|
Ligier JS47
The Ligier JS47 is an open-wheel formula race car, designed, developed and produced by French manufacturer Ligier, specifically built to Formula 3 Formula Three (F3) is a third-tier class of open-wheel formula racing. The various championships held in Europe, Australia, South America and Asia form an important step for many prospective Formula One drivers. History Formula Three (adop ... regulations, in 2004. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Ligier JS47 Formula Three cars Ligier racing cars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula Three
Formula Three (F3) is a third-tier class of open-wheel formula racing. The various championships held in Europe, Australia, South America and Asia form an important step for many prospective Formula One drivers. History Formula Three (adopted by the FIA in 1950) evolved from postwar auto racing, with lightweight tube-frame chassis powered by 500 cc motorcycle engines (notably Nortons and JAP speedway). The 500 cc formula originally evolved in 1946 from low-cost "special" racing organised by enthusiasts in Bristol, England, just before the Second World War; British motorsport after the war picked up slowly, partly due to petrol rationing which continued for a number of years and home-built 500 cc cars engines were intended to be accessible to the "impecunious enthusiast". The second post-war motor race in Britain was organised by the VSCC in July 1947 at RAF Gransden Lodge, 500cc cars being the only post-war class to run that day. Three of the seven entrants were non-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodemo Moteurs
Sodemo Moteurs is a motor vehicle engine tuning company based in Magny-Cours, near Nevers, France, owned by Guillaume Maillard. Formed in 1981, and based within the ground of the Circuit de Nevers Magny-Cours, Sodemo is most associated with the tuning of Renault engines for performance and motor racing purposes. Sodemo Moteurs is perhaps best known for its preparation of two litre racing engine for Formula 3. The firm has also been associated with the engine tuning of Alfa Romeo and Mercedes touring car engines and Range Rover rally raid engines and has worked with WilliamsF1 to win the British Touring Car Championship with Renault Laguna touring cars. Pescarolo Sport has also used Sodemo in preparation of its 24 Hours of Le Mans sportscars. The company also designed a series of liquid-cooled V2 aircraft engine An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula 3
Formula Three (F3) is a third-tier class of open-wheel formula racing. The various championships held in Europe, Australia, South America and Asia form an important step for many prospective Formula One drivers. History Formula Three (adopted by the FIA in 1950) evolved from postwar auto racing, with lightweight tube-frame chassis powered by 500 cc motorcycle engines (notably Nortons and JAP speedway). The 500 cc formula originally evolved in 1946 from low-cost "special" racing organised by enthusiasts in Bristol, England, just before the Second World War; British motorsport after the war picked up slowly, partly due to petrol rationing which continued for a number of years and home-built 500 cc cars engines were intended to be accessible to the "impecunious enthusiast". The second post-war motor race in Britain was organised by the VSCC in July 1947 at RAF Gransden Lodge, 500cc cars being the only post-war class to run that day. Three of the seven entrants were non-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula Racing
Formula racing, also known as open-wheel racing in North America, is any of several forms of open-wheeled single-seater motorsport. A "formula", first devised by FIA for its post–World War II single-seater races, is a set of regulations for a given type of car. The best known are Formula One, Formula E, Formula Two, Formula Three, regional Formula Three and Formula Four. Common usage of "formula racing" encompasses other single-seater series, including the IndyCar Series and the Super Formula Championship. Lower categories such as Formula Three and Formula Two are described as junior formulae, lower formulae, or feeder formulae, referring to their position below top-level series like Formula One on their respective career ladders of single-seater motor racing. There are two primary forms of racing formula: open formula, which allows a choice of chassis or engines; and control or "spec" formula, which specifies a single supplier for chassis and engines. Formula Three is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-wheel Car
An open-wheel car is a car with the wheels outside the car's main body, and usually having only one seat. Open-wheel cars contrast with street cars, Sports car racing, sports cars, Stock car racing, stock cars, and Touring car racing, touring cars, which have their wheels below the body or inside Fender (vehicle), fenders. Open-wheel cars are built both for road racing and oval track racing. Open-wheel cars licensed for use on public roads (Street-legal vehicle, street legal), such as the Ariel Atom, are uncommon, as they are often impractical for everyday use. History American racecar driver and constructor Ray Harroun was an early pioneer of the concept of a lightweight single-seater, open-wheel "monoposto" racecar. After working as a mechanic in the automotive industry, Harroun began competitive professional racing in 1906, winning the AAA National Championship in 1910. He was then hired by the Marmon Motor Car Company as chief engineer, charged with building a racecar intended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brembo
Brembo N.V. is an Italian manufacturer of automotive parts that most notably produces braking systems, for high-performance cars and for the sim racing series Gran Turismo. Its operational head office is in Curno, Bergamo, Italy, while Amsterdam, Netherlands, is the company's legal seat. History Brembo was established in Paladina, Italy, on January 11, 1961, by Emilio Bombassei and Italo Breda (father and uncle, respectively, to the current Chairman Alberto Bombassei). The company was named after the Brembo river. Bombassei lived in a village on the coast of the river before moving to Milan. Soon after Brembo was formed, it specialized in disc brakes, which were imported from the UK at the time. The company entered into a supply contract with Alfa Romeo in 1964 and became Moto Guzzi's brake component supplier in 1966. In the 1980s, Brembo also began supplying brakes to BMW, Chrysler, Ferrari, Mercedes-Benz, Nissan, and Porsche. Brembo went public on the Milan Stock Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Gearbox
A sequential manual transmission, also known as a sequential gearbox or sequential transmission, is a type of non-synchronous manual transmission used mostly in motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional synchronized manual transmissions, and restricts the driver to selecting either the next or previous gear, in a successive order. Design A sequential manual transmission is unsynchronized, and allows the driver to select either the next gear (e.g. shifting from first gear to second gear) or the previous gear (e.g., shifting from third gear to second gear), operated either via electronic paddle-shifters mounted behind the steering wheel or with a sequential shifter. This restriction avoids accidentally selecting the wrong gear; however, it also prevents the driver from deliberately "skipping" gears. The use of dog clutches (rather than synchromesh) results in faster shift speeds than a conventional manual transmission. On a sequential manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear-wheel Drive
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) is a form of engine and transmission layout used in motor vehicles, in which the engine drives the rear wheels only. Until the late 20th century, rear-wheel drive was the most common configuration for cars. Most rear-wheel drive vehicles feature a longitudinally-mounted engine at the front of the car. Layout The most common layout for a rear-wheel drive car is with the engine and transmission at the front of the car, mounted longitudinally. Other layouts of rear-wheel drive cars include front-mid engine, rear-mid engine, and rear-engine. Some manufacturers, such as Alfa Romeo, Lancia, Porsche (944, 924, 928) and Chevrolet (C5, C6, and C7 Corvettes), place the engine at the front of the car and the transmission at the rear of the car, in order to provide a more balanced weight distribution. This configuration is often referred to as a transaxle since the transmission and axle are one unit. History 1890s to 1960s Many of the cars built in the 19th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MR Layout
In automotive design, an RMR, or rear mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is one in which the rear wheels are driven by an engine placed with its center of gravity in front of the rear axle, and thus right behind the passenger compartment. Nowadays more frequently called 'RMR', to acknowledge that certain sporty or performance focused front-engined cars are also "mid-engined", by having the main engine mass behind the front axle, RMR layout cars were previously (until ca. the 1990) just called MR, or mid-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout), because the nuance between distinctly front-engined vs. front ''mid-engined'' cars often remained undiscussed. In contrast to the fully rear-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout, the center of mass of the engine is in front of the rear axle. This layout is typically chosen for its favorable weight distribution. Placing the car's heaviest component within the wheelbase minimizes its rotational inertia around the vertical axis, facilitating turn-in or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Engine
In automotive engineering, a longitudinal engine is an internal combustion engine in which the crankshaft is oriented along the long axis of the vehicle, from front to back. See also: transverse engine Use This type of motor is usually used for rear-wheel drive cars, except for some Audi, SAAB, the Oldsmobile Toronado, and the 1967 Cadillac Eldorado equipped with longitudinal engines in front wheel drive. In front-wheel drive cars a transverse engine is usually used. Trucks often have longitudinal engines with rear-wheel drive. For motorcycles, the use of a particular type depends on the drive: in the case of a chain or belt drive a transverse engine is usually used, and with shaft drives a longitudinal engine. Longitudinal engines in motorcycles do have one disadvantage: the "tipping point" of the crankshaft tilts along the entire motorcycle to a greater or lesser degree when accelerating. This is partly resolved by having other components, such as the generator and the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturally-aspirated
A naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine, and abbreviated to N/A or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Description In a naturally aspirated engine, air for combustion ( Diesel cycle in a diesel engine or specific types of Otto cycle in petrol engines, namely petrol direct injection) or an air/fuel mixture (traditional Otto cycle petrol engines), is drawn into the engine's cylinders by atmospheric pressure acting against a partial vacuum that occurs as the piston travels downwards toward bottom dead centre during the intake stroke. Owing to innate restriction in the engine's inlet tract, which includes the intake manifold, a small pressure drop occurs as air is drawn in, resulting in a volumetric efficiency of less than 100 percent—and a less than complete air charge in the cylinder. The density of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
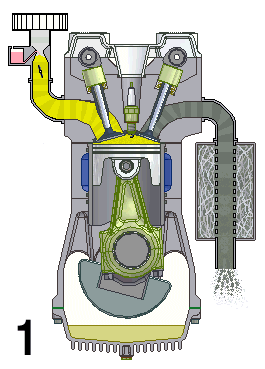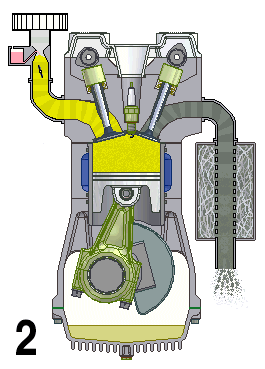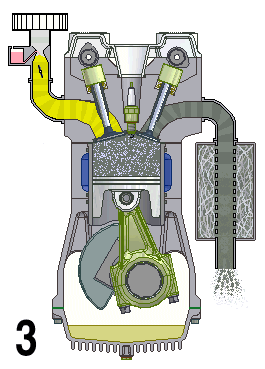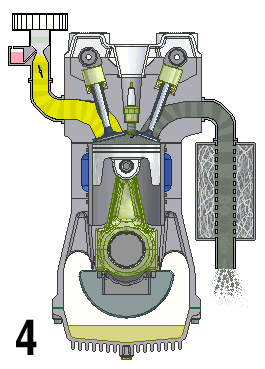
Inline-4
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the exceptions of the flat-four engines produced by Subaru and Porsche) and the layout is also very common in motorcycles and other machinery. Therefore the term "four-cylinder engine" is usually synonymous with straight-four engines. When a straight-four engine is installed at an inclined angle (instead of with the cylinders oriented vertically), it is sometimes called a slant-four. Between 2005 and 2008, the proportion of new vehicles sold in the United States with four-cylinder engines rose from 30% to 47%. By the 2020 model year, the share for light-duty vehicles had risen to 59%. Design A four-stroke straight-four engine always has a cylinder on its power stroke, unlike engines with fewer cylinders where there is no power str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |