|
List Of Wireless Router Firmware Projects
List of software created and maintained by people other than the manufacturer of the product. The extent of support for (and testing on) particular hardware varies from project to project. Embedded Notable custom-firmware projects for wireless routers. Many of these will run on various brands such as Linksys, Asus, Netgear, etc. * OpenWrt – Customizable FOSS firmware written from scratch; features a combined SquashFS/ JFFS2 file system and the package manager opkg with over 3000 available packages (Linux/ GPL); now merged with LEDE. ** LEDE – A fork of the OpenWrt project that shared many of the same goals; merged back into OpenWrt as of v. 18.06 (2018). ** Commotion Wireless – FOSS mesh networking. ** DD-WRT – Based on OpenWrt kernel since v. 23 (Dec. 2005), paid and free versions available. ** Gargoyle – A free OpenWrt-based Linux distribution for a range of Broadcom and Atheros chipset based wireless routers. ** LibreCMC – An FSF-endorsed derivation of OpenWR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Custom Firmware
Custom firmware, also known as aftermarket firmware, is an unofficial new or modified version of firmware created by third parties on devices such as video game consoles, mobile phones, and various embedded system, embedded device types to provide new features or to unlock hidden functionality. In the video game console community, the term is often written as custom firmware or simply CFW, referring to an altered version of the original system software (also known as the official firmware or simply OFW) inside a video game console such as the PlayStation Portable, PlayStation 3, PlayStation Vita/PlayStation TV, PlayStation 4, Nintendo 3DS, Wii U and Nintendo Switch. Installing custom firmware on some devices requires bootloader unlocking. Video game consoles Custom firmware often allow Homebrew (video games), homebrew applications or ROM image backups to run directly within the game console, unlike official firmware, which usually only allow signed or retailed copies of software t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment and other high-technology services and products. Cisco specializes in specific tech markets, such as the Internet of things (IoT), domain security, videoconferencing, and energy management with products including Webex, OpenDNS, Jabber, Duo Security, Silicon One, and Jasper. Cisco Systems was founded in December 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner, two Stanford University computer scientists who had been instrumental in connecting computers at Stanford. They pioneered the concept of a local area network (LAN) being used to connect distant computers over a multiprotocol router system. The company went public in 1990 and, by the end of the dot-com bubble in 2000, had a market capitali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M0n0wall
m0n0wall was an embedded firewall (networking), firewall distribution of FreeBSD, one of the Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD operating system descendants. It provided a small image which could be put on flash memory, Compact Flash cards as well as on CD-ROMs and hard disks. It ran on a number of embedded platforms and generic PCs. The PC version could be run with just a Live CD and a floppy disk to store configuration data, or on a single Compact Flash card (with an AT Attachment, IDE adapter). This eliminated the need for a hard drive, which reduces noise and heat levels and decreases the risk of system failure through elimination of moving parts found in older hard drives. On February 15, 2015 Manuel Kasper announced the "m0n0wall project has officially ended. No development will be done anymore, and there will be no further releases," encouraging "all current m0n0wall users to check out OPNsense and contribute if they can." Features m0n0wall provided an Internet, web-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable home-class hardware, and has since continuously been the most commonly used BSD-derived operating system. FreeBSD maintains a complete system, delivering a kernel, device drivers, userland utilities, and documentation, as opposed to Linux only delivering a kernel and drivers, and relying on third-parties such as GNU for system software. The FreeBSD source code is generally released under a permissive BSD license, as opposed to the copyleft GPL used by Linux. The project includes a security team overseeing all software shipped in the base distribution. Third-party applications may be installed using the pkg package management system or from source via FreeBSD Ports. The project is supported and promoted by the FreeBSD Foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Router (computing)
A router is a computer and networking device that Packet forwarding, forwards data packets between computer networks, including internetworks such as the global Internet. Routers perform the "traffic directing" functions on the Internet. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different IP networks. When a data packet comes in on a line, the router reads the network address information in the packet header to determine the ultimate destination. Then, using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet to the next network on its journey. Data packets are forwarded from one router to another through an internetwork until it reaches its destination Node (networking), node. The most familiar type of Internet Protocol, IP routers are Residential gateway, home and small office routers that forward IP packet (other), IP packets between the home computers and the Internet. More sophisticated routers, such as enterprise routers, conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalable Vector Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector graphics format for defining two-dimensional graphics, having support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999. SVG images are defined in a vector graphics format and stored in XML text files. SVG images can thus be scaled in size without loss of quality, and SVG files can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed. The XML text files can be created and edited with text editors or vector graphics editors, and are rendered by most web browsers. If used for images, SVG can host scripts or CSS, potentially leading to cross-site scripting attacks or other security vulnerabilities. History SVG has been in development within the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999 after six competing proposals for vector graphics languages had been submitted to the consortium during 1998 (see below). The early SVG Working Group decided not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajax (programming)
Ajax (also AJAX ; short for "asynchronous I/O, asynchronous JavaScript and XML") is a set of web development techniques that uses various web technologies on the client-side to create asynchronous web applications. With Ajax, web applications can send and retrieve data from a Web server, server asynchronously (in the background) without interfering with the display and behaviour of the existing page. By decoupling the data exchange, data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows web pages and, by extension, web applications, to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page. In practice, modern implementations commonly utilize JSON instead of XML. Ajax is not a technology, but rather a programming pattern. Hypertext Markup Language, HTML and Cascading Style Sheets, CSS can be used in combination to mark up and style information. The webpage can be modified by JavaScript to dynamically display (and allow the user to interact with) the new i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
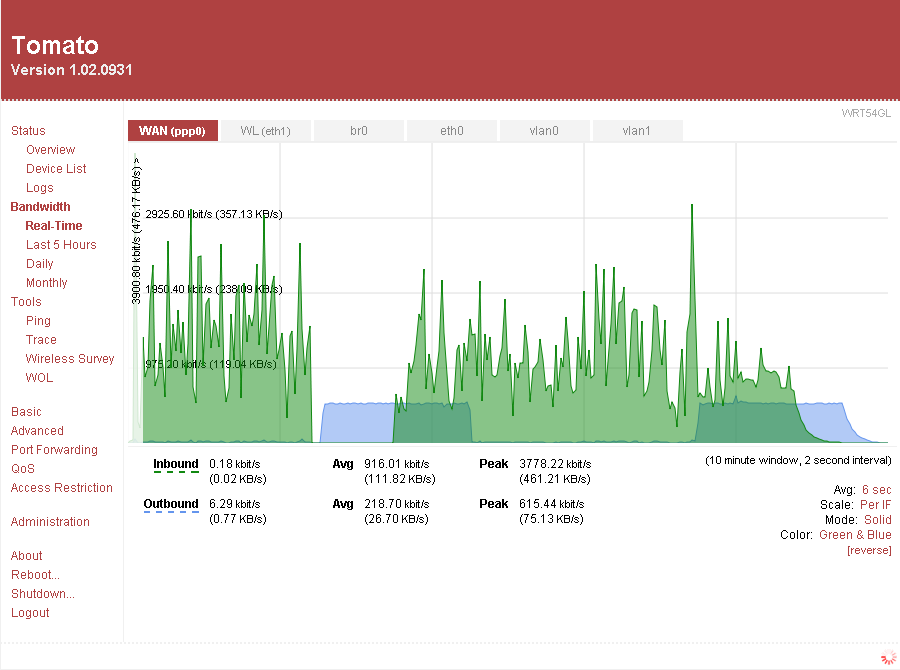
Tomato (firmware)
Tomato is a family of community-developed, custom firmware for consumer-grade computer networking routers and gateways powered by Broadcom chipsets. The firmware has been continually forked and modded by multiple individuals and organizations, with the most up-to-date fork provided by the FreshTomato project. History Tomato was originally released by Jonathan Zarate in 2006, using the Linux kernel and drawing extensively on the code of HyperWRT. It was targeted at many popular routers of the time, most notably the older Linksys WRT54G series, Buffalo AirStation, Asus routers and Netgear WNR3500L. His final release of the original Tomato firmware came in June 2010, by which point its popularity had grown large enough that development and support continued through the user community, resulting in a series of releases (dubbed " mods") by individual users or teams of them that continues to the present day. Fedor Kozhevnikov created a notable early mod he called ''TomatoUSB' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linksys WRT54G Series
The Linksys WRT54G Wi-Fi series is a series of Wi-Fi–capable residential gateways marketed by Linksys, a subsidiary of Cisco, from 2003 until acquired by Belkin in 2013. A ''residential gateway'' connects a local area network (such as a home network) to a wide area network (such as the Internet). Models in this series use one of various 32-bit MIPS architecture, MIPS Central processing unit, processors. All WRT54G models support Fast Ethernet for wired data links, and IEEE 802.11#802.11g, 802.11b/g for wireless data links. Hardware and revisions WRT54G File:WRT54G Linksys Router with 7 dBi Antennas Digon3.jpg, alt=The, WRT54G version 2.0 with upgraded antennas The original WRT54G was first released in December 2002. It has a 4+1 port network switch (the Internet/WAN port is part of the same internal network switch, but on a different VLAN). The devices have two removable antennas connected through Reverse Polarity Threaded Neill-Concelman connector, TNC connectors. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HyperWRT
HyperWRT is a defunct firmware project for the Linksys WRT54G and WRT54GS wireless routers based on the stock Linksys firmware, released under a GPL. The original goal of the HyperWRT project was to add a set of features—such as power boost—to the latest Linux-based Linksys firmware, extending its possibilities but staying close to the official firmware. Over time, it continued to be updated with newer Linksys firmware, and added many more features typically found in enterprise routing equipment. HyperWRT is no longer maintained, and has been succeeded by Tomato. History The original HyperWRT project was started in 2004 by Timothy Jans, with continued development into early 2005. programmer Rupan then continued HyperWRT development by integrating newer Linksys code as it was released. Later in 2005, developers called Tofu and Thibor picked up HyperWRT development with ''HyperWRT +tofu'' for the WRT54G and ''HyperWRT Thibor'' for the WRT54GS. Both developers collaborated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |