|
Lima-Hamilton
Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company's name is derived from the location of its main manufacturing plant in Lima, Ohio ( ). The shops were located between the Erie Railroad main line, the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line and the Nickel Plate Road main line and shops. The company produced the Shay geared logging steam locomotive, developed by Ephraim Shay, and for William E. Woodard's "Super Power" advanced steam locomotive concept – exemplified by the prototype 2-8-4 Berkshire, Lima demonstrator A-1. In World War II the Lima plant produced the M4A1 version of the M4 Sherman tank. History In 1878, James Alley contracted the Lima Machine Works to build a steam locomotive that Ephraim Shay had designed. In April 1880, Lima rebuilt Ephraim Shay's original design, using vertically side-mounted pistons mounted on the right, connected to a drive line on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
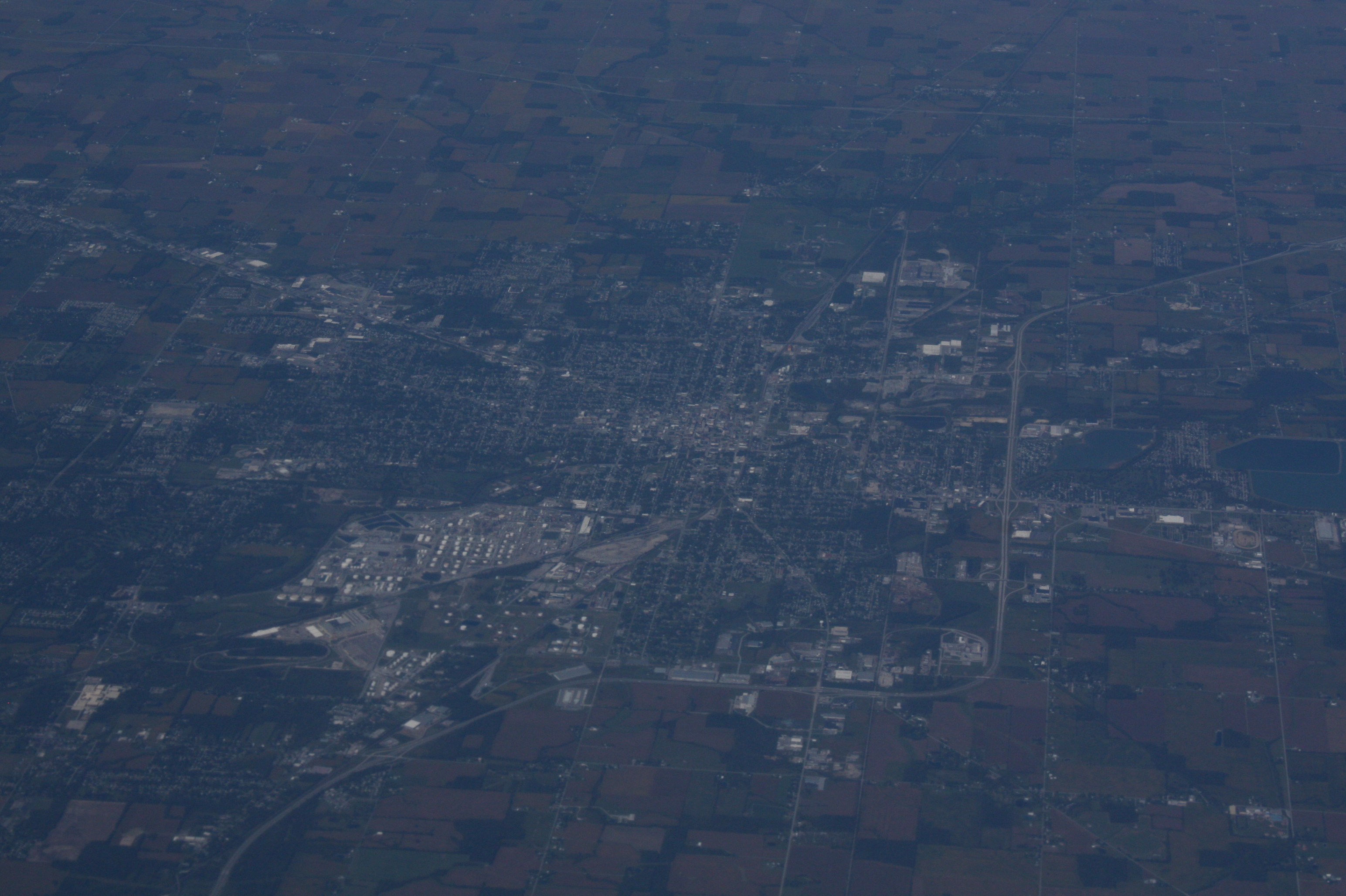
Lima, Ohio
Lima ( ) is a city in Allen County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 35,579. It is located in northwest Ohio along Interstate 75 in Ohio, Interstate 75, approximately north of Dayton, Ohio, Dayton, southwest of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo, and southeast of Fort Wayne, Indiana. Lima was founded in 1831. The Lima Army Tank Plant, officially called the Joint Systems Manufacturing Center, built in 1941, is the sole producer of the M1 Abrams. It is the principal city of the Lima metropolitan area, Ohio, Lima metropolitan area, which had 102,000 residents in 2020 and is included in the Lima–Van Wert–Wapakoneta, OH, combined statistical area, Lima–Van Wert–Wapakoneta combined statistical area. History Establishment In the years after the American Revolution, the Shawnee were the most prominent residents of west central Ohio, growing in numbers and permanency after the 1794 Treaty of Greenville. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shay Locomotive
The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a ''geared steam locomotive''. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track. Development Ephraim Shay (1839–1916), was a schoolteacher, a clerk in an American Civil War hospital, a civil servant, a logging, logger, a merchant, a railway owner, and an inventor who lived in Michigan. In the 1860s, he became a logger and wanted a better way to move logs to the sawmill, mill than on winter snow sleds. He built his own Tramway (industrial), tramway in 1875, on gauge rail tracks, track on wooden Railroad tie, ties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Plate
A builder's plate is usually a metal plate that is attached to railway locomotives and rolling stock, bogies, construction equipment, trucks, automobiles, large household appliances, bridges, ships and more. It gives such information as the name of the manufacturer, the place and country of manufacture, the model number, the serial number, as well as the date of manufacture or date of fabrication of the item or unit. Gallery File:Schenectady builder's plate.jpg, Schenectady Locomotive Works builder's plate File:New South Wales Government Locomotive No. 1c.jpg, New South Wales Government Railways Locomotive No. 1. Builders plate 958 File:Kerr Stuart Builder's plate 1327.jpg, Kerr, Stuart and Company File:T? Baldwin plate.jpg, Baldwin Locomotive Works builders plate File:Lima builder's plate.jpg, Lima Locomotive Works File:NSWGR AD60 Class Locomotive 6040 d.jpg, New South Wales AD60 class locomotive Beyer, Peacock and Company. builder's plate. File:SAR Class GMAM 4140 (4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M4 Sherman
The M4 Sherman, officially medium tank, M4, was the medium tank most widely used by the United States and Western Allies in World War II. The M4 Sherman proved to be reliable, relatively cheap to produce, and available in great numbers. It was also the basis of several other armored fighting vehicles including self-propelled artillery, tank destroyers, and armored recovery vehicles. Tens of thousands were distributed through the Lend-Lease program to the British Commonwealth, Soviet Union, and other Allied Nations. The tank was named by the British after the American Civil War General William Tecumseh Sherman. The M4 Sherman tank evolved from the M3 Lee, a medium tank developed by the United States during the early years of World War II. The M3, also known by its service names "Grant" and "Lee," was characterized by a unique design that featured the main armament mounted in a side sponson. The Grant variant, used by British forces, employed a lower-profile turret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pere Marquette 1225
Pere Marquette 1225 is an N-1 class 2-8-4 "Berkshire" type steam locomotive built in October 1941 by the Lima Locomotive Works for the Pere Marquette Railway (PM) in Lima, Ohio. No. 1225 is one of two surviving PM 2-8-4 locomotives, the other being Pere Marquette 1223, 1223, which was on display at the Tri-Cities Historical Society near the ex-Grand Trunk Western Railroad, Grand Trunk Western (GTW) coaling tower in Grand Haven, Michigan, and both have the distinction of being the only surviving Pere Marquette steam locomotive left in preservation. No. 1225 was well known to be the basis for the locomotive used in the 2004 film ''The Polar Express (film), The Polar Express,'' earning itself the nickname "the real Polar Express". The PM used No. 1225 in regular service from the locomotive's construction in 1941 until the railroad merged into the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) in 1947; It remained in use on C&O's Michigan lines until 1951. Avoiding the scrapyard, No. 1225 was ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Plate Road 765
Nickel Plate Road 765 is a preserved S-2 class 2-8-4 "Berkshire locomotive, Berkshire" type steam locomotive built by the Lima Locomotive Works for the New York, Chicago & St. Louis Railroad, commonly referred to as the "Nickel Plate Road". In 1963, No. 765, renumbered as 767, was donated to the city of Fort Wayne, Indiana, where it sat on display at the Lawton Park, while the real No. 767 was scrapped at Chicago in 1964. In the early 1970s, the newly formed Fort Wayne Railroad Historical Society (FWRHS) restored No. 765 and operated it in main line Excursion train, excursion service. During the 1980s to early 90s, No. 765 ran excursion trains on the ex-Southern Railway (U.S.), Southern Railway's Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway, CNO&TP division and ex-Chesapeake and Ohio Railway, Chesapeake and Ohio's New River (Kanawha River tributary), New River Gorge route. Taken out of service in 1993, No. 765 was added to the National Register of Historic Places on September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Central
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, is a railroad in the Central United States. Its primary routes connected Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama, and thus, the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. Another line connected Chicago west to Sioux City, Iowa (1870), while smaller branches reached Omaha, Nebraska (1899) from Fort Dodge, Iowa, and Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), from Cherokee, Iowa. The IC also ran service to Miami, Florida, on trackage owned by other railroads. The IC, founded in 1851, pioneered the financing later used by several long distance U.S. railroads whose construction was partially financed through a federal land grant. In 1998, the Canadian National Railway, via Grand Trunk Corporation, acquired control of the IC, and absorbed its operations the following year. The Illinois Central Railroad maintains its corporate existence as a non-operating subsidiary. In 1971, Steve Goodman rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-4
Under the Whyte notation, a 2-8-4 is a steam locomotive that has two unpowered leading wheels, followed by eight coupled and powered driving wheels, and four trailing wheels. This locomotive type is most often referred to as a Berkshire, though the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway used the name Kanawha for their 2-8-4s. In Europe, this wheel arrangement was mostly seen in mainline passenger express locomotives and, in certain countries, in tank locomotives. Overview In the United States of America, the 2-8-4 wheel arrangement was a further development of the enormously successful 2-8-2 Mikado. It resulted from the requirement for a freight locomotive with even greater steam heating capacity. To produce more steam, a solution was to increase the size of the locomotive's firebox, though the 2-8-2 wheel arrangement, with its single axle trailing truck, limited the permissible increased axle loading from a larger firebox. The most practical solution was to add a second trailing axle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailing Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients. Trailing wheels were used in some early locomotives but fell out of favor for a time during the latter 19th century. As demand for more powerful locomotives increased, trailing wheels began to be used to support the crew cab and rear firebox area. Trailing wheels first appeared on American locomotives between 1890 and 1895, but their axle worked in rigid pedestals. It enabled boilers to be lowered, since the top of the main frames was dropped down behind the driving wheels and under the firebox. The firebox could also be longer and wider, increasing the heating su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firebox (steam Engine)
In a steam engine, the firebox is the area where the fuel is burned, producing heat to boil the water in the boiler. Most are somewhat box-shaped, hence the name. The hot gases generated in the firebox are pulled through a rack of tubes running through the boiler. Steam locomotive fire tube firebox In the standard steam locomotive fire-tube boiler, the firebox is surrounded by water space on five sides. The bottom of the firebox is open to atmospheric pressure, but covered by fire grates (solid fuel) or a firing pan (liquid fuel). If the engine burns solid fuel, like wood or coal, there is a grate covering most of the bottom of the firebox to hold the fire. An ashpan, mounted underneath the firebox and below the grates, catches and collects hot embers, ashes, and other solid combustion waste as it falls through the grates. In a coal-burning locomotive, the grates may be shaken to clean dead ash from the bottom of the fire. They are shaken either manually or (in larger locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Central
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. The New York Central was headquartered in the New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal. The railroad was established in 1853, consolidating several existing railroad companies. In 1968, the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central. Penn Central went into bankruptcy in 1970 and, with extensive Federal government support, emerged as Conrail in 1976. In 1999, Conrail was broken up, and portions of its system were transferred to CSX and Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), with CSX acquiring most of the NYC's eastern trackage and NS acquiring most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |