which is composed to be recited. 'Stotra' derives from 'stu' meaning 'to praise' A stotra can be a prayer, a description, or a conversation, but always with a poetic structure. It may be a simple poem expressing praise and personal devotion to a deity for example, or poems with embedded spiritual and philosophical doctrines. A common feature of most stotras other than Nama stotras is the repetition of a line at the end of every verse. For example, the last line of every verse in the Mahiṣāsura Mardinī Stotra ends in "Jaya Jaya Hē Mahiṣāsura-mardini Ramyakapardini śailasute." Many ''stotra'' hymns praise aspects of the divine, such as Devi, Shiva, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itihasas
In Hinduism, Itihasa-Purana, also called the fifth Veda, refers to the traditional accounts of cosmogeny, myths, royal genealogies of the lunar dynasty and solar dynasty, and legendary past events, as narrated in the ''Itihasa'' (Mahabharata and the Ramayana) and the Puranas. They are highly influential in Indian culture, and many classical Indian poets derive the plots of their poetry and drama from the Itihasa. The Epic-Puranic chronology derived from the ''Itihasa-Purana''is an influential frame of reference in traditional Indian thought. Etymology ''Itihāsa'', इतिहास, derived from the phrase ''iti ha āsa'' , which means "so indeed it was". ''Puranas'', ; , ' literally means "ancient, old." Characterisation Itihasa refers to the Sanskrit Epics of the Mahabharata and the Ramayana. The Puranas are a vast genre of Hindu literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about cosmogony, myths, legends and purported history. Together they are also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puranas
Puranas (Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on "Puranas", , page 915) are a vast genre of Indian literature that include a wide range of topics, especially legends and other traditional lore. The Puranas are known for the intricate layers of symbolism depicted within their stories. Composed originally in Sanskrit and in Languages of India, other Indian languages,John Cort (1993), "An Overview of the Jaina Puranas" in ''Purana Perennis: Reciprocity and Transformation in Hindu and Jaina Texts,'' (Editor: Wendy Doniger), State University of New York Press, , pages 185-204 several of these texts are named after major Hindu deities such as Vishnu, Shiva, Brahma, and Mahadevi, Devi. The Puranic genre of literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism. The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist Tantras. They include Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Japanese Shingon Buddhism and Nepalese Newar Buddhism. Although Southern Esoteric Buddhism does not directly reference the tantras, its practices and ideas parallel them. In Bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |