|
Ligation
Ligation may refer to: * Ligation (molecular biology), the covalent linking of two ends of DNA or RNA molecules * In medicine, the making of a ligature (tie) * Chemical ligation, the production of peptides from amino acids * Tubal ligation, a method of female sterilization * Rubber band ligation, a treatment for hemorrhoids * In coordination chemistry, making a bond between a ligand and a Lewis acid * In orthodontics, a method of attaching the archwires to the brackets * KAHA Ligation * Ligation-independent cloning * Typographic ligature In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes or letters are joined to form a single glyph. Examples are the characters æ and œ used in English and French, in which the letters 'a' and 'e' are joined for the first li ... forming {{disambiguation pl:Ligacja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligation (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology, ligation is the joining of two nucleic acid fragments through the action of an enzyme. It is an essential laboratory procedure in the molecular cloning of DNA, whereby DNA fragments are joined to create recombinant DNA molecules (such as when a foreign DNA fragment is inserted into a plasmid). The ends of DNA fragments are joined by the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the 3'-hydroxyl of one DNA terminus with the 5'-phosphoryl of another. RNA may also be ligated similarly. A co-factor is generally involved in the reaction, and this is usually ATP or NAD+. Ligation in the laboratory is normally performed using T4 DNA ligase. However, procedures for ligation without the use of standard DNA ligase are also popular. Ligation reaction The mechanism of the ligation reaction was first elucidated in the laboratory of I. Robert Lehman. Two fragments of DNA may be joined by DNA ligase which catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 3' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAHA Ligation
The α-Ketoacid-Hydroxylamine (KAHA) Amide-Forming Ligation is a chemical reaction that is used to join two unprotected fragments in peptide synthesis.{{cite journal, last1=Pusterla, first1=Ivano, last2=Bode, first2=Jeffrey W., title=The Mechanism of the α-Ketoacid-Hydroxylamine Amide-Forming Ligation, journal=Angewandte Chemie, volume=124, issue=2, year=2012, pages=528–531, issn=0044-8249, doi=10.1002/ange.201107198 It is an alternative to the Native Chemical Ligation (NCL). KAHA Ligation was developed by Jeffrey W. Bode group at ETH Zürich (previously University of Pennsylvania). Overview An α-ketoacid at the C-terminus of one peptide fragment reacts with a hydroxylamine at the N-terminus of another to form a peptide bond (amide bond). The reaction can happen in the presence of unprotected side chains, and it does not require any coupling reagents or catalysts. The only byproducts are water and CO2. The first reported protein synthesized by KAHA ligation was huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Ligation
Chemical ligation is a set of techniques used for creating long peptide or protein chains. It is the second step of a convergent approach. First, smaller peptides containing 30-50 amino acids are prepared by conventional chemical peptide synthesis. Then, they are completely deprotected. Chemical ligation is the technique of coupling these peptides by chemoselective reaction to give a unique reaction product, usually in aqueous solution. With several coupling steps, proteins of up to 200-300 amino acids can be produced. Methods of chemical ligation There are various techniques described in literature. Native chemical ligation The most practical and robust method for the chemoselective reaction of unprotected peptides is native chemical ligation. Native chemical ligation has overcome the limitations of the classical synthetic organic chemistry approach to the total synthesis of proteins, and enables the routine total or semi- synthesis of protein molecules. The original chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligation-independent Cloning
Ligation-independent cloning (LIC) is a form of molecular cloning that is able to be performed without the use of restriction endonucleases or DNA ligase DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, () that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living org .... The technique was developed in the early 1990s as an alternative to restriction enzyme/ligase cloning. This allows genes that have restriction sites to be cloned without worry of chopping up the inserted gene of interest. Protocol #Design PCR Primers with LIC extension #Perform PCR to amplify gene #Purify PCR product #Create 5' overhangs #Incubate vector and PCR product to anneal #Transform References {{reflist Further readingLIC Primer Design Cloning Molecular biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation (commonly known as having one's "tubes tied") is a surgical procedure for female sterilization in which the fallopian tubes are permanently blocked, clipped or removed. This prevents the fertilization of eggs by sperm and thus the implantation of a fertilized egg. Tubal ligation is considered a permanent method of sterilization and birth control. Medical uses Female sterilization through tubal ligation is primarily used to permanently prevent a patient from having a spontaneous pregnancy (as opposed to pregnancy via in vitro fertilization) in the future. While both hysterectomy (the removal of the uterus) or bilateral oophorectomy (the removal of both ovaries) can also accomplish this goal, these surgeries carry generally greater health risks than tubal ligation procedures. Less commonly, tubal ligation procedures may also be performed for patients who are known to be carriers of mutations in genes that increase the risk of ovarian and fallopian tube cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber Band Ligation
Rubber band ligation (RBL) is an outpatient treatment procedure for internal hemorrhoids of any grade. There are several different devices a physician may use to perform the procedure, including the traditional metal devices, endoscopic banding, and the CRH O'Regan System. With rubber band ligation, a small band is applied to the base of the hemorrhoid, stopping the blood supply to the hemorrhoidal mass. The hemorrhoid will shrink and fibrose within a few days with shriveled hemorrhoidal tissue and band falling off during normal bowel movements - likely without the patient noticing. Rubber band ligation is a popular procedure for the treatment of hemorrhoids, as it involves a much lower risk of pain than surgical treatments of hemorrhoids, as well as a shorter recovery period (if any at all). It is a very effective procedure and there are multiple methods available. When done with the CRH O’Regan System, it is also associated with a recurrence rate of 5% at 2 years. The proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
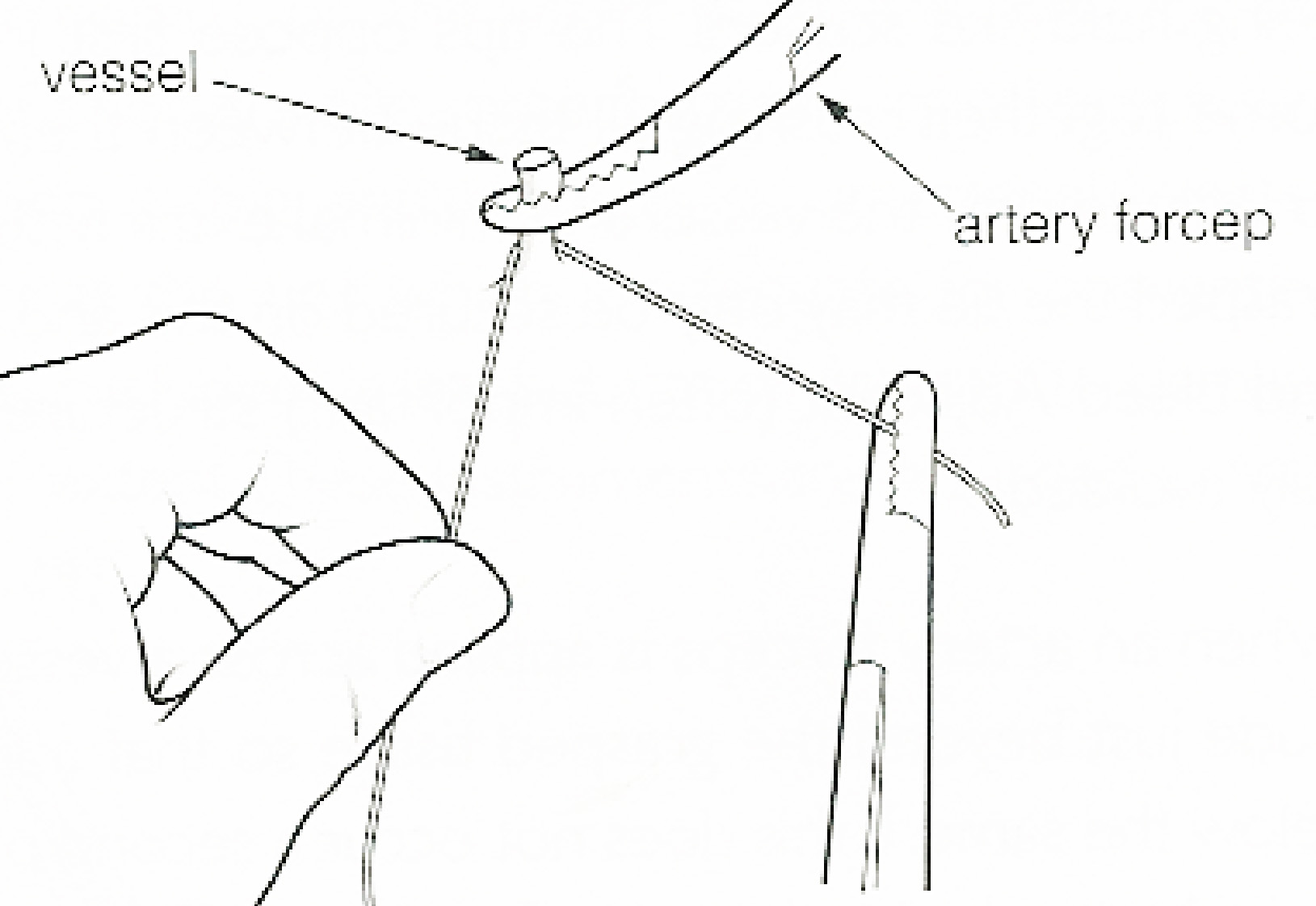
Ligature (medicine)
In surgery or medical procedure, a ligature consists of a piece of thread ( suture) tied around an anatomical structure, usually a blood vessel or another hollow structure (e.g. urethra) to shut it off. History The principle of ligation is attributed to Hippocrates and Galen. In ancient Rome, ligatures were used to treat hemorrhoids. The concept of a ligature was reintroduced some 1,500 years later by Ambroise Paré, and finally it found its modern use in 1870–80, made popular by Jules-Émile Péan. Procedure With a blood vessel the surgeon will clamp the vessel perpendicular to the axis of the artery or vein with a hemostat, then secure it by ligating it; i.e. using a piece of suture around it before dividing the structure and releasing the hemostat. It is different from a tourniquet in that the tourniquet will not be secured by knots and it can therefore be released/tightened at will. Ligature is one of the remedies to treat skin tag, or acrochorda. It is done by tying s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodontics
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics. Abnormal alignment of the teeth and jaws is very common. Nearly 50% of the developed world's population, according to the American Association of Orthodontics, has malocclusions severe enough to benefit from orthodontic treatment: although this figure decreases to less than 10% according to the same AAO statement when referring to medically necessary orthodontics. However, conclusive scientific evidence for the health benefits of orthodontic treatment is lacking, although patients with completed orthodontic treatment have reported a higher quality of life than that of untreated patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. Treatment may require several months to a few years, and entails using dental braces and other appliances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typographic Ligature
In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes or letters are joined to form a single glyph. Examples are the characters æ and œ used in English and French, in which the letters 'a' and 'e' are joined for the first ligature and the letters 'o' and 'e' are joined for the second ligature. For stylistic and legibility reasons, 'f' and 'i' are often merged to create 'fi' (where the tittle on the 'i' merges with the hood of the 'f'); the same is true of 's' and 't' to create 'st'. The common ampersand (&) developed from a ligature in which the handwritten Latin letters 'E' and 't' (spelling , Latin for 'and') were combined. History The earliest known script Sumerian cuneiform and Egyptian language, Egyptian hieratic both include many cases of character combinations that gradually evolve from ligatures into separately recognizable characters. Other notable ligatures, such as the Brahmic family, Brahmic abugidas and the Runes, Germanic bind rune, figure pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |