|
List Of Waste-water Treatment Technologies
This page consists of a list of wastewater treatment technologies: See also *Agricultural wastewater treatment *Industrial wastewater treatment *List of solid waste treatment technologies * Waste treatment technologies *Water purification Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ... * Sewage sludge treatment References * * Industrial Wastewater Treatment Technology DatabaseEPA. {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Waste Water Treatment Technologies Chemical processes Environmental engineering *List Water pollution Water technology Waste-water treatment technologies Sanitation * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater. It thus converts it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once back in the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment. It is also possible to reuse it. This process is called Reclaimed water, water reclamation. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater the treatment plant is called a Sewage Treatment. Municipal wastewater or sewage are other names for domestic wastewater. For industrial wastewater, treatment takes place in a separate Industrial wastewater treatment, or in a sewage treatment plant. In the latter case it usually follows pre-treatment. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include Agricultural wastewater treatment and leachate treatment plants. One common proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
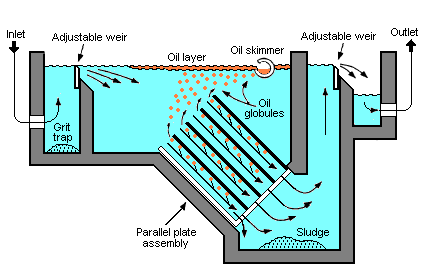
API Oil–water Separator
An API oil–water separator is a device designed to separate gross amounts of oil and suspended solids from industrial wastewater produced at oil refineries, petrochemical plants, chemical plants, natural gas processing plants and other industrial oily water sources. The API separator is a gravity separation device designed by using Stokes Law to define the rise velocity of oil droplets based on their density and size. The design is based on the specific gravity difference between the oil and the wastewater because that difference is much smaller than the specific gravity difference between the suspended solids and water. The suspended solids settles to the bottom of the separator as a sediment layer, the oil rises to top of the separator and the cleansed wastewater is the middle layer between the oil layer and the solids. The name is derived from the fact that such separators are designed according to standards published by the American Petroleum Institute (API). Description o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
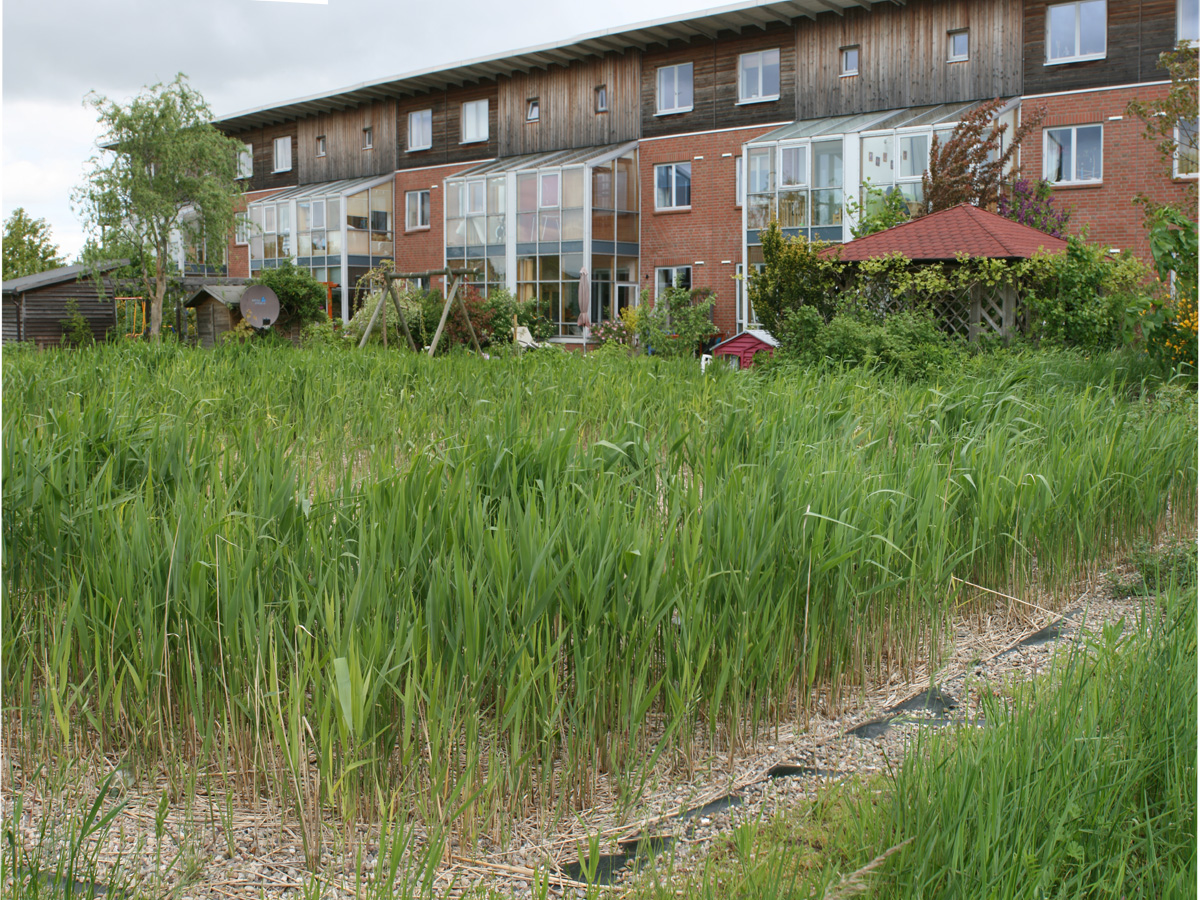
Constructed Wetland
A constructed wetland is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a Flood mitigation, mitigation step for natural areas lost to land development. Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that use the natural functions of vegetation, soil, and organisms to provide secondary treatment to wastewater. The design of the constructed wetland has to be adjusted according to the type of wastewater to be treated. Constructed wetlands have been used in both centralized and decentralized wastewater systems. Primary treatment is recommended when there is a large amount of suspended solids or soluble organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand). Similar to natural wetlands, constructed wetlands also act as a biofilter and/or can remove a range of pollutants (such as organic matter, Nutrient pollution, nutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composting Toilet
A composting toilet is a type of dry toilet that treats human waste by a biological process called composting. This process leads to the decomposition of organic matter and turns human waste into compost-like material. Composting is carried out by microorganisms (mainly bacteria and fungi) under controlled aerobic conditions. Most composting toilets use no water for flushing and are therefore called "dry toilets". In many composting toilet designs, a carbon additive such as sawdust, coconut coir, or peat moss is added after each use. This practice creates air pockets in the human waste to promote aerobic decomposition. This also improves the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio and reduces potential odor. Most composting toilet systems rely on mesophilic composting. Longer retention time in the composting chamber also facilitates pathogen die-off. The end product can also be moved to a secondary system – usually another composting step – to allow more time for mesophilic composting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coarse Bubble Diffusers
Coarse bubble diffusers are a pollution control technology used to aerate and or mix wastewater for sewage treatment. Description Coarse bubble diffusers produce 1/4 to 1/2 inch (6.4 to 13 mm) bubbles which rise rapidly from the floor of a wastewater treatment plant or sewage treatment plant tank. They are typically used in grit chambers, equalization basins, chlorine contact tanks, and aerobic digesters, and sometimes also in aeration tanks. Generally they are better at vertically "pumping" water than at mass transfer of oxygen. Coarse bubble diffusers typically provide half the mass transfer of oxygen as compared to fine bubble diffusers, given the same air volume. Application Often in non-Newtonian or pseudoplastic fluids, such as a digester with high solids concentration, it does make sense to use coarse bubble diffusers rather than fine bubble diffusers, due to the larger bubbles' ability to shear through more viscous wastewater. However, over the past t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
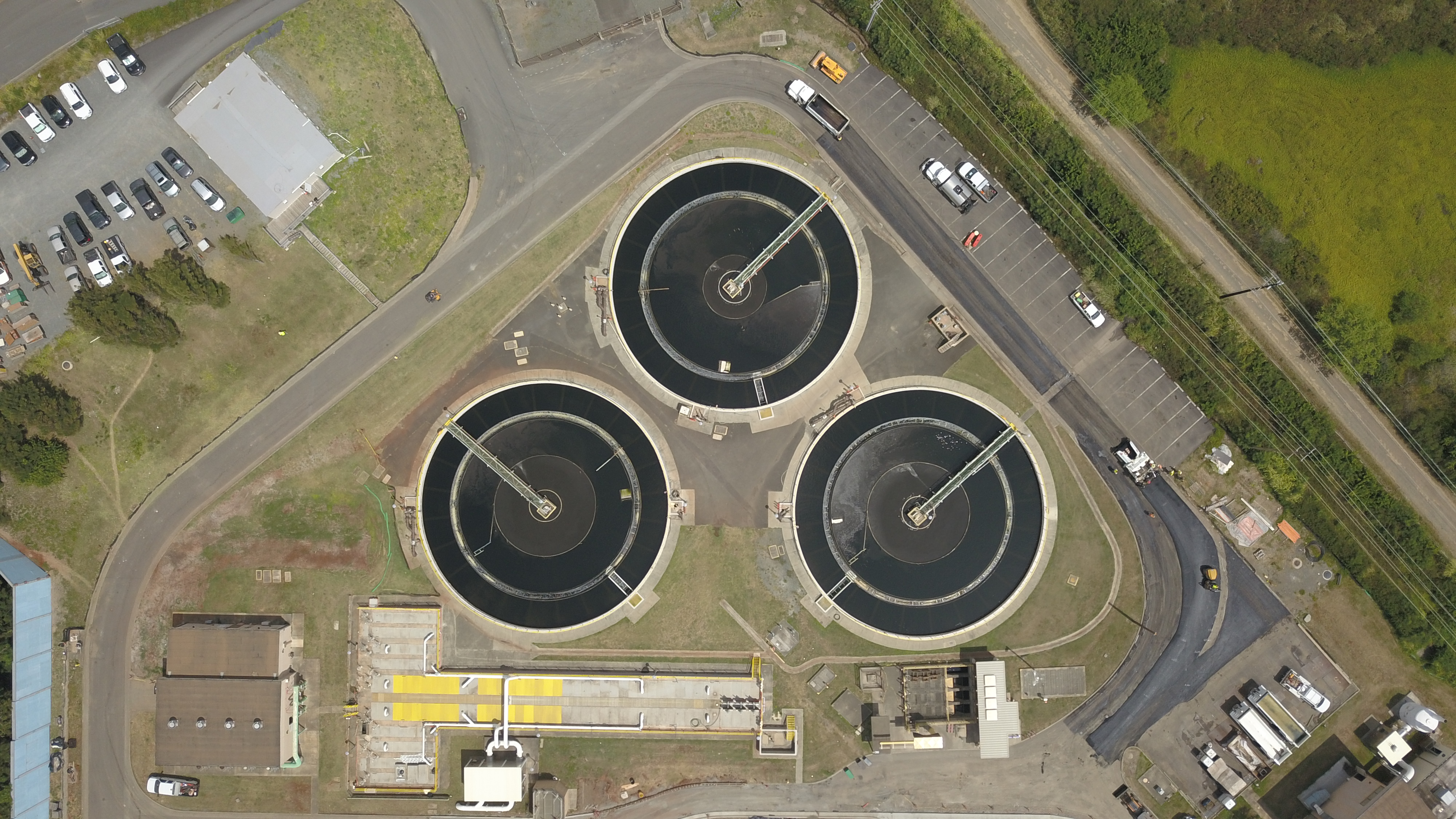
Clarifier
Clarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by Sedimentation (water treatment), sedimentation. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and/or thickening. Inside the clarifier, solid contaminants will settle down to the bottom of the tank where it is collected by a scraper mechanism. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank, are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum. Applications Pretreatment Before the water enters the clarifier, coagulation and flocculation reagents, such as polyelectrolytes and ferric sulfate,Brentwood Industries, Inc. (2013)"Tube Settler Systems For Clarification." Accessed 14 October 2013. can be added. These reagents cause finely suspended particles to clump together and form larger and denser particles, called flocs, that settle more quickly and stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Addition Wastewater Treatment
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bonded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cesspit
Cesspit, cesspool and soak pit in some contexts are terms with various meanings: they are used to describe either an underground holding tank (sealed at the bottom) or a Dry well, soak pit (not sealed at the bottom). A cesspit can be used for the temporary collection and storage of Human feces, feces, excreta, or fecal sludge as part of an on-site sanitation system and has some similarities with septic tanks or with soak pits. Traditionally, it was a deep cylindrical chamber dug into the ground, having approximate dimensions of diameter and depth. Its appearance was similar to that of a hand-dug water well. The pit can be lined with bricks or concrete, covered with a slab, and needs to be emptied frequently when in use as an underground holding tank. In other cases (if soil and groundwater conditions allow), it is not constructed watertight, to allow liquid to leach out (similar to a pit latrine or to a soak pit). Terminology In British English, historically, a cesspit wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Filtering
Carbon filtering is a method of filtering that uses a bed of activated carbon to remove impurities from a fluid using adsorption. Mechanism Carbon filtering works by adsorption, in which pollutants in the fluid to be treated are trapped inside the pore structure of a carbon substrate. The substrate is made of many carbon granules, each of which is itself highly porous. As a result, the substrate has a large surface area within which contaminants can be trapped. Activated carbon is typically used in filters, as it has been treated to have a much higher surface area than non treated carbon. One gram of activated carbon has a surface area in excess of 3,000 m2 (32,000 sq ft). Common uses Carbon filtering is commonly used for water purification, air filtering and industrial gas processing, for example the removal of siloxanes and hydrogen sulfide from biogas. It is also used in a number of other applications, including respirator masks, the purification of sugarcane, some methods of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Deionization
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a technology to deionize water by applying an electrical potential difference over two electrodes, which are often made of porous carbon. In other words, CDI is an electro-sorption method using a combination of a sorption media and an electrical field to separate ions and charged particles. Anions, ions with a negative charge, are removed from the water and are stored in the positively polarized electrode. Likewise, cations (positive charge) are stored in the cathode, which is the negatively polarized electrode. Today, CDI is mainly used for the desalination of brackish water, which is water with a low or moderate salt concentration (below 10 g/L). Other technologies for the deionization of water are, amongst others, distillation, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis. Compared to reverse osmosis and distillation, CDI is considered to be an energy-efficient technology for brackish water desalination. This is mainly because CDI removes the salt ions fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
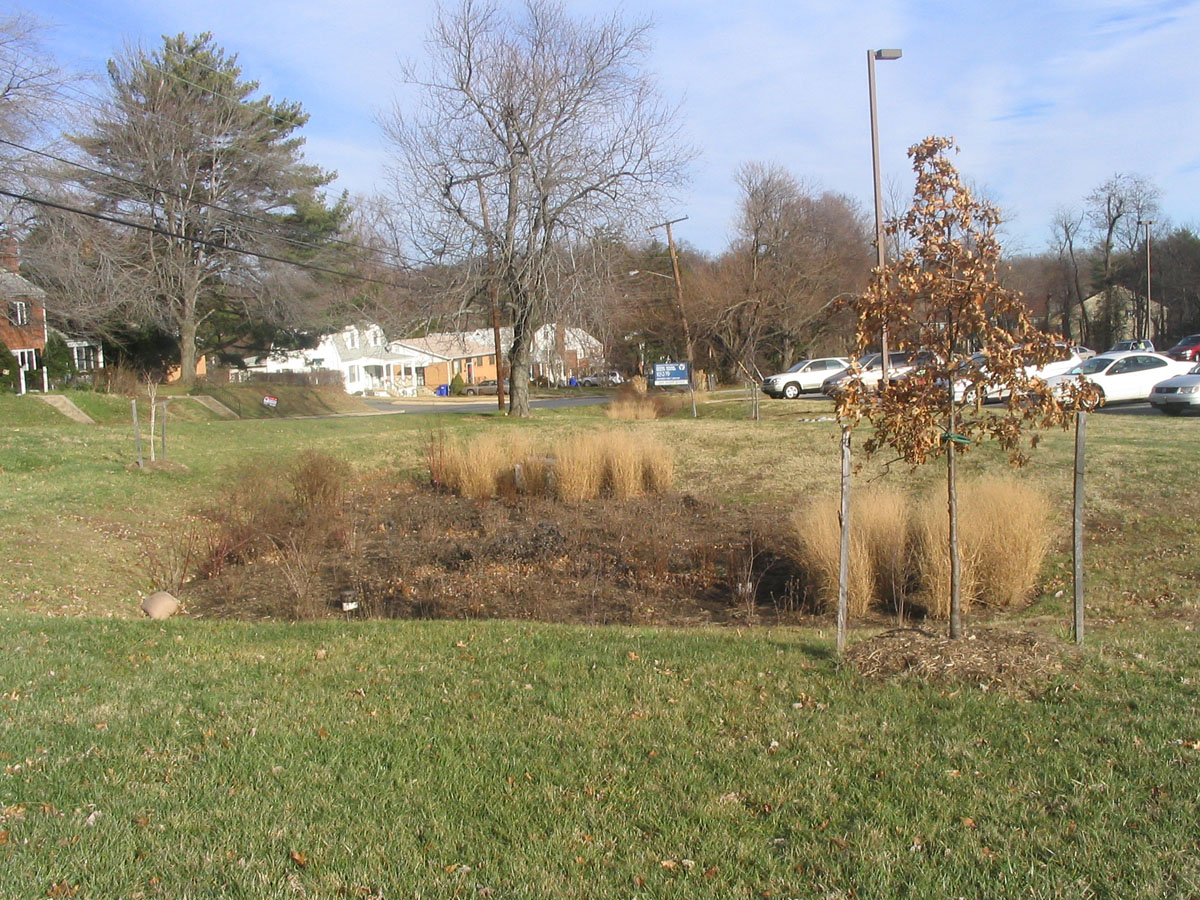
Bioretention
Bioretention is the process in which contaminants and sedimentation are removed from stormwater Surface runoff, runoff. The main objective of the bioretention cell is to attenuate peak runoff as well as to remove stormwater runoff pollutants. Construction of a bioretention area Stormwater is firstly directed into the designed treatment area, which conventionally consists of a sand bed (which serves as a transition to the actual soil), a filter media layer (which consists of layered materials of various composition), and plants atop the filter media. Various soil amendment such as water treatment residue (WTR), Coconut husk, biochar etc have been proposed over the years. These materials were reported to have enhanced performance in terms of pollutant removal. Runoff passes first over or through a sand bed, which slows the runoff's velocity, distributes it evenly along the length of the ponding area, which consists of a surface organic matter, organic layer and/or groundcover and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioreactor
A bioreactor is any manufactured device or system that supports a biologically active environment. In one case, a bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical reaction, chemical process is carried out which involves organisms or biochemistry, biochemically active chemical substance, substances derived from such organisms. This process can either be Aerobic organism, aerobic or Anaerobic organism, anaerobic. These bioreactors are commonly cylindrical, ranging in size from litres to cubic metres, and are often made of stainless steel. It may also refer to a device or system designed to grow Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues in the context of cell culture. These devices are being developed for use in tissue engineering or biochemical engineering, biochemical/bioprocess engineering, bioprocess engineering. On the basis of mode of operation, a bioreactor may be classified as batch reactor, batch, fed-batch, fed batch or continuous reactor, continuous (e.g. a continuous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |