|
Lietuvininkai
The Prussian Lithuanians, or Lietuvininkai (singular: ''Lietuvininkas'', plural: ''Lietuvininkai''), are Lithuanians, originally Lithuanian language speakers, who formerly inhabited a territory in northeastern East Prussia called Prussian Lithuania, or Lithuania Minor (, ), instead of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and, later, the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuania Major, or Lithuania proper). Prussian Lithuanians contributed greatly to the development of written Lithuanian, which for a long time was considerably more widespread and in more literary use in Lithuania Minor than in Lithuania proper. Unlike most Lithuanians, who remained Roman Catholic after the Protestant Reformation, most Lietuvininkai became Lutheran-Protestants (Evangelical-Lutheran). There were 121,345 speakers of Lithuanian in the Prussian census of 1890. Almost all Prussian Lithuanians were murdered or expelled after World War II, when East Prussia was divided between Poland and the Soviet Union. The northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
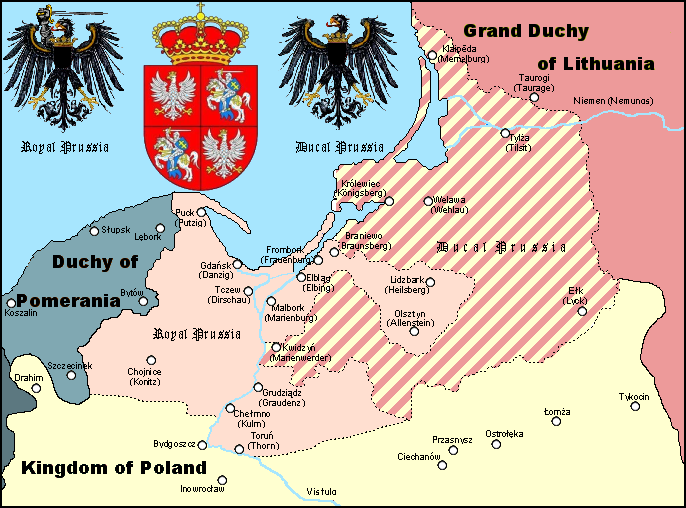
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor (; ; ) or Prussian Lithuania (; ; ) is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is a historical region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Lithuania and the Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the land was repopulated by Lithuanian newcomers, returning refugees, and the remaining indigenous Baltic peoples; the term Lithuania Minor appeared for the first time between 1517 and 1526. With the exception of the Klaipėda Region, which became a mandated territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region () or Memel Territory ( or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when, as Memelland, it was put under the administration of the Entente's Council of Ambassadors. The Memel Territory, together with other areas severed from Germany (the Saar and Danzig), was to remain under the control of the League of Nations until a future date, when the people of those regions would be allowed to vote on whether or not the land would return to Germany. Today, the former Memel Territory is controlled by Lithuania as part of Klaipėda and Tauragė counties. Historical overview In 1226, Duke Konrad I of Masovia requested assistance against the Prussians and other Baltic tribes, including the Skalvians who lived along the Neman (Memel) River. In March 1226, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II issued the Golden Bull of Rimini, which provided that the Teutonic Knight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United States, Lithuanians in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Lithuanian Brazilians, Brazil and Lithuanian Canadians, Canada. Their native language is Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, one of only two surviving members of the Baltic language family along with Latvian language, Latvian. According to the Lithuanian census of 2021, census conducted in 2021, 84.6% of the population of Lithuania identified themselves as Lithuanians. Most Lithuanians belong to the Catholic Church in Lithuania, Catholic Church, while the Lietuvininkai who lived in the northern part of East Prussia prior to World War II, were mostly Lutherans. History The territory of the Balts, including modern Lithuania, was once inhabited by several Baltic tribal entities (Sudovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the Prussia (region), region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Sea, Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the Northern Crusades, conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Polish people, Poles and Lithuanians formed sizeable minorities. From the 13th century, the region of Prussia was part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Poland to the south and Lithuania to the north and east. The largest city and administrative centre is the city of Kaliningrad. The port city of Baltiysk is Russia's only port on the Baltic Sea that remains ice-free in winter. Kaliningrad Oblast had a population of roughly one million in the 2021 Russian census. It has an area of . Various peoples, including Lithuanians, Germans, and Polish people, Poles, lived on the land which is now Kaliningrad. The territory was formerly the northern part of East Prussia. With the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II, the territory was annexed to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR by the Soviet Union. Following the Aftermath of World War II, post-war migration and Flight and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
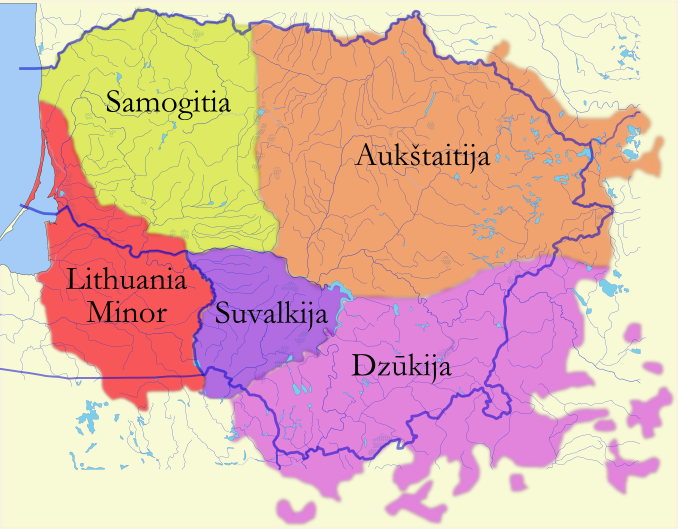
Samogitia
Samogitia, often known by its Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name ''Žemaitija'' (Samogitian language, Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see Samogitia#Etymology and alternative names, below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania alongside Lithuania proper. Žemaitija is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its capital city is Telšiai and the largest city is Šiauliai (located on the border between Samogitia and Aukštaitija). Throughout centuries, Samogitia developed a separate culture featuring diverse architecture, folk costumes, dances, songs, traditions, and a distinct Samogitian language. Famous landmarks include Tauragė Castle, Plungė Manor and Hill of Crosses. Etymology and alternative names The region is primarily referred to by its Lithuanian name, ''Žemaitija'', in both local and national contexts. The Latin language, Latin-derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kursenieki
The Kursenieki (, – 'Curonians', , ) are a nearly extinct Baltic ethnic group living along the Curonian Spit. "Kuršiai" refers only to inhabitants of Lithuania and former East Prussia that speak a southwestern dialect of Latvian. Some autochthonous inhabitants of Šventoji in Lithuania call themselves "kuršiai" as well. Confusion Kursenieki are often confused with the extinct Curonian Baltic tribe, as neighbouring ethnic groups called Kuršininkai/ Kursenieki as ''Curonians'': in German, Latvian and Lithuanian, Kursenieki and the Curonian tribes are known by the same terms (''Kuren'', ''kurši'' and ''kuršiai'' respectively). In Polish, they are referred to as either ''Kuronowie Pruscy,'' which translates to "Prussian Curonians", or ''Kurończycy,'' a name which distinguishes them from the autochthonous people of the Courland region in Latvia, known as Kurowie in Polish. In Lithuanian scholarly literature, the name ''kuršininkai'' is used to distinguish them from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
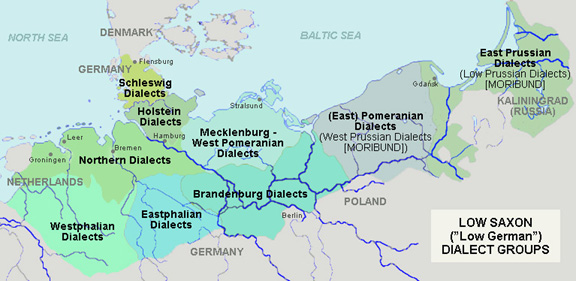
Low German Language
Low German is a West Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian and English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard High German, which is based on High German dialects. Low German evolved from Old Saxon (Old Low German), which is most closely related to Old Frisian and Old English (Anglo-Saxon). The Low German diale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words may often be synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Grunau
Simon Grunau () was the author of ''Preussische Chronik'',Full title: ''Cronika und beschreibung allerlüstlichenn, nützlichsten und waaren historien des namkundigenn landes zu Prewssen'' or ''Chronicle and description of the most amusing, useful and true known history of the Prussian land'' the first comprehensive history of Prussia. The only personal information available is what he wrote himself in his work: that he was a Dominican priest from Tolkemit ( Tolkmicko) near Frauenburg (Frombork) just north of Elbing (Elbląg) in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Order. He preached in Danzig (Gdańsk) and claimed to have met Pope Leo X and Polish King Sigismund I the Old. The chronicle was written in the German language sometime between 1517 and 1529. Its 24 chapters deal with Prussian landscape, agriculture, inhabitants, their customs, and history from earliest times to up to 1525 when the Protestant Duchy of Prussia was created. It also contains a short (about a hundred words) v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnonyms
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used by the ethnic group itself). For example, the dominant ethnic group of Germany is the Germans. The ethnonym ''Germans'' is a Latin-derived exonym used in the English language, but the Germans call themselves , an endonym. The German people are identified by a variety of exonyms across Europe, such as ( French), ( Italian), ( Swedish) and ( Polish). As a sub-field of anthroponymy, the study of ethnonyms is called ethnonymy or ethnonymics. Ethnonyms should not be confused with demonyms, which designate all the people of a geographic territory, regardless of ethnic or linguistic divisions within its population. Variations Numerous ethnonyms can apply to the same ethnic or racial group, with various levels of recognition, acceptance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |