|
List Of Laboratory Biosecurity Incidents
This list of laboratory biosecurity incidents includes accidental laboratory-acquired infections and laboratory releases of lethal pathogens, containment failures in or during transport of lethal pathogens, and incidents of exposure of lethal pathogens to laboratory personnel, improper disposal of contaminated waste, and/or the escape of laboratory animals. The list is grouped by the year in which the accident or incident occurred and does not include every reported laboratory-acquired infection. See also * Biological hazard * Biosafety level * Laboratory safety Many laboratories contain significant risks, and the prevention of laboratory accidents requires great care and constant vigilance. Examples of risk factors include high voltages, high and low pressures and temperatures, corrosive and toxic chem ... * List of anthrax outbreaks * Select agent * Cambridge Working Group External links A Review of Laboratory-Acquired Infections in the Asia-Pacific: Understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory-acquired Infection
A laboratory-acquired infection or LAI is an infection that is acquired in a laboratory, usually as part of a medical research facility or hospital. Causes There are various microbes, viruses, fungi, and parasites that can infect a host via several routes of transmission. Prevention Laboratory facilities handling microbes, viruses and/or parasites adhere to various biosecurity measures in order to prevent biosecurity accidents and incidents. OECD Best Practice Guidelines for Biological Resource Centres In 2001, experts from OECD countries created a consensus report called, calling upon "national governments to undertake actions to bring the BRC concept into being in concert with the international scientific community". The report details "Biological Resource Centres" (BRCs) as "repositories and providers of high-quality biological materials and information". History The first laboratory-acquired infection was reported at the time of Pasteur and Koch in 1890. Prior to 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marburg Virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the '' Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus '' Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring biosafety level 4-equivalent containment). In the United States, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group. The virus can be transmitted by exposure to one species of fruit bats or it can be transmitted between people via body fluids through unprotected sex and broken skin. The disease can cause haemorrhage, fever, and other symptoms similar to Ebola, which belongs to the same family of viruses. According to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibadan
Ibadan (, ; ) is the Capital city, capital and most populous city of Oyo State, in Nigeria. It is the List of Nigerian cities by population, third-largest city by population in Nigeria after Lagos and Kano (city), Kano, with a total population of 3,649,000 as of 2021, and nearly 4 million within its Metropolitan area, metropolitan area. At 3,080 square kilometres it is the country's largest city by land area. At the time of Nigeria's independence in 1960, Ibadan was the largest and most populous city in the country, and the second-most populous in Africa behind Cairo. Ibadan is ranked one of the fastest-growing cities in sub-Saharan Africa, according to the UN Human Settlements Program (2022). It is also ranked third in West Africa in the tech startups index. Ibadan joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2016. Ibadan is located in south-western Nigeria, inland northeast of Lagos and southwest of Abuja, the federal capital. It is a prominent Public transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift Valley Fever
Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a viral disease of humans and livestock that can cause mild to severe symptoms. The mild symptoms may include: fever, muscle pains, and headaches which often last for up to a week. The severe symptoms may include: loss of sight beginning three weeks after the infection, infections of the brain causing severe headaches and confusion, and bleeding together with liver problems which may occur within the first few days. Those who have bleeding have a chance of death as high as 50%. The disease is caused by the RVF virus. It is spread by either touching infected animal blood, breathing in the air around an infected animal being butchered, drinking raw milk from an infected animal, or the bite of infected mosquitoes. Animals like cows, sheep, goats, and camels may be affected. In these animals it is spread mostly by mosquitoes. It does not appear that one person can infect another. The disease is diagnosed by finding antibodies against the virus or the viru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orungo Virus
Orungo virus (ORUV) is an arbovirus of the genus ''Orbivirus'' and the family ''Sedoreoviridae''. There are four known subtypes of Orungo virus designated Orungo-1 (ORUV-1), Orungo-2 (ORUV-2), Orungo-3 (ORUV-3), and Orungo-4 (ORUV-4). It was first isolated by the Uganda Virus Research Institute in Entebbe, Uganda by Oyewale Tomori and colleagues. Antibodies to the virus have been found in humans, monkeys, sheep, and cattle. References Orbiviruses {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
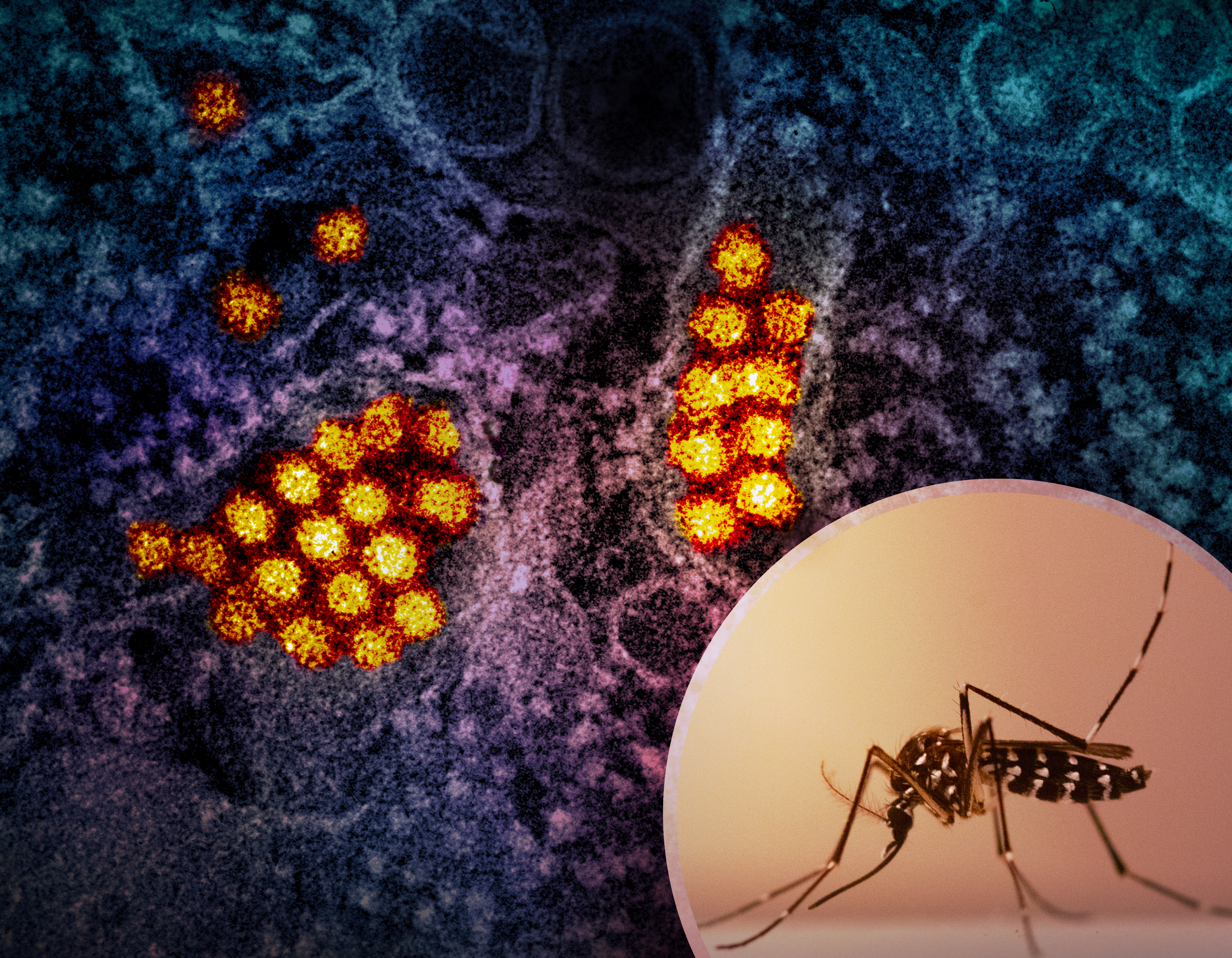
Dengue Virus
Dengue virus (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''; genus '' Flavivirus''. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, and a reported fifth has yet to be confirmed,Dwivedi, V. D., Tripathi, I. P., Tripathi, R. C., Bharadwaj, S., & Mishra, S. K. (2017). Genomics, proteomics and evolution of ''Dengue virus''. Briefings in functional genomics.16(4): 217–227, https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elw040 all of which can cause the full spectrum of disease. Nevertheless, the mainstream scientific community's understanding of dengue virus may be simplistic as, rather than distinct antigenic groups, a continuum appears to exist. This same study identified 47 strains of ''dengue virus''. Additionally, coinfection with and lack of rapid tests for Zika virus and chikungunya complicate matters in real-world infections. ''Dengue virus'' has increased dramatically within the last 20 years, becoming one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesselsbron Virus
Wesselsbron (WSL) virus is an arthropod-borne virus in the genus ''Flavivirus'' of the family ''Flaviviridae'' that causes Wesselsbron disease in cattle, sheep, goats, camels, pigs, donkeys, horses, ostriches, and wild ruminants with occasional incidental spillover to humans. It is transmitted by mosquitoes in the genus ''Aedes'' including ''A. caballus'' and '' A. circumluteolus''. __TOC__ History The first known outbreak was reported in 1955 on a sheep farm in the town of Wesselsbrons in Orange Free State Province, South Africa after an increase of lamb deaths and ewe abortions. Since the flock had been vaccinated 2 weeks before for protection against the Rift Valley virus, the possibility of a "new" disease was not put into consideration; the vaccine was assumed to be the culprit. Although they both share similarities, the WSL virus was isolated as distinct from the Rift Valley virus after the examination of a dead lamb's liver and brain. Geographical Distribution Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). The disease was first identified in 1952 in Tanzania and named based on the Kimakonde words for "to become contorted". Chikungunya has become a global health concern due to its rapid geographic expansion, recurrent outbreaks, the lack of effective antiviral treatments, and potential to cause high morbidity. Chikungunya virus is closely related to O'nyong'nyong virus (ONNV), which shares similar genetic and clinical characteristics. Symptoms include fever and joint pain. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a rash. Symptoms usually improve within a week; however, occasionally the joint pain may last for months or years. The risk of death is around 1 in 1,000. The very young, old, and those with other health problems are at risk of more severe disease. The virus is spread between people by two species of mosquitos in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aral Sea
The Aral Sea () was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south, which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up into desert by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhstan and the Karakalpakstan autonomous region of Uzbekistan. The name roughly translates from Mongolic and Turkic languages to "Sea of Islands", a reference to the large number of islands (over 1,100) that once dotted its waters. The Aral Sea drainage basin encompasses Uzbekistan and parts of Afghanistan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. Formerly the third-largest lake in the world with an area of , the Aral Sea began shrinking in the 1960s after the rivers that fed it were diverted by Soviet irrigation projects. By 2007, it had declined to 10% of its original size, splitting into four lakes: the North Aral Sea, the eastern and western basins of the once far larger South Aral Sea, and the smaller intermediate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1971 Aral Smallpox Incident
The Aral smallpox incident was a 30 July 1971 outbreak of the viral disease which occurred as a result of a field test at a Soviet biological weapons (BW) facility on an island in the Aral Sea. The incident sickened ten people, of whom three died, and came to widespread public notice only in 2002. Background In 1954, an existing biological weapons test site originally constructed on Vozrozhdeniya Island in the Aral Sea in 1948 was greatly expanded by the Soviet Ministry of Defence, including to the neighboring Komsomolskiy Island, and named Aralsk-7. A field scientific research laboratory to conduct biological experiments was expanded, and the town of Kantubek was constructed to house employees and scientists. Bio-agents tested there included ''Bacillus anthracis'', ''Coxiella burnetii'', ''Francisella tularensis'', ''Brucella suis'', ''Rickettsia prowazekii'', '' Variola major'' (smallpox), ''Yersinia pestis'', botulinum toxin, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. (By 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |