|
Line Splice
In telecommunications, a line splice is a method of connecting electrical cables (electrical splice) or optical fibers (optical splice). Splices are often housed in sleeves to protect against external influences. Splicing of copper wires The splicing of copper wires happens in the following steps: * The cores are laid one above the other at the junction. * The core insulation is removed. * The wires are wrapped two to three times around each other ( twisting). * The bare veins on a length of about 3 cm "strangle" or "twist". In some cases, the strangulation is soldered. * To isolate the splice, an insulating sleeve made of paper or plastic is pushed over it. The splicing of copper wires is mainly used on paper insulated wires. LSA techniques (LSA: soldering, screwing and stripping free) are used to connect copper wires, making the copper wires faster and easier to connect. LSA techniques include: * Wire connection sleeves (AVH = Adernverbindungshülsen) and other cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Fusion Splice
Fusion splicing is the act of joining two optical fibers end-to-end. The goal is to fuse the two fibers together in such a way that light passing through the fibers is not scattered or reflected back by the splice, and so that the splice and the region surrounding it are almost as strong as the intact fiber. The source of heat used to melt and fuse the two glass fibers being spliced is usually an electric arc, but can also be a laser, a gas flame, or a tungsten filament through which current is passed. Governing standards ANSI/EIA/TIA-455 See also * Fiber-optic communication * Optical fiber connector * Optical time-domain reflectometer An optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) is an optoelectronic instrument used to characterize an optical fiber. It is the optical equivalent of an electronic time domain reflectometer which measures the impedance of the cable or transmissi ... References * Further reading * "How to Precision Clean All Fiber Optic Connections": ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Electrical Wiring
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of Electrical cable, cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure. Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and installation. Allowable wire and electrical cable, cable types and sizes are specified according to the circuit operating voltage and electric current capability, with further restrictions on the environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature range, moisture levels, and exposure to sunlight and chemicals. Associated circuit protection, control, and distribution devices within a building's wiring system are subject to voltage, current, and functional specifications. Wiring safety codes vary by locality, country, or region. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to harmonise wiring standards among member countries, but significant variations in design and installation requirements still exist. Wiring methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical, or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry. Chemical processes by main basic material Certain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum, and fertilizer). However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of the chemical reactions. Cement (the paste within concrete) * Calcination – Limestone, which is largely composed of fossilized calcium carbonate (CaCO3), breaks down at high temperatures into useable calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (), which gets released as a by-product. This chemical reaction, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
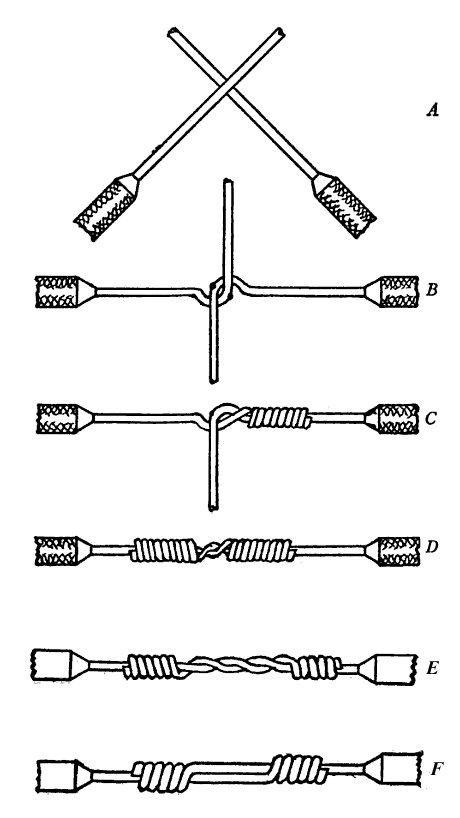 |
Western Union Splice
The Western Union splice or lineman splice is a method of joining electrical cable, developed in the nineteenth century during the introduction of the telegraph and named for the Western Union telegraph company. This method can be used where the cable may be subject to loading stress. The wrapping pattern design causes the join to tighten as the conductors pull against each other. History In 1915, ''Practical Electric Wiring'' described it as being "by far the most widely used splice" in practical electrical wiring work. NASA included the splice in its technical standard ''Workmanship Standard for Crimping, Interconnecting Cables, Harnesses, and Wiring'', first produced in 1998. Construction The 1915 textbook ''Practical Electric Wiring'' describes the construction of the Western Union splice; short tie and long tie. The short tie splice has it being formed after stripping the insulation from a pair of wires for several inches, each, crossing the wires left over right as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mechanical Splice
A mechanical splice is a junction of two or more optical fibers that are aligned and held in place by a self-contained assembly (usually the size of a large carpenter's nail). The fibers are not permanently joined, just precisely held together so that light can pass from one to another. This impermanence is an important advantage over fusion splicing, as splice loss, the amount of power that the splice fails to transmit, can be better measured and prevented. Designs and variations There are several designs in use for mechanical splicing, varying based on the method of fiber alignment; four common methods, according to the Fiber Optic Association, are the capillary tube, V-groove, elastometric, and rotary splice. * A capillary tube splice aligns the optical fibers inside of a glass tube, connecting them with a simple adhesive that matches the refractive index of the fibers. This setup allows for manual adjustments and is often a component in the more complex rotary splice. * A V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Fusion Splicing
Fusion splicing is the act of joining two optical fibers end-to-end. The goal is to fuse the two fibers together in such a way that light passing through the fibers is not scattered or reflected back by the splice, and so that the splice and the region surrounding it are almost as strong as the intact fiber. The source of heat used to melt and fuse the two glass fibers being spliced is usually an electric arc, but can also be a laser, a gas flame, or a tungsten filament through which current is passed. Governing standards ANSI/EIA/TIA-455 See also * Fiber-optic communication * Optical fiber connector An optical fiber connector is a device used to link optical fibers, facilitating the efficient transmission of light signals. An optical fiber connector enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing. They come in various types li ... * Optical time-domain reflectometer References * Further reading * "How to Precision Clean All Fiber Optic Connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Optical Time-domain Reflectometry
An optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) is an optoelectronic instrument used to characterize an optical fiber. It is the optical equivalent of an electronic time domain reflectometer which measures the impedance of the cable or transmission line under test. An OTDR injects a series of optical pulses into the fiber under test and extracts, from the same end of the fiber, light that is scattered ( Rayleigh backscatter) or reflected back from points along the fiber. The scattered or reflected light that is gathered back is used to characterize the optical fiber. The strength of the return pulses is measured and integrated as a function of time, and plotted as a function of length of the fiber. Reliability and quality of OTDR equipment The reliability and quality of an OTDR is based on its accuracy, measurement range, ability to resolve and measure closely spaced events, measurement speed, and ability to perform satisfactorily under various environmental extremes and after v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Single-mode Fiber
In fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber, also known as fundamental- or mono-mode, is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single mode of light - the transverse mode. Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions. These modes define the way the wave travels through space, i.e. how the wave is distributed in space. Waves can have the same mode but have different frequencies. This is the case in single-mode fibers, where we can have waves with different frequencies, but of the same mode, which means that they are distributed in space in the same way, and that gives us a single ray of light. Although the ray travels parallel to the length of the fiber, it is often called transverse mode since its electromagnetic oscillations occur perpendicular (transverse) to the length of the fiber. The 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Charles K. Kao for his th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Fiber-optic Connector
An optical fiber connector is a device used to link optical fibers, facilitating the efficient transmission of light signals. An optical fiber connector enables quicker connection and disconnection than splicing. They come in various types like SC, LC, ST, and MTP, each designed for specific applications. In all, about 100 different types of fiber optic connectors have been introduced to the market. These connectors include components such as ferrules and alignment sleeves for precise fiber alignment. Quality connectors lose very little light due to reflection or misalignment of the fibers. Optical fiber connectors are categorized into single-mode and multimode types based on their distinct characteristics. Industry standards ensure compatibility among different connector types and manufacturers. These connectors find applications in telecommunications, data centers, and industrial settings. Application Optical fiber connectors are used to join optical fibers where a connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Electrical Cable
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the Work (physics), work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Fiber-optic Cable
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for fiber-optic communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building. Design Optical fiber consists of a core and a cladding layer, selected for total internal reflection due to the difference in the refractive index between the two. In practical fibers, the cladding is usually coated with a layer of acrylate polymer or polyimide. This coating protects the fiber from damage but does not contribute to its optical waveguide properties. Individual coated fibers (or fibers formed into ribbons or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |