|
Limerick (poetry)
A limerick ( ) is a form of verse that appeared in England in the early years of the 18th century. In combination with a refrain, it forms a limerick (song), limerick song, a traditional humorous drinking song often with obscene verses. It is written in five-line, predominantly Anapaest, and amphibrach trimeter with a strict rhyme scheme of AABBA, in which the first, second and fifth line rhyme, while the third and fourth lines are shorter and share a different rhyme. It was popularized by Edward Lear in the 19th century, although he did not use the term. From a Folklore, folkloric point of view, the form is essentially transgressive; violation of taboo is part of its function. According to Gershon Legman, who compiled the largest and most scholarly anthology, this folk form is always obscene and the exchange of limericks is almost exclusive to comparatively well-educated men. Women are figuring in limericks almost exclusively as "villains or victims". Legman dismissed the "clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Thomlinson
John Thomlinson (1692–1761) was an English clergyman best known for his diary, covering 1715 to 1722. Life Thomlinson was born in the small farming village of Blencogo, near Wigton, Cumberland, on 29 September 1692, the eldest son of William Thomlinson (1657–1743). He was educated at Appleby-in-Westmorland and at St John's College, Cambridge, Matriculation, matriculating in 1709. Ordained a deacon in 1717, he obtained a Curate, curacy at Rothbury, Northumberland to one of his uncles, also John Thomlinson (1651–1720), who was rector there. He remained at Rothbury after his uncle's death in 1720, and in 1721, for unknown reasons, he moved to Navestock, Essex. The following year he was appointed rector of Glenfield, Leicestershire, doubtless thanks to his marriage to Catherine Winstanley, the daughter of his patron, James Winstanley of Braunston-in-Rutland, Braunston, Rutland. Thomlinson held this post until his death in Glenfield on 5 February 1761. The Diary The diary was st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot (prosody)
The foot is the basic repeating rhythmic unit that forms part of a line of verse in most Indo-European traditions of poetry, including English accentual-syllabic verse and the quantitative meter of classical ancient Greek and Latin poetry. The unit is composed of syllables, and is usually two, three, or four syllables in length. The most common feet in English are the iamb, trochee, dactyl, and anapaest. The foot might be compared to a bar, or a beat divided into pulse groups, in musical notation. A metrical foot is, in classical poetry, a combination of two or more short or long syllables in a specific order; although this "does not provide an entirely reliable standard of measurement" in heavily accented Germanic languages such as English. In these languages it is defined as a combination of one stressed and one or two unstressed syllables in a specific order. In general, lines of verse can be classified according to the number of feet they contain, using the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croom, County Limerick
Croom () is a village in County Limerick, Ireland. It is located just off the N20 (which has bypassed the town since 2001) on the River Maigue. It is 8 km southeast of Adare on the N20. The village is in a townland and civil parish of the same name. History Cromadh (now Croom) was a village in the territory of the Uí Fidgenti, and one of the seats of the O’Donovans of the Ui Fidgheinte, which flourished from the late 4th century to the mid 12th century. A hermitage, Dísert Óengusa, was founded nearby by Óengus of Tallaght around the year AD 780. The townland is located on the River Maigue, which although now having a tidal flow only to Adare, in ancient years the river had a tidal flow past Croom, making it a transit route for the Viking ships traversing inland from the Shannon during the 9th and 10th centuries. Contacts arising along the Maigue River between Danish Vikings and the Uí Donnabháins provide an insight into the alliance between the two groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Limerick
County Limerick () is a western Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. It is named after the city of Limerick. Limerick City and County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local council for the county. The county's population at the 2022 census was 209,536 of whom 102,287 lived in Limerick City, the county capital. Geography Limerick borders four other counties: County Kerry, Kerry to the west, County Clare, Clare to the north, County Tipperary, Tipperary to the east, and County Cork, Cork to the south. It is the fifth-largest of Munster's six counties in size and the second-largest by population. The River Shannon flows through the city of Limerick, then continues as the Shannon Estuary until it meets the Atlantic Ocean past the far western end of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
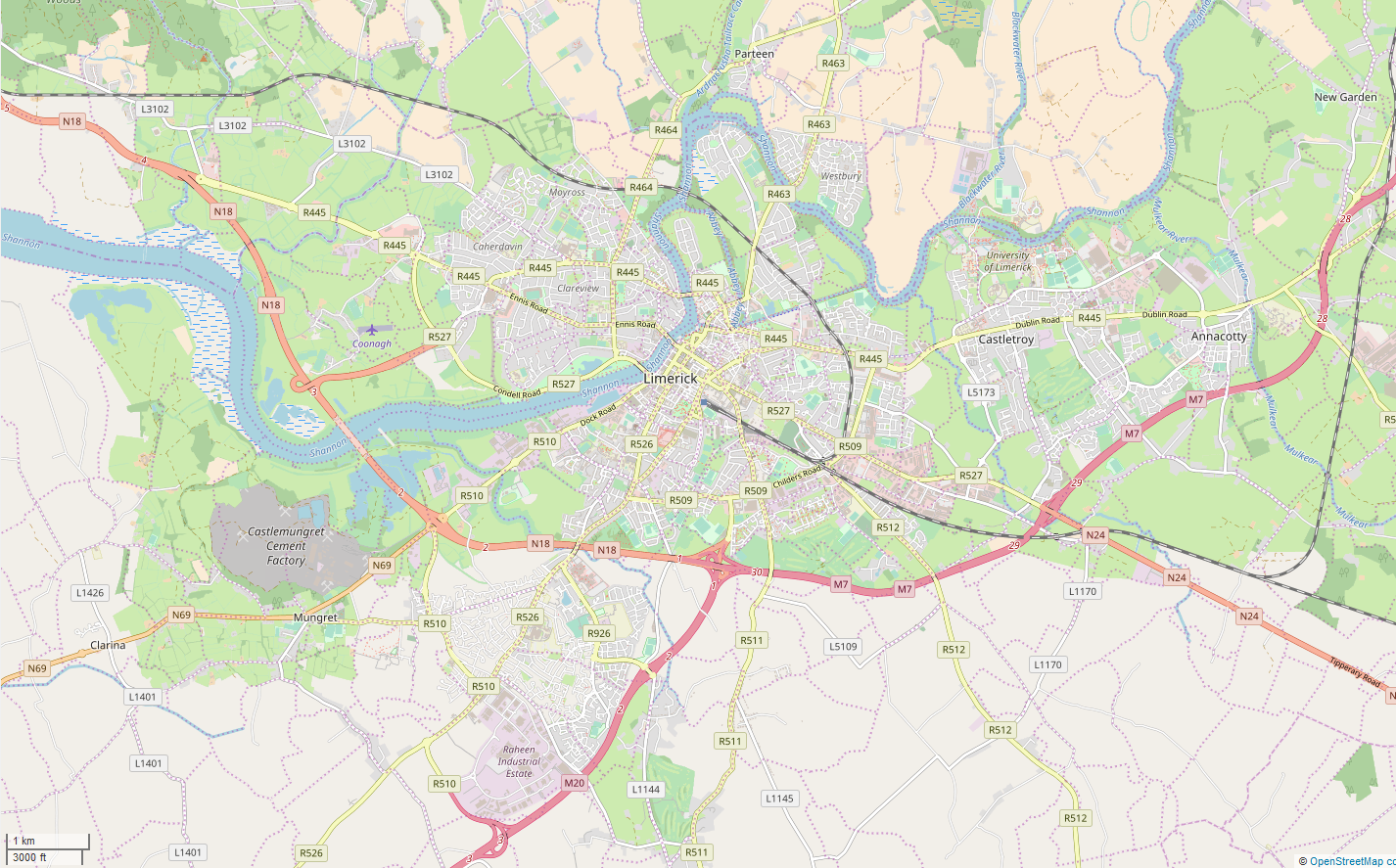
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. With a population of 102,287 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, Limerick is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, third-most populous urban area in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland. It was founded by Scandinavian settlers in 812, during the Viking Age. The city straddles the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, Limerick, King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey River, Limerick, Abbey Rivers. Limerick is at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the Local gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Abercrombie (linguist)
David Abercrombie (19 December 1909 – 4 July 1992) was a British phonetician who established the Department of Phonetics at the University of Edinburgh. He was a student of J. R. Firth and Daniel Jones. He retired as Professor of Phonetics in 1980 and died in Edinburgh at the age of 82. Biography Abercrombie was born in Birkenhead on 19 December 1909. His father, Lascelles Abercrombie was a poet and his mother was Catherine, née Gwatkin, one of his three younger siblings was Michael Abercrombie, biologist. He grew up in Ryton, Gloucestershire, before returning to Cheshire on the outbreak of World War I, and moving to Leeds in 1922, when his father became the chair of English Literature at Leeds University The University of Leeds is a public research university in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It was established in 1874 as the Yorkshire College of Science. In 1884, it merged with the Leeds School of Medicine (established 1831) and was renamed .... He attended Leeds G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Play
Word play or wordplay (also: play-on-words) is a literary technique and a form of wit in which words used become the main subject of the work, primarily for the purpose of intended effect or amusement. Examples of word play include puns, phonetic mix-ups such as spoonerisms, obscure words and meanings, clever rhetorical excursions, oddly formed sentences, double entendres, and telling character names (such as in the play '' The Importance of Being Earnest'', ''Ernest'' being a given name that sounds exactly like the adjective ''earnest''). Word play is quite common in oral cultures as a method of reinforcing meaning. Examples of text-based ( orthographic) word play are found in languages with or without alphabet-based scripts, such as homophonic puns in Mandarin Chinese. Techniques ; Tom Swifties: A form of humorous writing where adverbs are chosen to reflect the nature of the situation in a punning way. "Hurry up and get to the back of the ship", Tom said sternly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assonance
Assonance is the repetition of identical or similar phonemes in words or syllables that occur close together, either in terms of their vowel phonemes (e.g., ''lean green meat'') or their consonant phonemes (e.g., ''Kip keeps capes ''). However, in American usage, ''assonance'' exclusively refers to this phenomenon when affecting vowels, whereas, when affecting consonants, it is generally called ''consonance''. The two types are often combined, as between the words ''six'' and ''switch'', which contain the same vowel and similar consonants. If there is repetition of the same vowel or some similar vowels in literary work, especially in stressed syllables, this may be termed "vowel harmony" in poetry (though linguists have a different definition of "vowel harmony"). A special case of assonance is rhyme, in which the endings of words (generally beginning with the vowel sound of the last stressed syllable) are identical—as in ''fog'' and ''log'' or ''history'' and ''mystery''. Vocal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliteration
Alliteration is the repetition of syllable-initial consonant sounds between nearby words, or of syllable-initial vowels if the syllables in question do not start with a consonant. It is often used as a literary device. A common example is " Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers". Historical use The word ''alliteration'' comes from the Latin word ''littera'', meaning "letter of the alphabet". It was first coined in a Latin dialogue by the Italian humanist Giovanni Pontano in the 15th century. Alliteration is used in the alliterative verse of Old English poems like Beowulf, Middle English poems like Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, Old Norse works like the Poetic Edda, and in Old High German, Old Saxon, and Old Irish. It was also used as an ornament to suggest connections between ideas in classical Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit poetry. Today, alliteration is used poetically in various languages around the world, including Arabic, Irish, German, Mongolian, Hungari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Rhyme
In poetry, internal rhyme, or middle rhyme, is rhyme that occurs within a single line of verse, or between internal phrases across multiple lines. By contrast, rhyme between line endings is known as end rhyme. Internal rhyme schemes can be denoted with spaces or commas between lines. For example, denotes a three-line poem with the same internal rhyme on each line, and the same end rhyme on each line (which does not rhyme with the internal rhyme). Examples Poetry In the following limerick, each stressed syllable rhymes with another stressed syllable using one of three rhyme sets. Each rhyme set is indicated by a different highlight color. Note that the yellow rhyme set provides internal rhyme in lines 1, 2, and 5, and end rhymes in lines 3 and 4, but the blue set is entirely internal, and the pink is exclusively end rhymes. Each time alie for a She well that her are the Of the , and it , But this will ex More than , so some gape and . Samuel Taylor Coleridge's poem "Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term ''toponymy'' comes from / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876 in the context of geographical studies. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosody (poetry)
In poetry, metre ( Commonwealth spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) is the basic rhythmic structure of a verse or lines in verse. Many traditional verse forms prescribe a specific verse metre, or a certain set of metres alternating in a particular order. The study and the actual use of metres and forms of versification are both known as prosody. (Within linguistics, " prosody" is used in a more general sense that includes not only poetic metre but also the rhythmic aspects of prose, whether formal or informal, that vary from language to language, and sometimes between poetic traditions.) Characteristics An assortment of features can be identified when classifying poetry and its metre. Qualitative versus quantitative metre The metre of most poetry of the Western world and elsewhere is based on patterns of syllables of particular types. The familiar type of metre in English-language poetry is called qualitative metre, with stressed syllables coming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |