|
List Of Stars In Circinus ...
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Circinus, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also * List of stars by constellation References * * * * * * * {{Stars of Circinus *List Circinus Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass, referring to the drafting tool used for drawing circles (it should not be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Circini
Beta Circini, Latinized from β Circini, is an A-type main sequence star and is the second-brightest star in the constellation of Circinus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of approximately 4.069, which is bright enough to be viewed with the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 35.17 mas as seen from the Earth, it is located about 93 light years from the Sun. With a stellar classification of A3 Va, this is an A-type main-sequence star. It is between 370 and 500 million years old with around 1.3 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 19 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ... of 8,676 K. It has one known sub-stellar companion. Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Circini
Eta Circini, Latinisation of names, Latinized from η Circini, is the Bayer designation for a solitary star located in the southern constellation of Circinus (constellation), Circinus. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.17. The distance to this star, as determined from an annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of 11.82 milliarcsecond, mas, is around 276 light years. This is an stellar evolution, evolved G-type star, G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. It is radiating an estimated 64 times the solar luminosity from its stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 4,954 K. References External links *http://server3.wikisky.org/starview?object_type=1&object_id=2194 {{DEFAULTSORT:Eta Circini G-type giants, Circini, Eta Circinus Bayer objects, Circini, Eta Henry Draper Catalogue objects, 132905 Hipparcos objects, 073776 Bright Star Catalogue objects, 5593 Durchmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Circini
Theta Circini (θ Cir), is a binary star located in the southern constellation of Circinus, to the northwest of Alpha Circini. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.110. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 11.82 mas, it is located at a distance of about 276 light years from the Sun. This is an astrometric binary star system with an orbital period of about 39.6 years, an eccentricity of 0.3, and a semimajor axis of 85.64 mas. The pair show a combined stellar classification of B3 Ve, which matches a B-type main sequence star. The 'e' suffix on the class indicates this is a Be star. Alternate classifications include B4 Vnp and B4npe, with the 'n' indicating broad ("nebulous") absorption line A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algol Variable
Algol variables or Algol-type binaries are a class of eclipsing binary stars that are similar to the prototype member of this class, β Persei (Beta Persei, Algol). An Algol binary is a system where both stars are near-spherical such that the timing of the start and end of the eclipses is well-defined. The primary is generally a main sequence star well within its Roche lobe. The secondary may also be a main sequence star, referred to as a detached binary or it may an evolved star filling its Roche lobe, referred to as a semidetached binary. When the cooler component passes in front of the hotter one, part of the latter's light is blocked, and the total brightness of the binary, as viewed from Earth, temporarily decreases. This is the primary minimum of the binary. Total brightness may also decrease, but less so, when the hotter component passes in front of the cooler one; this is the secondary minimum. The period, or time span between two primary minima, is very regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
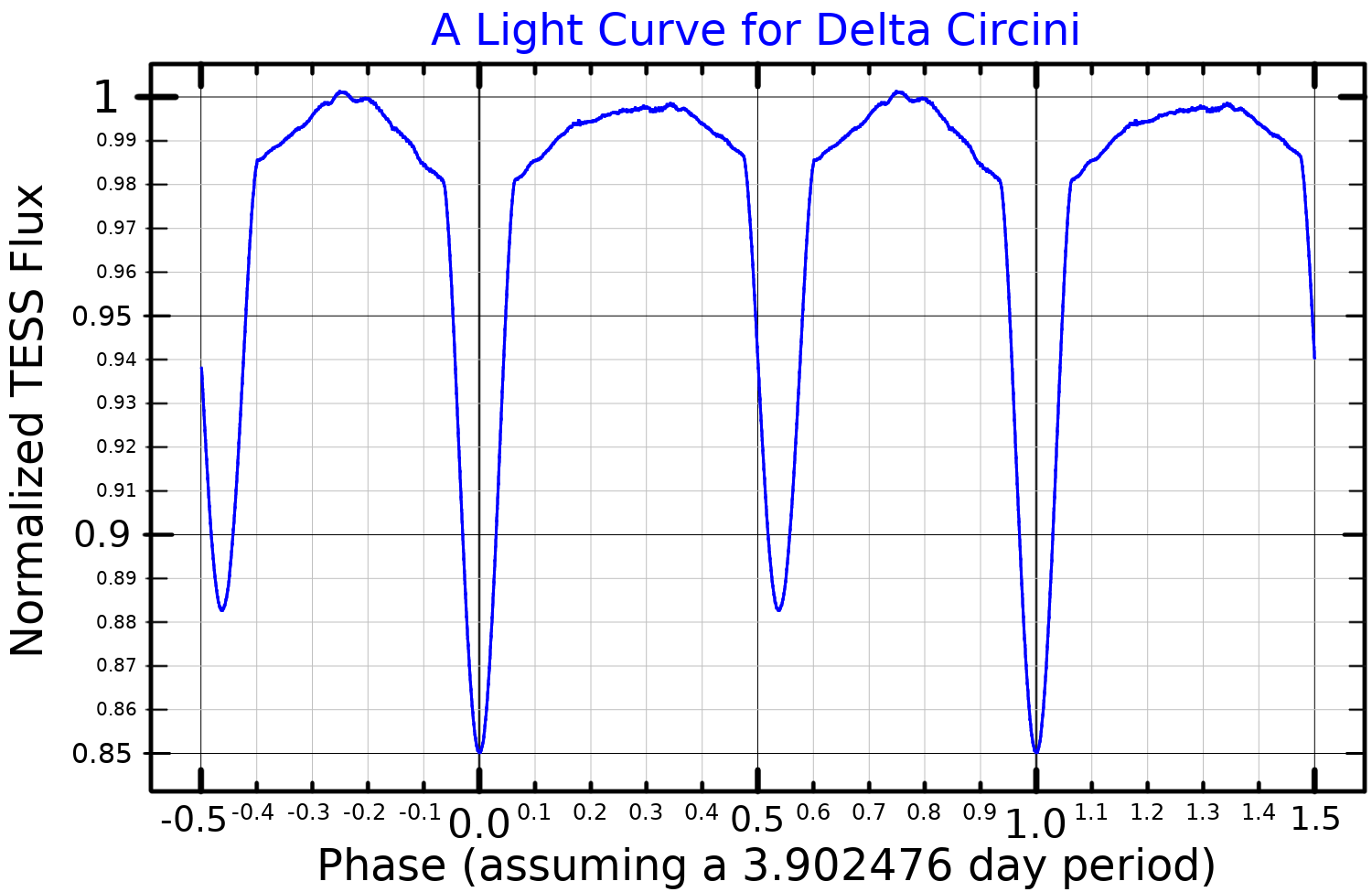
Delta Circini
Delta Circini (δ Cir), is a multiple star system located in the constellation Circinus. Delta Circini is also known as HR 5664, and HD 135240. The system has a combined apparent visual magnitude of +5.09, and is located at a distance of about 700 pc (2,300ly) from the Sun. Companions δ Circini A is a spectroscopic triple star, although the outer component has been resolved using the VLTI PIONIER instrument. The two inner components form an eclipsing binary A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in ... system. δ Circini B is a 13th magnitude companion nearly an arc-second away. It is unclear whether the two are physically associated and little is known about the fainter star although it has been reported to be a G5 main sequence star or giant. HD 135160 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Circini
Epsilon Circini, Latinized from ε Circini, is a solitary star located in the southern constellation of Circinus. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.86. The distance to this star, as determined by a measured annual parallax shift of , is around 428 light years. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −4 km/s. This is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K2.5 III. With the supply of hydrogen at its core exhausted, the star has cooled and expanded to 28.5 times the girth of the Sun. It radiates about 290 times the solar luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ... of 4,457 K. References {{DEF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Star
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes. This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a binary system of stars in mutual orbit, gravitationally bound to each other) or is an ''optical double'', a chance line-of-sight alignment of two stars at different distances from the observer. Binary stars are important to stellar astronomers as knowledge of their motions allows direct calculation of stellar mass and other stellar parameters. The only (possible) case of "binary star" whose two components are separately visible to the naked eye is the case of Mizar and Alcor (though actually a multiple-star system), but it is not known for sure whether Mizar and Alcor are gravitationally bound. Since the beginning of the 1780s, both professional and amateur double star observers have telescopically measured the distances and angles betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae Variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae. Variability γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically have amplitudes of the order of a magnitude. For example, γ Cassiopeiae is usually about magnitude 2.5 and has varied between magnitudes 1.6 and 3.0. The variations are associated with changes in the spectrum between normal absorption spectra and Be star spectra, often also including shell star characteristics. Pleione and γ Cassiopeiae itself are both variable stars that have intermittent shell episodes where strong shell features appear in the spectrum and the brightness increases or decreases significantly. At other times the shell is not detectable in the spectrum, and even the emission lines may disappear. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) categorises γ Cassiopeiae stars as eruptive variables and describes them as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |