|
Lincoln Peak (Nevada)
Lincoln Peak is an mountain summit in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. Description Lincoln Peak is part of the Snake Range which is a subrange of the Great Basin Ranges. The peak is located in Great Basin National Park and south of Wheeler Peak. It ranks as the seventh-highest peak in the park and 17th-highest in Nevada. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises above Lincoln Canyon in and over above Spring Valley in . The Highland Ridge Trail traverses the west slope of the peak, approximately 600 feet below the summit. This mountain's toponym has been officially adopted by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names. The southern tip of the Snake Range is in Lincoln County, Nevada, which is named for Abraham Lincoln. Climate Lincoln Peak is set within the Great Basin Desert which has hot summers and cold winters. The desert is an example of a cold desert climate as the desert's elevation makes temperatures cooler than lower elevation deserts. Due to the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Range
The Snake Range is a mountain range in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. The south-central portion of the range is included within Great Basin National Park, with most of the remainder included within the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest. The range reaches a maximum elevation of at the summit of Wheeler Peak, the tallest independent mountain within Nevada and the second highest point within the state (the highest point being Boundary Peak). The range also contains four of the five highest mountain peaks in Nevada, including all peaks greater than except for Boundary Peak. Geography Typical of other ranges in the Basin and Range Province, the Snake Range runs in a north–south direction, for approximately . To the west are Spring Valley and the Schell Creek Range, and to the east across the Utah border are Snake Valley and the Confusion Range. Sacramento Pass () is where U.S. Route 6- 50, the "Loneliest Highway in America", crosses the range. It is the principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Relief
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Bathymetry is the study of underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, drainage characteristics, drainage systems, groundwater systems, water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-thousanders Of The United States
Three-thousanders are mountains with a height of between , but less than above sea level. Similar terms are commonly used for mountains of other height brackets e. g. four-thousanders or eight-thousanders. In Britain, the term refers to mountains above . Climatological significance In temperate latitudes three-thousanders play an important role, because even in summer they lie below the zero degree line for weeks. Thus the chains of three-thousanders always form important climatic divides and support glaciation - in the Alps the contour is roughly the general limit of the "nival step"; only a few glaciated mountains are under (the Dachstein, the easternmost glaciated mountain in the Alps, is, at , not a three-thousander). In the Mediterranean, however, the three-thousanders remain free of ice and, in the tropics, they are almost insignificant from a climatic perspective; here the snow line lies at around to , and in the dry continental areas (Trans-Himalayas, Andes) it m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Nevada
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are inselberg, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. mountain formation, Mountains are formed through tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosystems of mountains: different elevations hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Basin
The Great Basin () is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrographic, biological, floristic, physiographic, topographic, and ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature of the landform as "having no connection to the ocean". The hydrographic defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Peak Formation
The Lincoln Peak Formation is a geologic formation in Nevada. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period. See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Nevada * Paleontology in Nevada Paleontology in Nevada refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the United States, U.S. state of Nevada. Nevada has a rich fossil Fossil record, record of plants and animal life spanning the past 650 million ... References * Cambrian geology of Nevada Cambrian southern paleotropical deposits {{Cambrian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
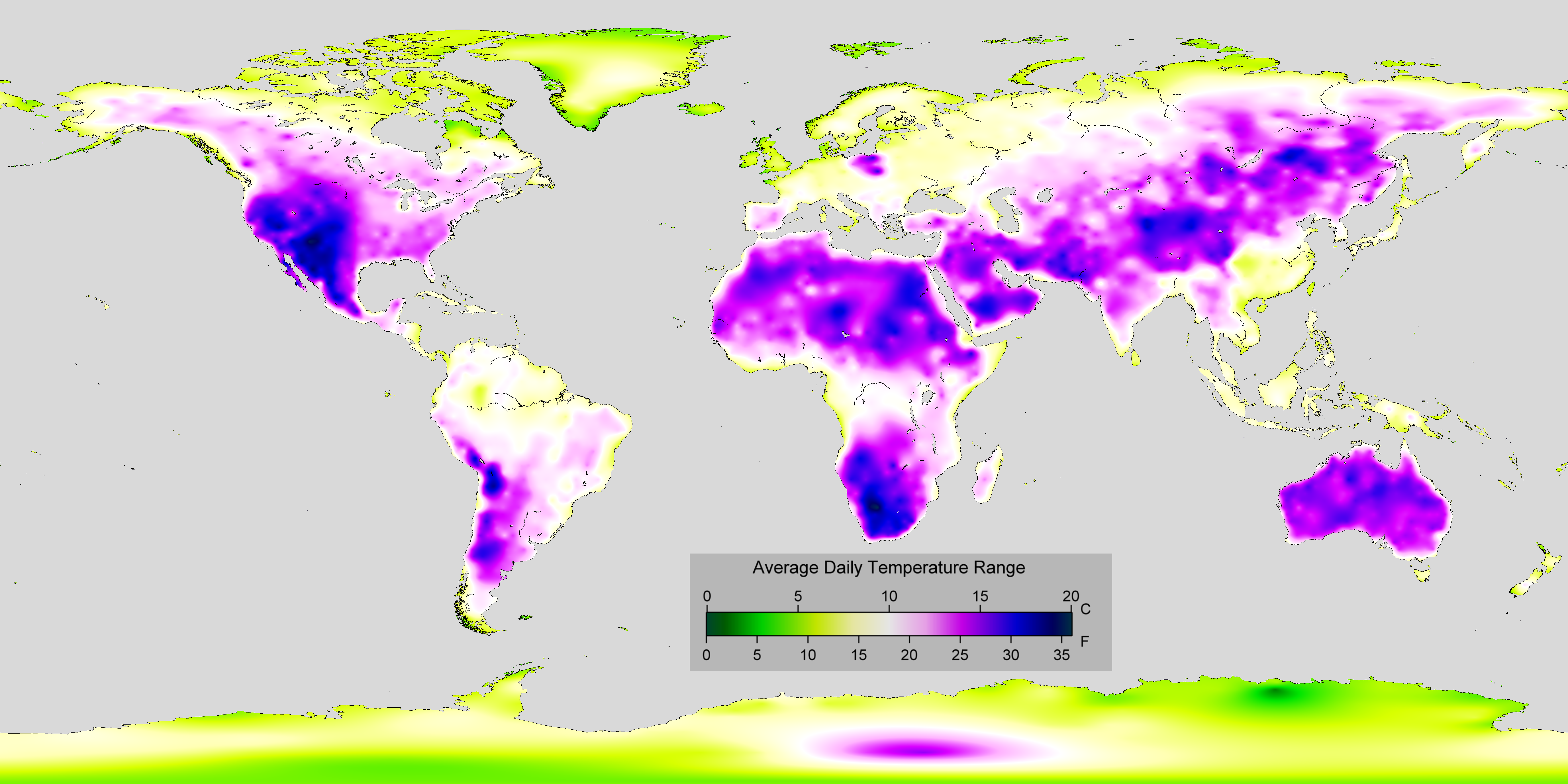
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of Earth's land area, hot deserts are the second-most common type of climate on Earth after the Polar climate. There are two variations of a desert climate according to the Köppen climate classification: a hot desert climate (''BWh''), and a cold desert climate (''BWk''). To delineate "hot desert climates" from "cold desert climates", a mean annual temperature of is used as an isotherm so that a location with a ''BW'' type climate with the appropriate temperature above this isotherm is classified as "hot arid subtype" (''BWh''), and a location with the appropriate temperature below the isotherm is classified as "cold a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Basin Desert
The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range in the western United States. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, and the Central Basin and Range ecoregion defined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and United States Geological Survey. It is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters. The desert spans large portions of Nevada and Utah, and extends into eastern California. The desert is one of the four biologically defined deserts in North America, in addition to the Mojave Desert, Mojave, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Chihuahuan Deserts. Basin and range topography characterizes the desert: wide valleys bordered by parallel mountain ranges generally oriented north–south. There are more than 33 peaks within the desert with summits higher than , but valleys in the region are also high, most with elevations above . The biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War, defeating the Confederate States of America and playing a major role in the End of slavery in the United States, abolition of slavery. Lincoln was born into poverty in Kentucky and raised on the American frontier, frontier. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Illinois state Illinois House of Representatives, legislator, and U.S. representative. Angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854, which opened the territories to slavery, he became a leader of the new History of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the Lincoln–Douglas debates, 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen A. Douglas. Lincoln won the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 presidential election, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln County, Nevada
Lincoln County is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 4,499, making it the fourth-least populous county in Nevada. Its county seat is Pioche, Nevada, Pioche. Like many counties in Nevada, it is dry and sparsely populated, though notable for containing the Area 51 government Air Force base. History Lincoln County was established in 1866 after Congress enlarged Nevada by moving its state line eastward and southward at the expense of Utah Territory, Utah and Arizona Territory, Arizona territories. It is named after Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States. Original legislation called for the creation of a "Stewart County", after Nevada Senator William M. Stewart, but this was later changed in a substitute bill. Crystal Springs, Nevada, Crystal Springs was the county's first county seat, seat in 1866, followed by Hiko, Nevada, Hiko in 1867 and Pioche, Nevada, Pioche in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |